Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 19 gauge steel
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, sourcing high-quality 19 gauge steel can be a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide addresses the complexities associated with procuring this essential material, which is widely utilized in various applications, from automotive parts to structural components. With the right information, buyers can navigate the diverse options available in the global market and make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their operational efficiency.
This comprehensive resource covers critical aspects of 19 gauge steel, including its specifications, various types, and applications across different industries. Additionally, it offers insights into supplier vetting processes, enabling buyers to identify reliable manufacturers and distributors that meet their quality and compliance standards. Cost analysis is also discussed, providing a clear understanding of pricing structures and market fluctuations that can impact procurement strategies.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical guidance, this guide empowers them to confidently approach their sourcing decisions. Whether you’re based in Vietnam, Nigeria, or elsewhere, the information presented here aims to streamline your purchasing process and ensure you secure the best value for your investment in 19 gauge steel.
Understanding 19 gauge steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | High ductility, weldability, and affordability | Structural components, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Prone to rust without coating. |
| Galvanized Steel | Coated with zinc for corrosion resistance | Outdoor structures, HVAC systems | Pros: Long-lasting, low maintenance; Cons: Higher upfront cost. |
| Stainless Steel | Contains chromium for enhanced corrosion resistance | Food processing, medical equipment | Pros: Durable, hygienic; Cons: Expensive, challenging to weld. |
| Cold Rolled Steel | Smooth finish and tighter tolerances | Precision parts, automotive applications | Pros: Excellent surface finish; Cons: More brittle than hot rolled. |
| Hot Rolled Steel | Produced at high temperatures, less precise tolerances | Heavy machinery, construction | Pros: Strong, cost-effective; Cons: Rough surface finish. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Mild Steel 19 Gauge?
Mild steel is one of the most common types of 19 gauge steel, renowned for its high ductility and excellent weldability. This material is widely used in structural applications, automotive parts, and general fabrication. When purchasing mild steel, B2B buyers should consider its susceptibility to rust, which necessitates protective coatings for outdoor use. Its affordability makes it a popular choice, but the need for maintenance can be a drawback.
How Does Galvanized Steel Differ from Other Types?
Galvanized steel is coated with zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as outdoor structures and HVAC systems. This type of 19 gauge steel is appreciated for its longevity and low maintenance requirements. However, the initial cost is higher compared to uncoated mild steel, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. Understanding the trade-off between upfront costs and long-term durability is crucial for B2B procurement decisions.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for 19 Gauge Applications?
Stainless steel 19 gauge is characterized by its chromium content, which provides exceptional corrosion resistance and hygienic properties, making it suitable for industries like food processing and healthcare. While its durability and aesthetic appeal are significant advantages, buyers must also weigh the higher cost and the challenges associated with welding and forming this material. For applications where cleanliness and strength are paramount, stainless steel is often the preferred choice.
What Are the Advantages of Cold Rolled Steel?
Cold rolled steel is processed at room temperature, resulting in a smooth finish and tighter tolerances compared to hot rolled steel. This type of 19 gauge steel is particularly advantageous for precision components and automotive applications where aesthetics and dimensional accuracy are critical. However, buyers should be aware that cold rolled steel can be more brittle than its hot rolled counterpart, which may affect its performance in certain applications.
When to Use Hot Rolled Steel in 19 Gauge Form?
Hot rolled steel is produced at high temperatures, making it strong and cost-effective for heavy machinery and construction applications. Its rough surface finish is a trade-off for its strength and lower price point. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, as the rough finish may require additional processing if a smoother surface is needed. While hot rolled steel is a versatile option, its suitability will depend on the intended use and aesthetic preferences.
Key Industrial Applications of 19 gauge steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 19 gauge steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural framing for buildings | Provides strength and durability for load-bearing structures | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Body panels and components | Enhances vehicle safety while reducing weight | Consider corrosion resistance and finish options |
| HVAC Systems | Ductwork and ventilation systems | Improves energy efficiency and air quality | Look for precise dimensions and thermal properties |
| Agriculture | Equipment housing and storage solutions | Protects machinery from the elements | Evaluate for weather resistance and fabrication options |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Metal frames for commercial furniture | Combines aesthetic appeal with structural integrity | Assess for customization options and surface treatments |
How is 19 Gauge Steel Used in Construction?
