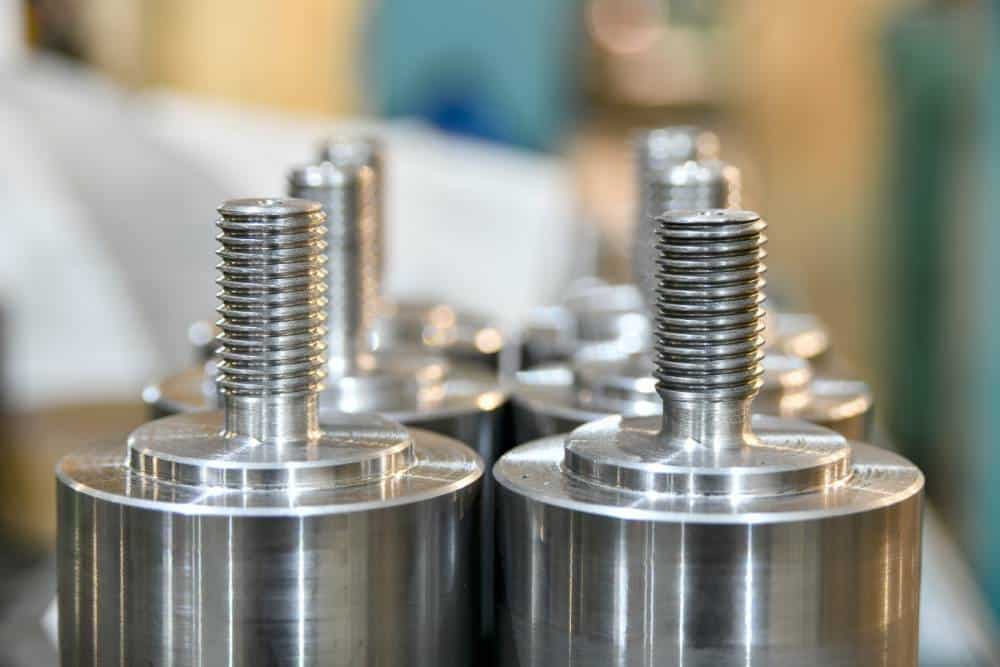
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 17 4 hardness
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality materials like 17-4 hardness stainless steel presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This precipitation-hardened alloy, renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, is crucial for applications across various industries, including aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing. However, navigating the complexities of sourcing can be daunting, particularly for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics and supplier reliability vary widely.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of 17-4 hardness stainless steel, offering insights into its different types, mechanical properties, and ideal applications. We will explore critical factors such as supplier vetting, quality certifications, and cost considerations, ensuring you are equipped to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the nuances of this material and the global market landscape, you can mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, whether you are operating in Vietnam, Nigeria, or elsewhere.
Ultimately, this guide empowers B2B buyers with the knowledge to identify reliable suppliers, evaluate product specifications, and negotiate favorable terms, all while enhancing your supply chain’s efficiency and effectiveness. Your journey towards successful procurement starts here, as we unlock the potential of 17-4 hardness stainless steel for your business needs.
Understanding 17 4 hardness Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | High strength, moderate hardness, good ductility | Aerospace components, oil and gas equipment | Pros: Excellent tensile strength; Cons: Limited corrosion resistance compared to other conditions. |
| H1025 | Balanced strength and toughness, good formability | Marine applications, chemical processing | Pros: Superior weldability; Cons: Slightly lower hardness than H900. |
| H1075 | Lower strength than H900, but improved ductility | Food processing, automotive parts | Pros: Better machinability; Cons: Reduced corrosion resistance. |
| H1150 | Enhanced toughness, lower yield strength | Pump shafts, mechanical seals | Pros: Good for dynamic loading; Cons: Not suitable for high-stress applications. |
| H1150D | Designed for high resistance to stress corrosion cracking | Aerospace and nuclear applications | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance; Cons: Requires precise heat treatment for optimal performance. |
What are the Characteristics of H900 Type 17-4 Hardness?
H900 is one of the most commonly used conditions of 17-4 PH stainless steel. It features high tensile strength and moderate hardness, making it suitable for demanding applications in the aerospace and oil and gas industries. Buyers should consider that while H900 offers excellent mechanical properties, its corrosion resistance is not as robust as that of other variants, which may be critical in highly corrosive environments.
How Does H1025 Differ from Other 17-4 Hardness Types?
