Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
The global market for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel is both expansive and complex, posing significant challenges for B2B buyers who must navigate varying standards, specifications, and supplier capabilities. As international businesses seek high-quality materials for diverse applications, understanding the nuances of 16 gauge stainless steel—measuring approximately 1.59 mm in thickness—becomes critical. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing essential aspects such as types of stainless steel, applications across industries, effective supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Germany and Vietnam, making informed purchasing decisions is crucial. The guide empowers these buyers by providing actionable insights and data-driven recommendations, ensuring they can source the right materials to meet their operational needs while optimizing costs. By exploring the unique properties and advantages of 16 gauge stainless steel, buyers can leverage this knowledge to enhance product quality, improve durability, and ultimately drive business growth.
As the demand for reliable and resilient materials continues to rise, this guide will equip you with the tools necessary to thrive in the competitive landscape of stainless steel procurement.
Understanding 16 gauge thickness stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability | Food processing, chemical containers, architecture | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective. Cons: Lower corrosion resistance than 316 in saline environments. |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments | Pharmaceutical, marine applications, medical devices | Pros: High durability, resistant to pitting. Cons: Higher cost compared to 304. |
| 430 Stainless Steel | Ferritic stainless steel, magnetic properties | Automotive trim, kitchen appliances, decorative applications | Pros: Cost-effective, good oxidation resistance. Cons: Limited corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades. |
| 201 Stainless Steel | Lower nickel content, good mechanical properties | Kitchen equipment, commercial appliances | Pros: Lower price, decent corrosion resistance. Cons: Less resistant to extreme environments than 304 or 316. |
| 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel | Combination of austenitic and ferritic properties, high strength | Oil and gas, chemical processing, pressure vessels | Pros: Excellent strength, high resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Cons: More challenging to weld. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 304 Stainless Steel?
304 stainless steel is one of the most commonly used grades in the industry due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good weldability. It is suitable for a variety of applications, especially in environments where hygiene is paramount, such as food processing and medical equipment. When purchasing, buyers should consider the thickness tolerances and ensure they are selecting the appropriate finish for their specific application.
How Does 316 Stainless Steel Stand Out in B2B Applications?
316 stainless steel is known for its superior resistance to corrosion, particularly in saline and marine environments. This makes it ideal for use in the pharmaceutical and marine industries, where exposure to harsh conditions is common. Buyers should evaluate the specific environmental conditions their products will face and consider the higher initial cost as a worthwhile investment for long-term performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using 430 Stainless Steel?
As a ferritic stainless steel, 430 offers good oxidation resistance and is often used in decorative applications, such as automotive trim and kitchen appliances. It is magnetic, which can be a deciding factor in specific applications. Buyers should weigh its cost-effectiveness against its lower corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades like 304 and 316.
When Is 201 Stainless Steel the Right Choice for Buyers?
201 stainless steel is an economical alternative to higher nickel grades like 304. It provides decent corrosion resistance and is often used in kitchen equipment and commercial appliances. Buyers should be aware of its limitations in extreme environments and consider the trade-off between cost and performance.
What Makes 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel a Strong Option?
2205 duplex stainless steel combines the best of both austenitic and ferritic properties, offering high strength and excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking. It is particularly suitable for oil and gas applications where durability is critical. Buyers must consider welding challenges and ensure they have the right expertise to work with this alloy effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 16 gauge thickness stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Fabrication of equipment such as tanks and conveyors | High corrosion resistance ensures product integrity | Compliance with food safety standards and certifications |
| Construction and Architecture | Structural components for buildings and facades | Provides strength and aesthetic appeal | Availability in various finishes and custom sizes |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of exhaust systems and structural parts | Durability and resistance to high temperatures | Need for precise specifications and certifications |
| Chemical Processing | Storage tanks and piping systems | Prevents contamination and withstands harsh chemicals | Compliance with industry standards and certifications |
| Electronics | Enclosures for electronic devices | Protects sensitive components from environmental factors | Custom fabrication capabilities and rapid prototyping |
How is 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, 16 gauge stainless steel is commonly used to fabricate equipment such as tanks, conveyors, and processing machinery. Its high corrosion resistance is crucial for maintaining product integrity and hygiene, as it prevents contamination from rust or other materials. International B2B buyers in Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers meet food safety standards and provide certifications, as these are critical for compliance in food-related applications.
What Role Does 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Play in Construction and Architecture?