In the construction sector, 19 gauge steel is often utilized for structural framing in buildings, particularly in areas requiring robust load-bearing capabilities. The thickness of 19 gauge ensures that the steel can support heavy loads while maintaining structural integrity. For international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to ensure that the steel complies with local building regulations and standards. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who can provide detailed certifications and quality assurance will mitigate risks associated with structural failures.
What Role Does 19 Gauge Steel Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, 19 gauge steel is commonly used for body panels and various components. The balance between weight and strength is vital in the automotive industry, as lighter vehicles tend to be more fuel-efficient. For B2B buyers, especially those from the Middle East and Europe, sourcing 19 gauge steel that meets specific safety standards and offers corrosion resistance is essential. Suppliers should also provide options for different finishes to enhance both aesthetics and durability.
How is 19 Gauge Steel Beneficial for HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, 19 gauge steel is often employed for ductwork and ventilation components. Its strength allows for the construction of sturdy ducts that can withstand high airflow and pressure, thus improving energy efficiency and air quality. Buyers from international markets should focus on sourcing steel that meets precise dimensional tolerances and thermal properties to ensure optimal performance. Evaluating suppliers for their ability to deliver custom sizes and shapes can also enhance project efficiency.
What Applications Does 19 Gauge Steel Have in Agriculture?
The agricultural sector frequently uses 19 gauge steel for constructing equipment housing and storage solutions. The durability of this steel gauge protects machinery from harsh environmental conditions, thereby extending the lifespan of agricultural equipment. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, it’s vital to assess the weather resistance properties of the steel. Additionally, sourcing options that allow for easy customization can help meet specific operational needs in diverse agricultural environments.
How is 19 Gauge Steel Utilized in Furniture Manufacturing?
In furniture manufacturing, 19 gauge steel is often utilized for creating metal frames in commercial furniture. This application combines aesthetic appeal with structural integrity, allowing for stylish yet durable furniture solutions. For international buyers, especially from Europe, evaluating suppliers for customization options and surface treatments is critical to achieving desired design outcomes. Ensuring that the steel meets specific design and safety standards will also enhance the marketability of the final products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’19 gauge steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Determining the Correct Specifications for 19 Gauge Steel
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to determine the exact specifications for 19 gauge steel for their projects. With varying standards across different regions, such as the Manufacturers’ Standard Gage and the Birmingham Gage, the actual thickness can differ. This confusion can lead to costly errors in sourcing, as buyers might end up ordering the wrong type of steel, resulting in delays and increased expenses. Additionally, projects requiring specific thicknesses for structural integrity may suffer if the incorrect gauge is used.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of gauge specifications, buyers should invest time in understanding the gauge system and its implications for their projects. Utilizing a comprehensive gauge conversion chart specific to their region and material type is essential. This chart should detail the actual thickness in both inches and millimeters, as well as the weight per area. Moreover, collaborating closely with suppliers who can provide precise data on the 19 gauge steel being offered is crucial. Establishing a clear communication channel with manufacturers or distributors can ensure that the specifications match project requirements, thus avoiding potential pitfalls.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality and Performance of 19 Gauge Steel Products
The Problem: Quality control can vary significantly between suppliers of 19 gauge steel, leading to inconsistencies in product performance. B2B buyers may find that steel sourced from one supplier does not meet the same standards as another, causing issues in fabrication, durability, and overall project outcomes. This inconsistency can be particularly problematic in industries like construction, automotive, or manufacturing, where material performance is critical.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process. This should include checking certifications, such as ISO or ASTM standards, that confirm the quality and reliability of the steel products. Additionally, requesting samples and conducting independent material testing can help verify the steel’s properties before making a bulk purchase. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers known for their quality control practices can also mitigate risks. It’s beneficial to engage in continuous dialogue with suppliers regarding their quality assurance processes and to stay informed about any changes in material sourcing or production methods.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Fabrication and Welding of 19 Gauge Steel
The Problem: Fabricators often face difficulties when working with 19 gauge steel due to its thinness, which can complicate welding and cutting processes. Inadequate techniques or equipment can lead to warping, burn-through, or weak joints, ultimately compromising the structural integrity of the final product. For B2B buyers who require precise fabrication for applications like HVAC systems, automotive parts, or custom metalwork, these challenges can result in wasted time and resources.