H1025 presents a balanced profile of strength and toughness, complemented by good formability and weldability. This makes it an ideal choice for marine applications and chemical processing, where both mechanical integrity and resistance to corrosion are important. While H1025 provides superior weldability compared to H900, it has slightly lower hardness, which might influence its suitability for certain high-stress applications.
What Makes H1075 Suitable for Food Processing?
H1075 is characterized by lower strength than H900 but enhanced ductility, which allows for better machinability. This condition is often chosen for food processing and automotive parts due to its ability to withstand moderate mechanical stress while providing sufficient corrosion resistance. However, buyers should be aware that the trade-off for improved machinability is a reduction in overall hardness.
Why Choose H1150 for Mechanical Seals?
H1150 is recognized for its enhanced toughness and lower yield strength, making it suitable for applications involving dynamic loading, such as pump shafts and mechanical seals. Its ability to absorb shock and resist fracture makes it a preferred choice in scenarios where mechanical integrity is paramount. However, it is essential for buyers to note that H1150 may not be ideal for high-stress applications due to its lower strength.
What Benefits Does H1150D Offer for High-Stress Applications?
H1150D is specifically engineered to provide high resistance to stress corrosion cracking, making it an excellent choice for aerospace and nuclear applications. Its superior corrosion resistance makes it particularly valuable in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern. However, achieving optimal performance with H1150D requires precise heat treatment, which buyers must consider when planning their procurement and processing strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of 17 4 hardness
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 17 4 hardness | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components (e.g., landing gear, valves) | High strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance | Certification standards (e.g., AS9100), heat treatment options |
| Oil and Gas | Pump shafts and mechanical seals | Durability under extreme conditions and reduced downtime | Compatibility with fluids, corrosion resistance specifications |
| Chemical Processing | Equipment and piping systems | Ability to withstand harsh chemicals and high temperatures | Material certifications, fabrication methods, and lead times |
| Food Processing | Processing equipment (e.g., mixers, conveyors) | Hygiene and corrosion resistance in food environments | Compliance with food safety standards, ease of cleaning |
| Defense and Military | Weapon systems and components | Reliability and performance in high-stress situations | Military-grade certifications, stringent quality control |
How is 17-4 Hardness Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, 17-4 PH stainless steel is extensively utilized in critical components such as landing gear and valves. The material’s high strength-to-weight ratio ensures structural integrity while minimizing weight, which is essential for fuel efficiency. Additionally, its corrosion resistance is vital for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Buyers must ensure that the materials meet aerospace certification standards, such as AS9100, and consider the heat treatment options available to achieve the desired hardness.
What Role Does 17-4 Hardness Play in the Oil and Gas Sector?
The oil and gas industry relies on 17-4 PH stainless steel for applications like pump shafts and mechanical seals. These components face extreme operational conditions, including high pressures and corrosive environments. The durability provided by 17-4 hardness minimizes the risk of equipment failure, which can lead to costly downtimes. Buyers should assess the compatibility of the material with specific fluids and ensure that corrosion resistance specifications align with their operational needs.
How is 17-4 Hardness Beneficial in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, 17-4 PH stainless steel is employed in equipment and piping systems that must endure aggressive chemicals and elevated temperatures. The alloy’s exceptional toughness and corrosion resistance help maintain operational efficiency and safety. For international buyers, it is crucial to obtain material certifications that verify the steel’s performance under specific conditions, alongside considerations for fabrication methods that meet project timelines.
Why is 17-4 Hardness Important in Food Processing?
The food processing industry uses 17-4 PH stainless steel for equipment such as mixers and conveyors, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount. This material ensures compliance with food safety standards while providing durability against wear and tear from continuous use. Buyers must focus on sourcing materials that meet health regulations and consider the ease of cleaning to maintain high hygiene standards in production environments.
How is 17-4 Hardness Utilized in Defense and Military Applications?