In construction and architecture, 16 gauge stainless steel serves as a vital material for structural components, including beams, columns, and facades. Its strength allows for the creation of durable structures, while its aesthetic appeal enhances the visual aspects of buildings. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, should consider the availability of various finishes and custom sizes to meet specific design requirements, ensuring that the material aligns with architectural standards.
How is 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry utilizes 16 gauge stainless steel primarily in the manufacturing of exhaust systems and various structural parts. The material’s durability and resistance to high temperatures are essential for components that endure extreme conditions. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers who can provide precise specifications and necessary certifications to comply with automotive industry standards, particularly in markets like Vietnam.
What are the Applications of 16 Gauge Stainless Steel in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, 16 gauge stainless steel is employed for constructing storage tanks and piping systems due to its ability to withstand harsh chemicals without degrading. This ensures safe handling and storage of potentially hazardous substances. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with industry standards and certifications, as this guarantees the reliability and safety of the materials used in chemical applications.
Why is 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Important for Electronics?
In the electronics sector, 16 gauge stainless steel is used for manufacturing enclosures that protect sensitive components from environmental factors. Its non-reactive properties prevent contamination and ensure the longevity of electronic devices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer custom fabrication capabilities and rapid prototyping to meet their specific design needs, ensuring that the enclosures align with technological advancements and market demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’16 gauge thickness stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Material
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality 16 gauge stainless steel that meets industry standards. In regions such as Africa and South America, limited access to reliable suppliers can lead to purchasing subpar materials, resulting in product failures or costly delays. Buyers may struggle with identifying trustworthy vendors and ensuring that the specifications match their requirements, which can cause issues in the manufacturing process.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should perform comprehensive market research before selecting suppliers. Utilize online platforms that specialize in stainless steel products and consult industry directories for reputable manufacturers. When engaging with suppliers, request detailed documentation such as material certifications, mill test reports, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). This ensures that the material meets necessary specifications. Additionally, consider establishing partnerships with suppliers who offer consistent quality checks and after-sales support, as this can provide peace of mind and streamline the procurement process.
Scenario 2: Understanding Thickness Variations in 16 Gauge Stainless Steel
The Problem: One common pain point is the confusion surrounding the gauge system and its thickness variations. Buyers may not fully understand the implications of the 16 gauge thickness (approximately 1.6 mm) and how it differs across various metal types. This misunderstanding can lead to improper applications, where the material is either over-engineered or under-engineered for its intended use, resulting in inefficiencies and increased costs.
The Solution: B2B buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the gauge system and its relationship to material properties. This involves studying gauge thickness charts and understanding how different types of stainless steel (like 304 vs. 316) may perform under various conditions. When specifying materials, provide clear documentation that outlines the intended application, load requirements, and environmental factors. Consulting with engineers or material specialists can also enhance understanding, ensuring that the selected gauge is appropriate for the specific application, thus optimizing performance and minimizing waste.
Scenario 3: Fabrication and Handling Issues with 16 Gauge Stainless Steel
The Problem: Fabrication of 16 gauge stainless steel can present its own set of challenges, particularly in terms of cutting, welding, and bending. Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties during the manufacturing phase, such as warping or difficulty in achieving clean cuts, which can result in increased scrap rates and labor costs. Additionally, improper handling can lead to surface damage, compromising the material’s aesthetic and functional qualities.
The Solution: To mitigate fabrication issues, buyers should ensure their teams are trained in best practices for handling and processing 16 gauge stainless steel. Invest in high-quality cutting tools and equipment designed for stainless steel to achieve precise cuts without warping. It’s also advisable to establish standard operating procedures for handling to prevent scratches or contamination. Collaborating with experienced fabricators who understand the nuances of working with stainless steel can also provide valuable insights and techniques. This proactive approach not only enhances production efficiency but also reduces costs associated with rework and material wastage.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
When selecting materials for applications involving 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, it is essential to consider various types of stainless steel and their unique properties. Here, we analyze four common materials that are frequently utilized in B2B contexts, providing insights into their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
What are the Key Properties of 304 Stainless Steel for 16 Gauge Applications?
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used grades due to its excellent corrosion resistance and versatility. It can withstand temperatures up to 870°C (1600°F) in intermittent service and 925°C (1700°F) in continuous service. This material is non-magnetic and has good weldability, making it suitable for various fabrication processes. Its resistance to oxidation and corrosion makes it ideal for environments exposed to moisture and chemicals.