The Solution: To address fabrication challenges, buyers should invest in training for their workforce on the best practices for handling and working with 19 gauge steel. This includes utilizing appropriate welding techniques, such as using a TIG welder or employing spot welding for thin materials, which minimizes heat input. Additionally, implementing proper handling procedures can prevent distortion and damage during processing. Collaborating with experienced fabricators who specialize in thin gauge materials can provide valuable insights and techniques tailored to specific applications. Furthermore, ensuring access to the right tools and equipment, such as plasma cutters or laser cutting systems designed for thin sheets, can enhance fabrication efficiency and quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 19 gauge steel
When selecting materials for 19 gauge steel applications, it is essential to evaluate various alternatives based on their properties, advantages, limitations, and specific considerations relevant to international B2B buyers. Below, we analyze four common materials that could serve as alternatives or complements to 19 gauge steel.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum Compared to 19 Gauge Steel?
Aluminum, particularly in 19 gauge thickness, is known for its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 150°C (302°F) and can withstand moderate pressure, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
Pros: Aluminum is highly durable and resistant to rust, which makes it ideal for outdoor applications. Its lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and enhances energy efficiency in end products.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to steel, which can affect budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, aluminum may not be as strong as steel in high-stress applications, leading to potential failures under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and air, but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments without additional reinforcement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and JIS is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should also consider local availability and pricing fluctuations.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare to 19 Gauge Steel?
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, making it a preferred choice for food processing and chemical applications. Its temperature rating can exceed 300°C (572°F) under specific conditions.
Pros: The durability and aesthetic appeal of stainless steel make it ideal for applications requiring hygiene and visual quality. It is also highly resistant to oxidation and staining.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than both 19 gauge steel and aluminum. Its manufacturing complexity can also lead to increased production times and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including acids and bases, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4301. Additionally, understanding local market conditions is essential for cost-effective procurement.
What Are the Benefits of Galvanized Steel in Comparison to 19 Gauge Steel?
Galvanized steel, which is coated with zinc, provides enhanced corrosion resistance compared to standard steel. It is typically rated for temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and can handle moderate pressure.
Pros: The zinc coating significantly extends the lifespan of the material, making it suitable for outdoor and marine applications. It is also more cost-effective than stainless steel.
Cons: While galvanized steel is resistant to rust, it can still corrode under harsh conditions, especially if the coating is damaged. Additionally, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Galvanized steel is compatible with water and many chemicals, but it may not perform well in acidic environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A653 is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of galvanized products in their local markets.
How Does Copper Compare as a Material for 19 Gauge Applications?
Copper, while not as commonly used as steel, offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and is often used in electrical and plumbing applications.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications, while its natural antimicrobial properties are beneficial in plumbing.
Cons: The cost of copper is significantly higher than that of steel, which can be a limiting factor for large-scale projects. Additionally, its softness can lead to wear and deformation under mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Copper is highly compatible with water and various chemicals, making it suitable for plumbing and electrical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fluctuating prices of copper and ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B75. Understanding local market dynamics is crucial for effective procurement.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 19 Gauge Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for 19 gauge steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, Aerospace | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, Chemical handling | Superior corrosion resistance | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Outdoor structures, Marine applications | Cost-effective and durable | Corrosion risk if coating is damaged | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, Plumbing | Excellent conductivity | High cost and softness | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of materials relevant to 19 gauge steel, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 19 gauge steel
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 19 Gauge Steel?
Manufacturing 19 gauge steel involves a series of meticulously planned processes that ensure the material meets industry standards for quality and performance. The main stages of manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques that are critical to the overall integrity of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for 19 Gauge Steel Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which begins with sourcing high-quality steel. The steel is then subjected to various processes, including:
-
Cutting: The steel sheets are cut to the required dimensions using shearing or laser cutting techniques. Precision is crucial at this stage to minimize waste and ensure uniformity.
-
Cleaning: After cutting, the steel may go through a cleaning process to remove contaminants such as oil, rust, or dirt. This step is vital for achieving optimal adhesion during subsequent processes.
-
Coating: Depending on the application, the steel may be coated with a protective layer, such as galvanization, to enhance corrosion resistance. This is particularly important for industries operating in humid or corrosive environments.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming 19 Gauge Steel?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the steel into its final configuration, which can be achieved through various methods:
-
Bending: Steel sheets can be bent into specific angles using press brakes. This technique allows for precise control over the bend radius and angle, ensuring that the final product meets design specifications.