In defense and military sectors, 17-4 PH stainless steel is critical for manufacturing weapon systems and components that require reliability under extreme conditions. The material’s high strength and toughness ensure performance in high-stress situations, which is vital for operational success. Buyers in this sector should prioritize military-grade certifications and stringent quality control measures to guarantee that the materials meet the rigorous demands of military applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’17 4 hardness’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Quality Across Different Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in maintaining consistent quality when sourcing 17-4 PH stainless steel from multiple suppliers. Variability in hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance can lead to failures in critical applications, particularly in industries like aerospace and oil and gas. Buyers may struggle with varying specifications, which complicates their quality control processes and can result in costly reworks or product recalls.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should establish clear specifications based on industry standards such as AMS 5643 and ASTM A564. When evaluating suppliers, prioritize those who are ISO certified and have a proven track record in quality assurance. Implement a robust supplier evaluation process that includes reviewing their quality documentation and conducting periodic audits. Additionally, consider investing in advanced material testing techniques to ensure that the 17-4 hardness meets the required standards before it is put into production. This proactive approach can help ensure consistency and reliability across different batches and suppliers.
Scenario 2: Navigating Heat Treatment Variability
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the variability in heat treatment processes for 17-4 PH stainless steel, which can significantly affect the material’s hardness and overall performance. Different heat treatment conditions—such as H900, H1025, and H1150—yield different mechanical properties, complicating the selection process for specific applications. Buyers may find themselves inadvertently using the wrong heat-treated material, leading to structural failures in their products.
The Solution: To effectively navigate heat treatment variability, buyers should work closely with metallurgists or materials engineers to determine the optimal heat treatment condition for their specific application. Documenting and sharing application requirements with suppliers can help them recommend the appropriate heat treatment process. Additionally, implementing a testing protocol that includes hardness testing and tensile strength assessments on incoming materials can serve as a quality check. By understanding the nuances of heat treatment and establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers, buyers can ensure they procure the right material for their needs.
Scenario 3: Addressing Corrosion Resistance Concerns in Harsh Environments
The Problem: Buyers often encounter issues with corrosion resistance when using 17-4 PH stainless steel in harsh environments, such as offshore oil rigs or chemical processing plants. While 17-4 offers good corrosion resistance, it may not be sufficient in highly corrosive settings, leading to premature failure of components and increased maintenance costs. This challenge is particularly significant for buyers in regions with extreme environmental conditions, where durability is paramount.
The Solution: To tackle corrosion resistance issues, buyers should consider specifying additional treatments or coatings that enhance the corrosion resistance of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Options such as passivation, which removes free iron and enhances the protective oxide layer, can significantly improve performance. Additionally, buyers should evaluate the potential for using alternative alloys or hybrid materials that offer better resistance in specific environments. Engaging in thorough environmental assessments prior to material selection can also aid in determining the most suitable solution. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can extend the lifespan of their components and reduce overall operational costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 17 4 hardness
What Are the Key Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel for B2B Buyers?
17-4 PH stainless steel is a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel known for its exceptional strength, toughness, and moderate corrosion resistance. It typically contains 15-17.5% chromium and 3-5% nickel, making it suitable for high-temperature applications, such as in the aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing industries. The material can withstand temperatures up to 600°F (316°C) and is available in various heat-treated conditions (e.g., H900, H1025) that influence its mechanical properties, including yield strength and hardness.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using 17-4 PH Stainless Steel?
Pros:
– Durability: 17-4 PH offers high tensile strength and hardness, which enhances its durability in demanding environments.
– Corrosion Resistance: The alloy’s composition provides good resistance to various corrosive media, making it suitable for applications exposed to harsh chemicals.
– Customizability: The material can be tailored through heat treatment to meet specific performance requirements, allowing for versatility across different applications.
Cons:
– Cost: Compared to standard stainless steels, 17-4 PH can be more expensive due to its alloying elements and processing requirements.
– Manufacturing Complexity: The need for precise heat treatment processes can complicate manufacturing and increase lead times.
– Weldability Limitations: While it can be welded, the heat treatment can affect its properties, necessitating careful consideration during fabrication.
How Does 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Impact Specific Applications?