Pros: 304 stainless steel offers high durability and is relatively easy to machine and weld. It is also cost-effective compared to other stainless steel grades.
Cons: While it performs well in many environments, it is not suitable for high chloride environments, as it can lead to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Impact on Application: 304 stainless steel is commonly used in food processing, chemical storage, and architectural applications due to its aesthetic appeal and hygienic properties.
How Does 316 Stainless Steel Compare for 16 Gauge Thickness?
316 stainless steel is often chosen for applications requiring enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments or where exposure to harsh chemicals is expected. It can handle temperatures up to 870°C (1600°F) in intermittent service and is known for its ability to withstand saltwater and acidic conditions.
Pros: The addition of molybdenum enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it a superior choice for challenging environments.
Cons: 316 stainless steel is generally more expensive than 304, which can impact project budgets. It is also more challenging to machine due to its higher strength.
Impact on Application: This material is commonly used in marine applications, chemical processing, and pharmaceutical equipment, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount.
What are the Benefits of Using 430 Stainless Steel in 16 Gauge Thickness?
430 stainless steel is a ferritic grade that offers moderate corrosion resistance and is often used in applications where aesthetics are important. It is magnetic and can be heat treated, making it suitable for various decorative applications.
Pros: This material is more affordable than austenitic grades like 304 and 316, and it has good formability.
Cons: Its corrosion resistance is lower than that of 304 and 316, making it less suitable for harsh environments. It also has limited weldability.
Impact on Application: 430 stainless steel is often used in kitchen equipment, automotive trim, and appliances, where appearance and moderate corrosion resistance are key factors.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing 16 Gauge Stainless Steel?
When selecting stainless steel materials, international buyers must consider compliance with local standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards). Understanding these standards ensures that the materials meet the necessary quality and safety requirements for their specific applications. Additionally, buyers should be aware of the local availability of these materials and the potential impact of tariffs and trade agreements on costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical storage, architectural applications | Excellent corrosion resistance and weldability | Not suitable for high chloride environments | Medium |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Marine applications, chemical processing, pharmaceutical equipment | Superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| 430 Stainless Steel | Kitchen equipment, automotive trim, appliances | Cost-effective and good formability | Moderate corrosion resistance, limited weldability | Low |
| 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, marine, and chemical processing industries | High strength and excellent corrosion resistance | More complex fabrication and higher cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel?
Manufacturing 16 gauge thickness stainless steel involves a series of carefully controlled processes to ensure the material meets specific industry requirements. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in determining the final quality of the product.
How Is Material Prepared for Stainless Steel Production?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-grade stainless steel, commonly either 304 or 316 alloys due to their excellent corrosion resistance and strength. The steel is typically supplied in sheet form, which is cut to the required dimensions.
Next, surface preparation is essential. This may involve cleaning the sheets to remove any contaminants, such as oil or dust, that could affect the subsequent processes. Techniques like sandblasting or chemical cleaning are often employed to achieve a smooth surface finish, ensuring better adhesion during the forming and finishing stages.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Once the material is prepared, the forming process can commence. There are several key techniques utilized in the manufacturing of 16 gauge stainless steel:
-
Shearing: This is the initial cutting process where sheets are cut to specific sizes using shear blades. Precision is vital to ensure the dimensions are within tolerance levels.
-
Bending: Utilizing press brakes or roll formers, the sheets are bent into the desired shapes. This process requires careful calculations to prevent material fatigue and ensure structural integrity.
-
Punching and Notching: These processes create holes and notches in the stainless steel sheets for assembly purposes. Automated CNC machines are often used to enhance precision and efficiency.
-
Welding: For products requiring assembly, welding is a critical step. Techniques such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are commonly employed due to their strong joint capabilities and suitability for stainless steel.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional properties of stainless steel. Common techniques include:
-
Passivation: This process enhances corrosion resistance by removing free iron from the surface. It often involves chemical treatments that create a thin oxide layer.
-
Polishing: To achieve a smooth and reflective surface, polishing is performed using abrasive materials. This step is especially important in applications where appearance is critical.