-
Stamping: For high-volume production, stamping is often employed. This method uses dies to create complex shapes and features in the steel, making it suitable for parts like automotive components and appliances.
-
Welding: In cases where multiple pieces are required, welding techniques such as MIG or TIG welding are used to join components together. The choice of welding method depends on the thickness and type of steel being used.
How Is Assembly Conducted in the Manufacturing of 19 Gauge Steel?
The assembly stage involves putting together the formed parts to create the final product. This process may include:
-
Fastening: Components are typically fastened using bolts, screws, or rivets, depending on the design requirements. This stage may also involve the use of adhesives for additional strength.
-
Quality Checks: During assembly, quality checks are conducted to ensure that all parts fit correctly and meet design specifications. This may include visual inspections and measurements.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to 19 Gauge Steel Products?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the appearance and durability of 19 gauge steel products. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Painting: A protective paint or powder coating may be applied to improve aesthetics and corrosion resistance. This process not only enhances the product’s look but also adds a layer of protection against environmental factors.
-
Polishing: For applications requiring a smooth surface, polishing techniques are employed. This is particularly important in industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness is paramount.
-
Final Inspection: Before the products are shipped, a final inspection is conducted to verify that they meet all specifications and standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for 19 Gauge Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing 19 gauge steel, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Adhering to recognized standards not only enhances product quality but also builds trust with B2B buyers.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
The most relevant international standards for quality assurance include:
-
ISO 9001: This is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems. It focuses on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction. Manufacturers certified to ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for B2B buyers in Europe who require assurance that products meet EU regulations.
-
API Standards: In industries such as oil and gas, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary. These standards ensure that products are suitable for use in high-pressure environments.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications. This includes checking dimensions, material properties, and surface conditions.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections are performed to ensure that processes are being followed correctly. This includes monitoring equipment calibration and adherence to production standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, final inspections are conducted to verify that the products meet all specifications. This may involve dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality assurance processes of their suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits is a practical way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes and compliance with standards. Audits can uncover potential issues and provide insight into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports can provide detailed information about the supplier’s QC processes, including results from inspections and tests performed during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly valuable for international buyers who may be unable to visit the supplier’s facilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are unique considerations to keep in mind:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local laws and standards in their respective regions.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can aid in establishing effective communication and expectations regarding quality assurance.
-
Logistics and Transportation: Quality can be affected during transportation. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have appropriate packaging and handling procedures to maintain product integrity during shipping.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for 19 gauge steel are pivotal in ensuring the delivery of high-quality products that meet global standards. B2B buyers must be diligent in evaluating suppliers’ capabilities and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations to foster successful international partnerships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’19 gauge steel’
In the competitive landscape of metal procurement, sourcing 19 gauge steel requires careful consideration and a structured approach. This guide offers a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of sourcing this material effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications for the 19 gauge steel you require. This includes understanding its dimensions, weight, and any particular characteristics such as corrosion resistance or coating types. Precise specifications help avoid miscommunications with suppliers and ensure the material meets your application needs.
- Consider the application: Different industries may require specific grades or treatments of steel.
- Consult relevant standards: Familiarize yourself with industry standards that apply to your sector, such as ASTM or ISO.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in 19 gauge steel. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors. A comprehensive supplier list allows for better comparisons in terms of pricing, quality, and service.
- Look for local and international suppliers: Depending on your logistics and cost considerations.
- Assess supplier capabilities: Ensure they have the capacity to meet your volume requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any contracts, verify the certifications and compliance of your shortlisted suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry-related standards ensure that suppliers adhere to quality management practices.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of certifications and relevant quality assurance processes.
- Check for industry recognition: Look for awards or recognitions that indicate a supplier’s reliability.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request detailed quotes for the 19 gauge steel. Ensure that each quote includes specifications, pricing, lead times, and shipping options. Comparing multiple quotes will help you identify the best value for your investment.
- Be clear about your needs: Provide suppliers with the same specifications to ensure comparability.
- Consider total cost: Look beyond the price per unit and factor in shipping and handling costs.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Options
Understanding lead times and delivery logistics is crucial in the procurement process. Inquire about production schedules and delivery methods to ensure they align with your project timelines.