The application of 17-4 PH stainless steel varies widely based on the specific media it will encounter. For instance, in the aerospace industry, components made from this alloy can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while maintaining structural integrity. In the oil and gas sector, its resistance to corrosive environments makes it ideal for pump shafts and mechanical seals. However, buyers must ensure compatibility with the specific media involved in their applications, as some aggressive chemicals may still pose a risk to the alloy’s performance.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting 17-4 PH Stainless Steel?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of compliance with local standards and certifications. Common standards include ASTM, DIN, and JIS, which dictate the material’s quality and performance characteristics. Additionally, understanding the local market dynamics, such as availability and pricing fluctuations, can help buyers make informed decisions. For instance, sourcing from suppliers with robust supply chains can mitigate risks associated with lead times and material shortages.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 17-4 Hardness
| Material | Typical Use Case for 17 4 hardness | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH Stainless Steel | Aerospace components, oil and gas applications | High strength and toughness in extreme conditions | Higher cost compared to standard stainless steels | High |
| Cronidur® 30 | Medical engineering, precision mechanics | Excellent corrosion resistance and wear properties | Limited availability in some regions | Medium |
| 440C Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, tooling | Good hardness and wear resistance | Lower corrosion resistance compared to 17-4 PH | Medium |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Marine applications, chemical processing | Superior corrosion resistance in saline environments | Lower strength compared to 17-4 PH | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of 17-4 PH stainless steel and its alternatives, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 17 4 hardness
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for 17-4 PH Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing process for 17-4 PH stainless steel involves several critical stages that ensure the material meets the stringent requirements of various industries, particularly aerospace, chemical processing, and oil and gas. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for 17-4 Stainless Steel Production?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials that meet the specific chemical composition requirements for 17-4 PH stainless steel. This alloy typically contains around 17% chromium and 4% nickel, among other elements. Suppliers often conduct a thorough analysis to verify the composition of the raw materials.
Once the materials are sourced, they undergo melting and refining processes, usually in vacuum or argon atmosphere furnaces to minimize contamination. This stage is crucial to achieving the desired mechanical properties and ensuring uniformity in the alloy’s structure.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel?
Forming processes for 17-4 PH stainless steel include forging, rolling, and extrusion. These methods shape the material into usable forms while maintaining its integrity.
- Forging: This technique involves shaping the heated metal using compressive forces, which enhances its strength through grain refinement.
- Rolling: Hot or cold rolling processes are used to produce sheets, plates, and bars, allowing for precise control over the thickness and dimensions of the material.
- Extrusion: This method forces the molten metal through a die to create complex shapes, which is particularly useful for specialized applications.
Each of these forming techniques must be performed under controlled conditions to ensure that the material retains its desirable properties, including hardness and corrosion resistance.
How Is Assembly Conducted for 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Products?
The assembly of components made from 17-4 PH stainless steel often requires specialized techniques due to the alloy’s unique properties. Welding is common, but it must be approached with caution to prevent issues such as cracking. Techniques like shielded fusion welding or resistance welding are preferred due to their ability to produce strong joints without compromising the material’s integrity.
Additionally, components may undergo machining processes such as CNC machining, grinding, and stamping to achieve the final specifications. These processes are critical for ensuring tight tolerances and surface finishes that meet industry standards.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for 17-4 Stainless Steel?
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality and functional properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel products. Common techniques include:
- Heat Treatment: This involves aging the material at specific temperatures to achieve the desired hardness and strength. For 17-4 PH, this typically ranges from 480 °C to 760 °C, depending on the required properties.
- Surface Treatment: Methods such as passivation and polishing are employed to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Passivation removes free iron and other surface contaminants, enhancing the material’s durability in harsh environments.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for 17-4 PH Stainless Steel?
Quality assurance is a vital component of the manufacturing process for 17-4 PH stainless steel. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality across all stages of production. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are crucial for products intended for specialized applications, particularly in Europe and the oil and gas sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically implemented throughout the manufacturing process to maintain high standards. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production to identify defects or deviations from standards early in the process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to assess their performance against required specifications.
Common testing methods for 17-4 PH stainless steel include tensile tests, hardness tests, and corrosion resistance tests. These assessments provide critical data on the material’s properties and ensure compliance with industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are key strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall facility conditions.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed reports from suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems, testing results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the materials and products can enhance confidence in the supplier’s quality assurances.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control Certification for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control certifications. Different regions may have varying requirements and standards, which can affect the acceptance of products in specific markets. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East may look for compliance with local standards.
Understanding these nuances enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers and ensures that their products meet the regulatory requirements of their respective markets.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for 17-4 PH stainless steel are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these stages and quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality materials that meet their specific needs and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’17 4 hardness’
In this guide, we provide a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure 17-4 hardness stainless steel. This material is renowned for its strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for various industrial applications. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions when sourcing this critical alloy.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential to ensure the sourced material meets your project needs. Consider factors such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and intended applications. For instance, determine whether you require specific heat treatment conditions like H900 or H1150, as these will significantly affect the material’s performance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Thorough research is crucial when identifying potential suppliers of 17-4 hardness stainless steel. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation in the industry and a proven track record. Utilize platforms like industry forums, trade shows, and supplier databases to compile a list of candidates that specialize in stainless steel alloys.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with any supplier, ensure they possess the necessary certifications to guarantee quality and compliance. Look for ISO certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Additionally, check for any industry-specific certifications relevant to your application, such as AS9100 for aerospace components.