-
Coating: In some cases, a protective coating may be applied to enhance durability or alter the surface finish. Options include powder coating and anodizing.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Stainless Steel Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of stainless steel products, especially in international markets where standards may vary. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for maintaining quality throughout the production process.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines criteria for a quality management system. It ensures that organizations consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. In addition to ISO, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be required depending on the intended application of the stainless steel products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers must provide certificates of compliance to verify material specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to ensure that each stage meets the predefined specifications. This can include dimensional checks and visual inspections for surface defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, a thorough inspection is performed. This may involve destructive and non-destructive testing methods to ensure the product’s integrity, including tensile strength tests, corrosion resistance tests, and dimensional accuracy assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive measures to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess compliance with quality standards and review the processes in place.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality control reports that outline testing procedures and results. This transparency can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and provide a certificate of inspection.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control and certifications:
-
Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Documentation: Maintaining thorough documentation is crucial. Buyers should ensure that all certificates, inspection reports, and compliance documents are readily available for review.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication with suppliers and foster strong relationships.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality materials that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’16 gauge thickness stainless steel’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure 16 gauge thickness stainless steel. Given its widespread applications in various industries, understanding the nuances of sourcing this material is essential for ensuring quality, compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Follow these steps to navigate the procurement process efficiently.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the stainless steel you need. This includes specifications such as grade (e.g., 304 or 316), thickness (1.59 mm for 16 gauge), and any specific finishes or treatments. Defining these parameters early on helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that you receive material that meets your operational needs.
- Consider applications: Different applications may require specific properties like corrosion resistance or weldability.
- Quality standards: Align your specifications with industry standards relevant to your sector.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Identify a list of potential suppliers who specialize in stainless steel products. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry referrals to compile a comprehensive list. Researching suppliers helps you gauge their market presence and reliability.
- Supplier experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region or industry.
- Product range: Ensure they offer the specific gauge and grade of stainless steel you require.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This evaluation will help you assess their reliability and capacity to meet your needs.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO or ASTM standards.
- Customer feedback: Seek reviews or testimonials from previous clients to understand their satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request quotes for your required stainless steel. Ensure that each quote includes details on pricing, lead times, and any additional costs such as shipping or handling.
- Cost breakdown: Analyze the quotes for transparency in pricing to avoid hidden costs.
- Delivery timelines: Consider the lead times offered by suppliers to align with your project schedules.
Step 5: Assess Quality Control Measures
Inquire about the quality control processes each supplier employs. Understanding their quality assurance protocols can give you confidence in the consistency and reliability of the stainless steel they provide.
- Testing procedures: Ask about material testing, including tensile strength and corrosion resistance tests.
- Return policies: Familiarize yourself with their return or replacement policies in case the material does not meet your specifications.
Step 6: Finalize Contract Terms
Once you’ve selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize the contract terms. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, delivery timelines, and pricing structures are clearly documented.
- Payment terms: Discuss payment options and any potential discounts for bulk purchases.
- Liability clauses: Clarify liability in case of non-compliance with the agreed specifications.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
After finalizing the contract, set up a communication plan with your supplier. Regular communication can help address any potential issues that arise during production or delivery.
- Point of contact: Designate a specific contact person on both sides for efficient communication.
- Progress updates: Schedule regular check-ins to monitor the status of your order and ensure it remains on track.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel?
When sourcing 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base cost of stainless steel fluctuates based on global market conditions, alloy composition (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel), and supplier contracts. Buyers should monitor market trends to capitalize on price dips.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by local wage standards and the complexity of the manufacturing processes. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, the total expense can be significantly impacted.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production techniques can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs refer to the investment needed for production equipment and molds. Customization can lead to higher tooling costs, but it may be necessary for specific applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures that the stainless steel meets required specifications and certifications. This may include testing for corrosion resistance and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the supplier to the buyer’s location and the chosen mode of transport. International shipping can introduce additional complexities such as customs fees and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding the supplier’s margin can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 16 Gauge Stainless Steel?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 16 gauge stainless steel:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs to determine whether to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom orders tailored to specific applications can lead to increased costs due to additional manufacturing steps and requirements. Standard products may be more cost-effective.
-
Materials: The choice of stainless steel grade significantly impacts pricing. Higher-grade materials, such as 316 stainless steel, typically cost more due to enhanced corrosion resistance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet higher quality standards or have specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certification against the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capacity of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping can affect total costs. For instance, choosing Ex Works (EXW) may result in lower upfront costs but could lead to higher logistics expenses compared to Delivered Duty Paid (DDP).