- Evaluate flexibility: Determine if suppliers can accommodate rush orders or changes in delivery schedules.
- Consider shipping options: Look into domestic vs. international shipping implications.
Step 6: Conduct a Trial Order
Before committing to a large order, consider placing a trial order for a smaller quantity of 19 gauge steel. This trial will allow you to evaluate the quality of the material and the reliability of the supplier.
- Inspect the material: Check for compliance with your specifications upon delivery.
- Assess customer service: Take note of how the supplier handles your inquiries and any issues that arise.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Once you’ve successfully sourced your 19 gauge steel, focus on building a long-term relationship with your supplier. A reliable partnership can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into future material trends.
- Maintain open communication: Regularly discuss your needs and any market changes.
- Provide feedback: Offer constructive feedback to help the supplier improve their offerings and services.
This checklist serves as a roadmap for B2B buyers to efficiently procure 19 gauge steel, ensuring a smooth and effective sourcing process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 19 gauge steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in 19 Gauge Steel Pricing?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing 19 gauge steel, several components contribute to the final price. These components include:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver, material prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and the type of steel used (e.g., mild, galvanized). As of late 2023, prices for 19 gauge steel range from $0.50 to $0.80 per pound, depending on quality and sourcing location.
-
Labor: This encompasses wages for workers involved in manufacturing and processing the steel. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region—countries with lower wage standards may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Overhead can represent a significant portion of the total cost, especially in regions with high energy costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized production runs, which can add to initial costs. Investing in versatile tooling can enhance efficiency and reduce long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with industry standards and certifications can incur additional costs. However, robust QC processes can mitigate the risk of defects and reduce long-term warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must be factored in, particularly for international shipments. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and tariffs can significantly impact total logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will incorporate their profit margins into pricing, which can vary widely depending on their business model and market competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 19 Gauge Steel Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 19 gauge steel, particularly in international markets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their demand forecasts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or customizations can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality steel or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) often come at a premium. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications based on their end-use applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Different suppliers may have varying pricing strategies based on their operational efficiencies, market presence, and relationships with raw material providers. Building long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for determining who bears the shipping costs and risks. This can significantly impact total landed costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing 19 Gauge Steel?
International B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation Tactics: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Strong negotiation can lead to significant savings.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may not always equate to a better deal.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand the economic and regulatory environments of supplier countries. Factors such as currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import regulations can affect pricing.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid reliance on a single supplier to mitigate risks associated with price increases or supply chain disruptions. This approach can also foster competition, potentially leading to better pricing.
-
Long-Term Contracts: Consider establishing long-term agreements with suppliers for consistent pricing and availability, especially in volatile markets.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market fluctuations, supplier negotiations, and regional economic conditions. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 19 gauge steel With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to 19 Gauge Steel
When considering materials for construction or manufacturing applications, it’s essential to explore alternatives to 19 gauge steel. This comparison can reveal options that may offer improved performance, cost-effectiveness, or specific advantages based on your project’s requirements. Below, we examine two notable alternatives: aluminum and fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP).
| Comparison Aspect | ’19 Gauge Steel’ | Aluminum | Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Strong and durable, suitable for structural applications | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good strength-to-weight ratio | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate cost, varies by market | Generally higher initial cost than steel | Competitive pricing, often lower than aluminum |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires heavy machinery for cutting and shaping | Easier to work with, can be cut with standard tools | Can be molded into complex shapes, but requires specialized skills |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to prevent rust | Minimal maintenance, excellent longevity | Low maintenance, does not corrode |
| Best Use Case | Structural supports, automotive parts, appliances | Aerospace, automotive, marine applications | Chemical storage tanks, architectural features, automotive components |
Analyzing Aluminum as an Alternative to 19 Gauge Steel
Aluminum is a popular alternative to 19 gauge steel, particularly in applications where weight is a critical factor. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where reducing weight can lead to improved fuel efficiency. Additionally, aluminum’s corrosion resistance means it requires less maintenance compared to steel. However, it typically has a higher initial cost, which can impact budget-sensitive projects. Moreover, while aluminum offers good strength, it may not match the load-bearing capabilities of 19 gauge steel in certain applications.