Step 4: Request Material Data Sheets
Request detailed material data sheets (MDS) from potential suppliers to assess the properties of their 17-4 stainless steel offerings. These sheets should include information on chemical composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment conditions. Analyzing these details helps verify that the material aligns with your defined specifications.
Step 5: Assess Cost and Lead Times
Cost and lead times are critical factors in the procurement process. Request quotes from multiple suppliers and compare them, taking note of any hidden costs such as shipping or handling. Additionally, inquire about lead times to ensure they meet your project deadlines. A reliable supplier should provide transparent pricing and realistic delivery schedules.
Step 6: Conduct Supplier Audits
If possible, conduct audits or site visits to assess the capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This step allows you to evaluate their production processes, quality control measures, and overall operational efficiency. Engaging directly with the supplier can also foster better communication and trust, essential for long-term partnerships.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, finalize contracts that clearly outline terms and conditions, including pricing, delivery schedules, and quality expectations. Ensure that all parties agree on the specifications and responsibilities to prevent disputes later. Clear contractual terms will protect your interests and facilitate smoother transactions.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for 17-4 hardness stainless steel, ensuring they select the best suppliers and receive high-quality materials tailored to their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 17 4 hardness Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing 17-4 Hardness Materials?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing 17-4 hardness stainless steel, several key components come into play. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The price of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. 17-4 PH stainless steel contains essential elements such as chromium and nickel, which are subject to market fluctuations. Buyers should stay informed about global commodity prices and seek suppliers who can provide competitive pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing processes involved. Skilled labor is essential for tasks such as machining and heat treatment, particularly for achieving the desired hardness levels.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Understanding these costs helps in evaluating the total pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized parts. Buyers should account for these expenses when considering bespoke manufacturing solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the 17-4 hardness material meets industry standards and specifications requires a robust QC process. This includes testing for tensile strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and the destination. International buyers must consider freight, customs duties, and insurance when calculating logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on competition, demand, and the supplier’s operational efficiency. Buyers should negotiate to achieve a favorable margin without compromising on quality.
What Factors Influence Pricing for 17-4 Hardness Stainless Steel?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 17-4 hardness stainless steel. Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their needs carefully and negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized specifications can lead to increased costs due to unique tooling and processing requirements. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: The presence of quality certifications (such as ISO) adds value but can also increase costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, production capacity, and history of on-time delivery can all affect pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will impact the total cost of ownership. For instance, FOB (Free On Board) pricing might lead to additional shipping costs, while DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) pricing includes shipping and customs duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for International Sourcing?
For international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency.
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive negotiations with suppliers. Highlighting long-term partnerships or larger order volumes can yield better pricing and terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Assess TCO by considering all associated costs, including logistics, duties, and potential downtime due to quality issues.
-
Leverage Technology: Use digital platforms for sourcing and supplier evaluation. This can streamline the procurement process and provide access to a wider range of suppliers.
-
Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with import regulations and tariffs specific to your region to avoid unforeseen costs.
-
Risk Mitigation: Diversify suppliers to reduce dependency on a single source, minimizing risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for 17-4 hardness stainless steel can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific buyer requirements. It is essential for buyers to conduct their due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 17 4 hardness With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to 17-4 Hardness
In the realm of materials engineering, selecting the right alloy or treatment method is crucial for achieving the desired performance characteristics in various applications. 17-4 PH stainless steel is renowned for its impressive hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice across several industries. However, there are alternative solutions that might better suit specific needs depending on factors such as cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements. This analysis compares 17-4 hardness with two viable alternatives: Cronidur® 30 and 440C stainless steel.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 17-4 Hardness | Cronidur® 30 | 440C Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, good corrosion resistance | Superior corrosion resistance, excellent wear resistance | High hardness, lower corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires heat treatment for optimal properties | Similar processing, specialized techniques needed | Easier to machine and fabricate |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance due to corrosion resistance | Low maintenance, highly durable | Moderate, prone to rust without treatment |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, oil and gas, food processing | Aerospace, medical, high-stress applications | Cutlery, industrial blades, ball bearings |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cronidur® 30
Cronidur® 30 is a martensitic stainless steel that offers enhanced corrosion resistance compared to 440C, making it suitable for applications in aggressive environments. Its superior wear resistance is particularly beneficial in high-stress situations, such as in aerospace and medical engineering. However, Cronidur® 30 comes at a higher cost, which may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects. The processing of this alloy requires specialized techniques, which can complicate its implementation in some scenarios. Despite these challenges, its low maintenance requirements and durability can lead to cost savings over time.