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize their sourcing of 16 gauge stainless steel:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Leverage long-term relationships or potential bulk orders to secure better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and lifecycle costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: When dealing with suppliers from different regions, be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that can affect pricing.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid dependency on a single supplier by establishing relationships with multiple vendors. This can provide leverage in negotiations and mitigate risks related to supply chain disruptions.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes that could impact pricing and availability. This knowledge empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering the various cost components and pricing influencers, buyers can negotiate better deals and make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs. Keep in mind that prices are indicative and can vary based on market conditions and specific buyer requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 16 gauge thickness stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel
In the quest for effective materials in manufacturing and construction, 16 gauge thickness stainless steel is often a popular choice due to its durability and corrosion resistance. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative materials that may offer different advantages, depending on their specific needs and applications. This analysis compares 16 gauge stainless steel with galvanized steel and aluminum, two viable alternatives in the market.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel | Galvanized Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High corrosion resistance, strong, durable | Moderate corrosion resistance, good strength | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost | Moderate initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tools for cutting and welding | Easier to work with, readily available | Easy to fabricate and weld |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Moderate maintenance due to potential rust | Low maintenance, does not rust |
| Best Use Case | High-stress environments, food processing, marine applications | Construction, automotive components | Aerospace, packaging, decorative applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. This alternative is significantly less expensive than 16 gauge stainless steel, making it an appealing choice for budget-conscious projects. It performs well in many applications, particularly in construction and automotive components. However, its corrosion resistance is moderate compared to stainless steel, and in highly corrosive environments, it may require more maintenance to prevent rust. Additionally, galvanized steel is easier to work with, as it requires less specialized equipment for cutting and welding.
Aluminum
Aluminum is another viable alternative that offers a unique set of benefits. It is lightweight, making it easy to transport and handle, which can reduce labor costs in manufacturing and installation. Aluminum also boasts excellent corrosion resistance, often outperforming steel in certain environments, particularly where moisture is prevalent. However, its strength-to-weight ratio means that it may not be suitable for high-stress applications where steel excels. The cost of aluminum can be moderate, but it generally falls between galvanized steel and stainless steel, making it a versatile option for various applications, including aerospace and decorative uses.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting between 16 gauge thickness stainless steel and its alternatives, it is crucial for B2B buyers to assess their specific requirements. Factors such as environmental conditions, budget constraints, and application demands will guide the decision-making process. While 16 gauge stainless steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for high-stress environments, alternatives like galvanized steel and aluminum may provide cost savings and ease of fabrication for less demanding applications. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material will enable buyers to choose the best solution tailored to their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel?
When considering 16 gauge thickness stainless steel for various applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are some essential specifications:
Material Grade
The most common material grade for 16 gauge stainless steel is 304, which is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability, and formability. This grade is particularly useful in environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is frequent, making it ideal for applications in food processing, chemical handling, and architectural features. Understanding the material grade helps B2B buyers assess the suitability of the steel for specific applications.
Thickness and Tolerance
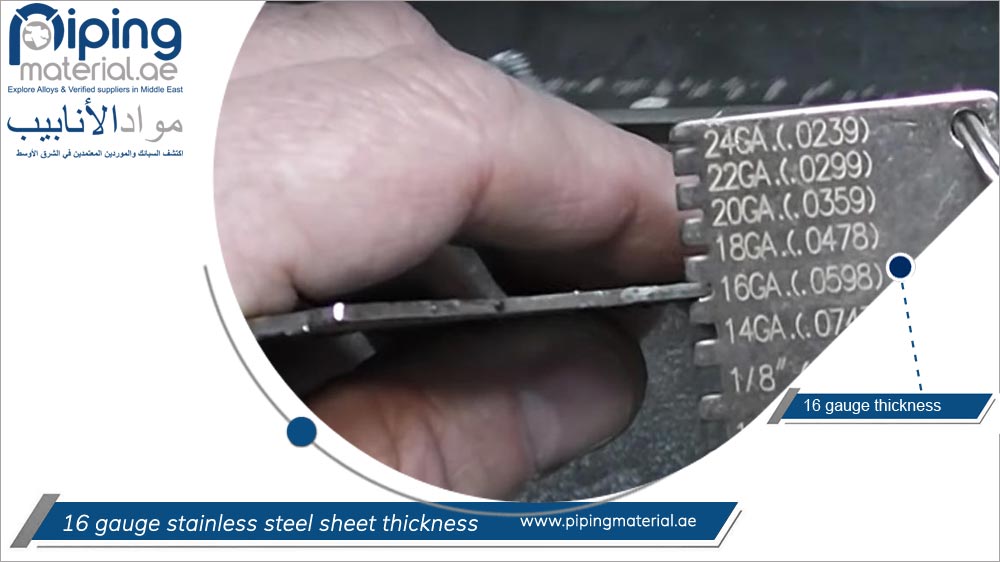
16 gauge stainless steel has a nominal thickness of 0.0595 inches (1.511 mm), but it’s important to note the tolerance levels, which can typically range from ±0.15 mm. Tolerance is critical as it affects the final fit and function of components in manufacturing processes. Tight tolerances are essential in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount.