Exploring Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
FRP is another viable alternative, particularly noted for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. This material is often used in environments where exposure to chemicals is a concern, making it suitable for applications in the chemical processing and marine industries. FRP can be molded into intricate shapes, allowing for design flexibility that steel cannot provide. Additionally, it tends to be competitively priced compared to aluminum and offers low maintenance. However, working with FRP can require specialized skills for installation and repair, which may complicate implementation in some projects.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
Selecting the right material depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your project, budget constraints, and performance expectations. B2B buyers should carefully consider the trade-offs between 19 gauge steel, aluminum, and FRP. While steel provides robust structural integrity, aluminum excels in weight-sensitive applications, and FRP offers unique advantages in corrosive environments. Conducting a thorough analysis of these alternatives against your project criteria will enable informed decision-making, ultimately leading to a successful outcome.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 19 gauge steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 19 Gauge Steel?
When considering 19 gauge steel for your projects, understanding its technical specifications is crucial. Here are some essential properties to keep in mind:
-
Thickness: 19 gauge steel measures approximately 0.0418 inches (1.062 mm) in thickness. This specification is vital because it influences the material’s strength, weight, and application suitability. In various industries, the thickness may dictate the type of tools and processes used for fabrication.
-
Material Grade: Typically, 19 gauge steel falls under the category of mild steel, often designated as ASTM A569 or A36. The material grade determines the steel’s mechanical properties, including yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. Buyers should align the grade with their project’s requirements to ensure structural integrity and performance.
-
Weight per Area: The weight of 19 gauge steel is around 8.326 kg/m² (1.705 lb/ft²). Understanding the weight is essential for logistics and handling, as it affects transportation costs and the choice of equipment during installation.
-
Tolerance: Tolerances for 19 gauge steel typically range from ±0.005 to ±0.015 inches. Tolerance specifications are crucial for ensuring that the steel components fit together correctly in assemblies, avoiding issues during manufacturing and reducing waste.
-
Corrosion Resistance: While not inherently corrosion-resistant, 19 gauge steel can be treated with coatings such as galvanization. This property is particularly significant for applications in humid or corrosive environments, where the longevity of materials is paramount.
-
Formability: 19 gauge steel exhibits good formability, allowing it to be easily shaped and welded. This property is essential for manufacturers looking to create complex structures or components with specific geometries.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 19 Gauge Steel?
Understanding industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some key terms to be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of 19 gauge steel, OEMs often require specific grades and specifications to meet their product standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQs can help in planning purchases and budget allocation.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. For 19 gauge steel, this process helps buyers gather competitive pricing and assess potential suppliers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead time is crucial for project planning, especially for industries that require timely delivery of materials like 19 gauge steel.
-
Certification: This term indicates that a material meets specific industry standards or regulations, often verified by a third-party organization. Certifications for 19 gauge steel can include quality assurance metrics, which are essential for industries such as construction and automotive, where safety is paramount.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 19 gauge steel, ensuring that they meet their project requirements efficiently and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 19 gauge steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the 19 Gauge Steel Sector?
The global 19 gauge steel market is witnessing robust growth, driven primarily by the increasing demand for durable and versatile materials in construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. One of the key trends is the shift towards lightweight materials that do not compromise strength, making 19 gauge steel an attractive option for various applications. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, seek to optimize their supply chains, the focus is on sourcing high-quality steel that meets specific project requirements while balancing cost-efficiency.
Emerging technologies such as automation in manufacturing processes and advancements in steel production techniques are transforming how businesses source 19 gauge steel. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are becoming increasingly vital, allowing buyers to easily compare suppliers, evaluate product specifications, and negotiate prices. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 has introduced smart manufacturing practices, enhancing transparency and traceability in the supply chain, which is crucial for international buyers looking to mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Moreover, geopolitical factors and economic fluctuations significantly impact the availability and pricing of steel. As countries navigate trade tariffs and regulatory changes, B2B buyers must remain agile and informed about market conditions to make strategic sourcing decisions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the 19 Gauge Steel Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern procurement practices, particularly in the steel industry. The environmental impact of steel production is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Therefore, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as recycling scrap steel and utilizing renewable energy sources in production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies strive to ensure their supply chains are free from human rights violations and adverse environmental impacts. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and the ResponsibleSteel certification are gaining traction, providing buyers with assurance that their steel is sourced responsibly. By opting for 19 gauge steel from certified suppliers, companies not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials is leading to innovations in steel production, including the development of low-carbon steel options. These advancements not only appeal to environmentally conscious buyers but also align with regulatory requirements in various regions, making them a prudent choice for international B2B transactions.