440C Stainless Steel
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon martensitic alloy known for its excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for manufacturing cutlery, industrial blades, and ball bearings. While it is easier to machine and fabricate compared to 17-4 and Cronidur® 30, its corrosion resistance is not as robust, making it less suitable for applications exposed to harsh environments. The lower cost of 440C can be appealing, especially for projects where budget constraints are a primary concern. However, without proper treatment, 440C can be prone to rust, necessitating regular maintenance to ensure longevity.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between 17-4 hardness and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including performance characteristics, cost, and maintenance expectations. For applications demanding high strength and moderate corrosion resistance, 17-4 PH is a strong candidate. However, if enhanced corrosion resistance and wear performance are paramount, Cronidur® 30 may be worth the investment. Conversely, for projects with tighter budgets where ease of machining is a priority, 440C could be the most practical choice. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational demands and financial constraints of the business to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 17 4 hardness
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 17-4 Hardness?
When considering 17-4 PH stainless steel, understanding its critical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are some of the most important specifications:
1. Material Grade
17-4 PH stainless steel is categorized under various material grades, including UNS S17400, AMS 5643, and ASTM A564. These classifications indicate the alloy’s composition and mechanical properties, making them vital for industries that require stringent material standards, such as aerospace and chemical processing. B2B buyers should ensure that the material grade aligns with industry specifications to avoid compliance issues.
2. Hardness
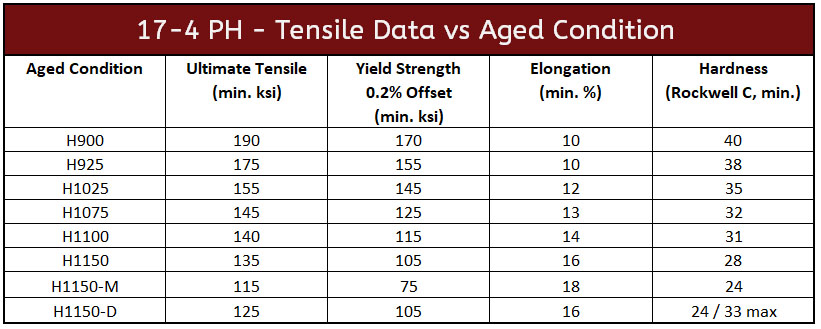
Hardness is a crucial property that indicates the material’s resistance to deformation and wear. For 17-4 PH, hardness values can vary significantly based on heat treatment, ranging from 255 HB (Brinell) to 388 HB depending on the condition (H900 to H1150). Understanding these hardness levels helps buyers select the appropriate grade for applications that experience high wear or stress.
3. Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
The ultimate tensile strength of 17-4 PH varies from 115,000 PSI to 190,000 PSI, depending on the heat treatment condition. This property is critical as it reflects the maximum stress the material can withstand while being stretched or pulled. Buyers in sectors like oil and gas or aerospace should prioritize UTS to ensure that the selected material can handle operational stresses.
4. Yield Strength
Yield strength is another vital specification that indicates the material’s ability to return to its original shape after deformation. For 17-4 PH, yield strength ranges from 75,000 PSI to 170,000 PSI. This property is particularly important in applications where structural integrity is paramount, such as in pump shafts or mechanical seals.
5. Elongation
Elongation measures the material’s ability to stretch before breaking, expressed as a percentage. In 17-4 PH, elongation values range from 10% to 18%, depending on the treatment condition. Higher elongation indicates better ductility, which is crucial for parts that must undergo significant deformation during manufacturing or operation.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in B2B Transactions for 17-4 Hardness?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are some commonly used terms in the B2B space related to 17-4 hardness:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of 17-4 PH, OEMs often require specific material grades and properties to meet the performance standards of their products. Understanding OEM requirements can help buyers ensure compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. For 17-4 PH stainless steel, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific material treatment. Buyers need to be aware of MOQ to plan their inventory and budget effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities of materials. When dealing with 17-4 PH, issuing an RFQ can help buyers gauge market pricing and availability, enabling more informed procurement decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions involving 17-4 PH stainless steel, as it clarifies who is responsible for costs and risks during transport.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment refers to the processes used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. For 17-4 PH, this includes processes like solution treatment and aging, which are essential for achieving desired hardness and strength. Buyers should understand heat treatment specifications to ensure they receive the correct material properties.