Yield Strength
Yield strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. For 16 gauge stainless steel, the yield strength is typically around 30,000 psi (207 MPa). This property is vital for B2B buyers as it indicates the material’s ability to handle operational stresses in various applications, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the standout features of stainless steel, particularly grade 304, is its high resistance to corrosion. This property is critical for businesses in sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where contamination can lead to serious health risks. Knowing the corrosion resistance helps buyers evaluate the long-term durability of the material in specific environments.
Fabricability
16 gauge stainless steel is known for its excellent formability, making it easy to cut, bend, and weld. This characteristic is particularly important for manufacturers looking for materials that can be easily shaped into complex designs without compromising structural integrity. Understanding fabricability aids in selecting the right material for custom projects.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Stainless Steel Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of stainless steel, an OEM might source 16 gauge stainless steel sheets for their product line. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential suppliers and partners in their supply chain.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For stainless steel, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels effectively and ensure that they are not overcommitting to purchases.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the case of 16 gauge stainless steel, an RFQ would outline the required specifications, such as material grade and quantity. This term is essential for initiating the procurement process and obtaining competitive bids.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international B2B transactions to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. For 16 gauge stainless steel, lead times can vary based on availability and manufacturing processes. Awareness of lead times is essential for planning production schedules and ensuring timely project completion.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, ensuring that their investments meet their operational needs and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 16 gauge thickness stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel Sector?
The global stainless steel market, particularly for 16 gauge thickness, is witnessing robust growth driven by several key factors. Firstly, the increasing demand for corrosion-resistant materials across various industries, such as construction, automotive, and consumer goods, is a significant driver. Countries in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are experiencing infrastructure booms, which create a heightened need for durable materials like 16 gauge stainless steel. Additionally, the European market, particularly Germany, is focusing on high-quality manufacturing, further boosting demand for this material.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include the adoption of digital platforms for procurement, which facilitate easier access to suppliers and streamline the purchasing process. Technologies such as blockchain are also being integrated to enhance supply chain transparency and traceability, ensuring that buyers can verify the quality and origin of the materials they are purchasing. International buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also assurance of quality and compliance with international standards.
Furthermore, market dynamics are influenced by fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical factors that may impact trade agreements. Buyers must stay informed about these fluctuations and consider diversifying their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B Decisions in the Stainless Steel Sector?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the stainless steel sector. The environmental impact of steel production, including energy consumption and carbon emissions, has prompted many companies to seek sustainable alternatives. For 16 gauge thickness stainless steel, sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize environmentally friendly practices is increasingly important.
Ethical sourcing is not just about environmental concerns; it also encompasses fair labor practices and responsible governance. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers that possess green certifications, such as LEED or ISO 14001, which signify adherence to sustainability standards. These certifications can be a decisive factor for buyers in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks around environmental impact are stringent.
Moreover, the push for recycled materials is gaining traction. Utilizing recycled stainless steel not only reduces the carbon footprint but also aligns with the circular economy principles that many businesses are adopting. Buyers should consider suppliers who offer products made from recycled materials, thereby contributing to sustainability while also meeting their operational needs.
What Is the Historical Context of 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel in B2B Markets?
The use of stainless steel in various applications can be traced back to the early 20th century, when its corrosion-resistant properties were first recognized. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy led to the development of various stainless steel grades, with 304 and 316 being among the most popular. The 16 gauge thickness, which measures approximately 1.6 mm, became a standard for many industrial applications due to its balance of strength and weight, making it ideal for everything from kitchen equipment to structural components.
As industries evolved, so did the demand for stainless steel products, including the 16 gauge variety. The material’s versatility, coupled with innovations in fabrication techniques, has cemented its place in modern manufacturing. Today, B2B buyers benefit from a well-established supply chain and a wealth of options, allowing them to select materials that not only meet technical specifications but also align with their strategic goals in terms of sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
-
How do I choose the right supplier for 16 gauge stainless steel?