What Is the Historical Context of 19 Gauge Steel and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The gauge system for steel, including 19 gauge, has its roots in the British wire industry, where it was initially used to describe wire diameters. Over time, this system evolved into a standard for measuring the thickness of sheet metals, with each gauge number corresponding to a specific thickness. For 19 gauge steel, the thickness measures approximately 0.0418 inches (1.062 mm), making it a popular choice for applications requiring a balance of weight and strength.
Understanding the historical context of gauge measurements is essential for B2B buyers as it allows them to navigate industry standards and specifications effectively. The consistency in gauge measurements across various materials and their applications facilitates informed decision-making, ensuring that the selected steel meets specific project requirements. As buyers engage in international sourcing, awareness of gauge standards and their historical evolution enhances their ability to communicate specifications clearly and negotiate effectively with suppliers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 19 gauge steel
-
How do I determine the thickness of 19 gauge steel?
The thickness of 19 gauge steel is approximately 0.0418 inches or 1.062 millimeters. When sourcing steel, it’s crucial to refer to a gauge conversion chart to ensure accurate specifications. Different standards may apply depending on the material type, so verifying thickness according to the specific gauge system used in your region is essential. This ensures compatibility with your project requirements and aids in avoiding potential manufacturing discrepancies. -
What industries commonly use 19 gauge steel?
19 gauge steel is widely utilized in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. It is often used for applications such as HVAC ductwork, metal roofing, and cabinetry, owing to its balance of strength and weight. Buyers should assess their specific industry needs and consider how 19 gauge steel meets durability and structural requirements for their intended applications. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for 19 gauge steel?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize factors such as their production capacity, quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards), and past client references. Evaluate their ability to provide consistent thickness and quality, as well as their experience with international shipping, particularly if you are sourcing from regions like Africa or South America. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with local regulations and industry standards to mitigate risks in your supply chain. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 19 gauge steel?
MOQs for 19 gauge steel can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Generally, larger suppliers may offer lower MOQs, while smaller manufacturers might require higher minimums to cover production costs. It is advisable to directly communicate with potential suppliers to discuss your specific needs, as some may be willing to negotiate terms based on your project size or long-term purchasing agreements. -
How can I customize 19 gauge steel for my project?
Customization options for 19 gauge steel include cutting, bending, and surface treatments such as galvanization or powder coating. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and drawings to ensure the supplier fully understands your needs. Be aware that customized orders may affect lead times and pricing. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 19 gauge steel internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common options include upfront payments, deposits, or letters of credit. It is essential to clarify payment methods and timelines before finalizing any agreements. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow needs and project timelines. Always ensure that the terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
What quality assurance measures should I request from suppliers?
Request quality assurance documentation, including mill test reports and certifications that verify the steel’s composition and mechanical properties. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s internal quality control processes, such as inspections and testing procedures. Establishing clear quality expectations upfront can help prevent issues during production and delivery, ensuring that the 19 gauge steel meets your specifications. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of 19 gauge steel?
Logistics play a critical role in sourcing 19 gauge steel, particularly in terms of shipping times, costs, and compliance with import regulations. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to navigate customs requirements effectively. Additionally, consider factors such as shipping methods, insurance, and delivery schedules to ensure timely receipt of materials. Proper logistics planning can help mitigate delays and optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 19 Gauge Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
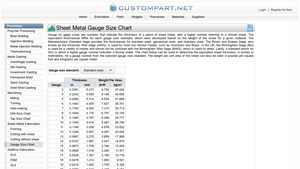
1. Custom Part Net – Gauge Size Standards
Domain: custompartnet.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Gauge sizes indicate the thickness of sheet metal, with higher numbers corresponding to thinner sheets. Different gauge size standards exist, including:
1. Manufacturers’ Standard Gage for standard steel, galvanized steel, and stainless steel.
2. Brown and Sharpe Gage (American Wire Gage) for non-ferrous metals like Aluminum and Brass.
3. Birmingham Gage in the UK for various metals, distinct f…
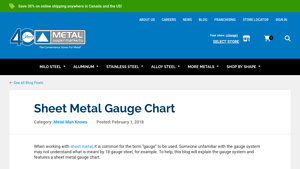
2. Metal Supermarkets – Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Chart – Metal Supermarkets offers a variety of metals including Mild Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, Bronze, and Copper. The chart provides gauge numbers and their corresponding thickness in inches and millimeters for different metals. For example, 18 gauge steel is 0.0478 inches (1.214 mm) thick, while 18 gauge aluminum is 0.0403 inches (1.024 mm) thick. Th…
3. Metals Depot – Hot Rolled Steel Sheet
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“type”:”Hot Rolled Steel Sheet”,”specification”:”ASTM A1011 CS Type B”,”description”:”Economical steel sheets with a slightly grainy surface, ideal for painting.”,”popular_uses”:[“general fabrication”,”equipment panels”,”tool boxes”,”hoppers”,”drip pans”],”thicknesses”:[{“gauge”:”16 GA”,”thickness”:”.060″”,”weight”:”2.50 lb/sqft”},{“gauge”:”14 GA”,”thickness”:”.075″”,”weight”:”3.13 l…
4. MK Metal – CRS Sheet 19 Ga x 48 x 120
Domain: mkmetal.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “CRS SHEET 19 GA X 48 X 120”, “Alloy”: “1008”, “Thickness”: “19”, “Width”: “48”, “Length”: “120”, “Weight per Foot (SQFT)”: “0.7”, “Price per Piece”: “$63.53”, “Price Each”: “$162.99”}
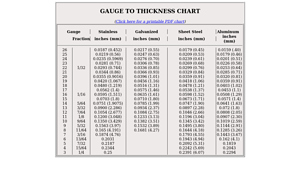
5. Stainless Supply – Gauge to Thickness Chart
Domain: stainlesssupply.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Gauge to Thickness Chart for Stainless, Galvanized Sheet Steel, and Aluminum. Includes measurements in inches and millimeters for gauges 26 to 3, with thickness values ranging from 0.0187 inches (0.452 mm) to 0.25 inches (6.07 mm).
6. US General – Series 3 Toolbox
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: US General series 3 toolbox; steel gauge thickness not specified; comparison with Husky HD 52″ cabinet ($800) noted; Husky has 19 gauge steel frame; US General lacks detailed specifications; intended for home mechanic use.
7. McNichols – Square Wire Mesh
Domain: mcnichols.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Square Wire Mesh – Galvanized – 340242”, “Item Number”: “3402423610”, “Product Line”: “Wire Mesh”, “Mesh Type”: “Square”, “Series Name”: “HARDWARE & INDUSTRIAL CLOTH”, “Series Number”: “1984”, “Construction Type”: “Welded”, “Primary Material”: “Galvanized Steel (GV)”, “Alloy/Grade/Type”: “Hot Dipped (HD)”, “Material Finish”: “Mill Finish”, “Weave/Trim Type”: “Welded – Trimmed”, “…
8. Triumph Exp – Steel Gauge Solutions
Domain: triumphexp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Gauge: 18, 20, 22; Type: Aluminized Steel, Cold Rolled Steel (CRS), Hot Rolled Steel (HR); Specific Products Mentioned: Eastwood panel patch kit (20 gauge Aluminized Steel), C1008/1010 HR Steel Sheet, C1008/1010 CRS Steel Sheet; Tools Suggested: Angle grinder with zip wheel, Beverly shear, pneumatic nibbler, electric shears.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 19 gauge steel
In the dynamic landscape of steel sourcing, 19 gauge steel stands out as a versatile choice for various applications, from construction to manufacturing. Its thickness, at approximately 1.062 mm, strikes a balance between durability and weight, making it ideal for structural components, automotive parts, and HVAC systems. For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of gauge standards and sourcing strategies is crucial. By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can not only optimize costs but also ensure consistent quality and timely delivery.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for reliable suppliers of 19 gauge steel will likely increase. Buyers should focus on establishing relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide transparency and flexibility in their operations. Additionally, exploring regional suppliers may enhance logistics and reduce lead times.
Looking ahead, the future of sourcing 19 gauge steel is promising. With advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability, companies that adapt their sourcing strategies will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Now is the time for B2B buyers to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with suppliers, and secure the best materials for your projects.