Incorporating this knowledge into procurement strategies can significantly enhance decision-making, ensuring that B2B buyers from diverse regions can navigate the complexities of sourcing 17-4 hardness effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 17 4 hardness Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Driving the 17-4 Hardness Sector?
The global market for 17-4 hardness, particularly in the stainless steel sector, is significantly influenced by several key drivers. Demand for high-performance materials in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing continues to grow, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As these regions industrialize, the need for durable, corrosion-resistant materials that can withstand extreme conditions is paramount. Furthermore, the versatility of 17-4 PH stainless steel—due to its exceptional strength, toughness, and excellent machinability—positions it as a preferred choice among international B2B buyers.
Technological advancements are reshaping sourcing trends, with an increasing emphasis on automation and data analytics in procurement processes. B2B buyers are leveraging digital platforms for streamlined sourcing, allowing for better price comparisons and access to a wider range of suppliers. Additionally, the rise of additive manufacturing is allowing for more innovative applications of 17-4 stainless steel, enhancing its appeal in custom fabrication projects. Buyers are also focusing on supply chain transparency and efficiency, seeking suppliers that can provide quick turnaround times while maintaining quality.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the 17-4 Hardness Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the sourcing of 17-4 hardness materials. The environmental impact of steel production is significant, leading many companies to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in their supply chains, seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and possess relevant certifications. This includes using recycled materials and implementing processes that reduce carbon emissions.
Furthermore, the availability of “green” certifications can enhance the marketability of products made from 17-4 stainless steel. Buyers are more likely to choose suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability standards. This shift is not just about compliance; it also reflects a growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products, which can positively impact brand reputation and customer loyalty. As such, companies that prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies will likely gain a competitive advantage in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of 17-4 Hardness in B2B Sourcing?
The evolution of 17-4 hardness stainless steel can be traced back to its development in the 1950s as a solution for demanding applications in aerospace and defense. Initially recognized for its exceptional mechanical properties, including high strength and corrosion resistance, 17-4 PH stainless steel quickly became a go-to material for manufacturers in various sectors. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and heat treatment processes have further enhanced its performance characteristics, making it a versatile choice for both standard and specialized applications.
As global industries evolved, so did the demand for high-quality materials, leading to a broader acceptance of 17-4 stainless steel in fields beyond aerospace, such as medical devices and food processing. The historical context underscores its sustained relevance in the market, driven by ongoing innovations and a growing need for materials that meet stringent performance criteria. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it informs sourcing decisions and highlights the reliability of 17-4 hardness as a material of choice for future projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 17 4 hardness
-
How do I determine the right heat treatment for 17-4 PH stainless steel?
Selecting the appropriate heat treatment for 17-4 PH stainless steel largely depends on the desired mechanical properties for your application. Common heat treatment conditions include H900, H1025, H1075, H1150, and H1150D, each providing different levels of hardness and strength. For example, H900 offers the highest strength, while H1150 provides improved ductility. It’s essential to collaborate with your supplier to understand your specific requirements and ensure the heat treatment aligns with your operational needs. -
What are the typical applications for 17-4 hardness stainless steel?
17-4 PH stainless steel is widely utilized in industries requiring high strength and moderate corrosion resistance, such as aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing. Typical applications include pump shafts, mechanical seals, and components in aircraft. Its versatility and excellent mechanical properties make it suitable for demanding environments, where durability and reliability are paramount. -
What is the best grade of 17-4 for aerospace applications?
For aerospace applications, the H900 condition of 17-4 PH stainless steel is often considered the best choice due to its exceptional tensile strength and fatigue resistance. This grade can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, making it ideal for critical aerospace components. Always consult with engineering experts to ensure compliance with aerospace standards and specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 17-4 stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities for 17-4 stainless steel can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific product form (e.g., bars, sheets, or custom components). Typically, MOQs can range from a few kilograms to several tons. Discuss your project requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are sourcing for large-scale projects. -
How can I vet suppliers of 17-4 hardness stainless steel?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their certifications, quality assurance processes, and track record in the industry. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, as this indicates adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, request references from previous clients and evaluate their responsiveness and technical support capabilities. It’s advisable to conduct site visits if possible to inspect their facilities and production processes. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 17-4 stainless steel?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days. International buyers should clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or bulk orders. Always ensure that the payment terms align with your cash flow management practices. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for 17-4 stainless steel?
Quality assurance for 17-4 stainless steel should include comprehensive inspection and testing protocols. Common measures include verifying material certifications, conducting tensile tests, and performing corrosion resistance evaluations. Suppliers should provide documentation such as Certificates of Compliance (CoC) and material test reports to confirm that the steel meets specified standards and conditions. -
How is logistics managed when importing 17-4 hardness stainless steel?
Logistics for importing 17-4 hardness stainless steel involves coordinating shipping, customs clearance, and delivery to your location. It’s crucial to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) that clarify responsibilities. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates, is prepared in advance to facilitate smooth customs processing and minimize delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 17 4 Hardness Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AZOM – 17-4 Precipitation-Hardened Stainless Steel
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Grade: 17-4 (UNS S17400)
Type: Precipitation-hardened stainless steel
Chemical Composition:
– Iron (Fe): 73%
– Chromium (Cr): 15.0 – 17.5%
– Nickel (Ni): 3.0 – 5.0%
– Copper (Cu): 3.0 – 5.0%
– Manganese (Mn): 1.0%
– Silicon (Si): 1.0%
– Tantalum (Ta): 0.45%
– Niobium (Nb): 0.45%
– Carbon (C): 0.070%
– Phosphorous (P): 0.040%
– Sulfur (S): 0.030%
Physical Properties:
– Density: 7.75 g/cm³ (0.280 lb…
2. Premium Alloys – 17-4 Stainless Steel
Domain: premiumalloys.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 17-4 stainless steel is a popular alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and versatility. It contains approximately 17% chromium and 4% nickel, making it suitable for high-temperature applications up to 600°F (316°C). It is ideal for industries such as gas, chemical, and aviation. Key properties include:
– **Physical Properties:**
– H900: Tensile Strength: 190 KSI, Yield …
3. Stainless Shapes – 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Solutions
Domain: stainlessshapes.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 17-4 PH stainless steel, H condition designations (H900, H1025, H1075, H1100, H1150, Double H1150, H1150M) refer to different heat treatment conditions that affect mechanical properties. H900: Precipitation hardened at 900°F (482°C), hardness 35-43 HRC, high strength and hardness. H1025: Precipitation hardened at 1025°F (552°C), hardness 30-36 HRC, balance of strength and toughness. H1075: Precipi…
4. SSA Corp – 17-4 Stainless AMS 5643 Properties
Domain: ssa-corp.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, SSA Corp – 17-4 Stainless AMS 5643 Properties, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Best Stainless – 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Bar
Domain: beststainless.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ’17-4 PH Stainless Steel Bar’, ‘chemical_composition’: {‘chromium’: ‘17%’, ‘nickel’: ‘4%’, ‘carbon’: ‘0.070 max’, ‘copper’: ‘3.00 – 5.00’, ‘manganese’: ‘1.00 max’, ‘phosphorus’: ‘0.040 max’, ‘silicon’: ‘1.00 max’, ‘sulfur’: ‘0.030 max’, ‘columbian_tantalum’: ‘0.15 – 0.45’}, ‘standards’: [‘UNS S17400’, ‘AMS 5643’, ‘ASTM A564’, ‘ASTM A693’, ‘Grade 630’, ‘NACE MR0175/MR0103 (H-1150D …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 17 4 hardness
In the competitive landscape of international B2B sourcing, understanding the nuances of 17-4 PH stainless steel is essential for making informed decisions. This alloy’s superior strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility make it a preferred choice across various industries, including aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide detailed specifications, heat treatment options, and customized solutions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality materials but also enhances supply chain resilience. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and distributors who understand local market dynamics in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses can secure competitive pricing and reliable delivery schedules.
Looking ahead, the demand for 17-4 PH stainless steel is projected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and industry needs for durable materials. B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage this opportunity by assessing their current suppliers and exploring new partnerships that align with their long-term goals. Take action now to position your business advantageously in the evolving global market.