Choosing the right supplier involves evaluating their experience, reputation, and product quality. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in international trade, especially those who have successfully served clients in your region. Request samples to assess material quality and confirm they adhere to international standards. Additionally, verify their certifications, such as ISO or ASTM compliance, and inquire about their production capabilities and lead times. Establishing clear communication channels can also help ensure your specific needs are met effectively. -
What are the common applications for 16 gauge stainless steel?
16 gauge stainless steel is widely used in various applications, including construction, automotive, and food processing industries. Its thickness provides a balance of strength and weight, making it suitable for structural components, enclosures, and kitchen equipment. Additionally, its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. Understanding the specific requirements of your project can help you leverage the benefits of 16 gauge stainless steel effectively. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 16 gauge stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities for 16 gauge stainless steel can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from 100 kg to several tons, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the specific product form (sheets, plates, etc.). When negotiating, consider your project size and budget, and discuss the possibility of smaller orders if needed. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for new clients or ongoing contracts. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 16 gauge stainless steel internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or upfront payments, particularly for first-time buyers. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing your order. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable terms over time. -
How can I ensure the quality of 16 gauge stainless steel during sourcing?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test reports for the stainless steel you plan to purchase. Key certifications include ASTM or ISO standards, which demonstrate adherence to industry quality benchmarks. Consider third-party inspections during production or before shipping to verify compliance. Additionally, engage in regular communication with your supplier to address any concerns and establish quality expectations clearly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing 16 gauge stainless steel?
When importing stainless steel, consider shipping methods, customs clearance, and tariffs that may apply. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, taxes, and handling fees, to ensure your budget aligns with the project. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling metal shipments to streamline logistics. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides appropriate documentation to facilitate customs clearance, reducing the risk of delays. -
Can I customize my order for 16 gauge stainless steel?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for 16 gauge stainless steel, including cutting, finishing, and fabrication services. When discussing your order, specify your requirements, such as dimensions, surface finish, or additional treatments like passivation. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your customization needs within the required timeframe. Customization may incur additional costs, so clarify pricing and lead times upfront. -
What are the advantages of using 304 vs. 316 stainless steel in 16 gauge thickness?
304 stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for a wide range of applications. However, 316 stainless steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments or when exposed to chemicals. If your application involves harsh conditions, 316 may be the better choice despite a higher cost. Evaluate the specific environmental conditions your stainless steel will face to make an informed decision between the two grades.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 16 Gauge Thickness Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Protocase – Stainless Steel Enclosures
Domain: protocase.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel for General Purpose Enclosures. Premium solution to corrosion resistance. Same stiffness advantage of steel yet even higher strength. Non-painted Stainless is ‘passivated’ using Citric Acid to remove any iron contamination that may show up as rust spots. Finish options include Powdercoat, Passivate, Grained Finish. Typically uses stainless fasteners and PEMS. Highly weldable (unles…
2. Metal Supermarkets – Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Chart – Metal Supermarkets offers various metal types including Mild Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, Bronze, and Copper. Each metal type has specific gauge charts detailing thickness in inches and millimeters for gauges ranging from 7 to 30. For example, 18 gauge Mild Steel is 0.0478 inches or 1.214 mm thick, while 18 gauge Aluminum is 0.0403 inches or 1.024…
3. Metals Depot – T304 Stainless Steel Sheet
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “T304 Stainless Steel Sheet”, “Material”: “304 Stainless Steel”, “Corrosion Resistance”: “Good corrosion resistance to many chemical corrodents, industrial atmospheres, and marine environments”, “Magnetic Properties”: “May become slightly magnetic when worked”, “Heat Treatable”: “Not heat treatable”, “Grain Direction”: “Random and not guaranteed unless specified or custom quoted”,…
4. CustomPartNet – Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart
Domain: custompartnet.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart: Gauge sizes indicate the thickness of sheet metal, with higher numbers representing thinner sheets. Different gauge size standards exist, including: 1. Manufacturers’ Standard Gage for standard steel, galvanized steel, and stainless steel. 2. Brown and Sharpe Gage (American Wire Gage) for non-ferrous metals like Aluminum and Brass. 3. Birmingham Gage (UK) for various …
5. Reddit – Stainless Steel Table Options
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Stainless steel table options: 18, 16, and 14 gauge thickness. Dimensions: 30×72 inches. Price difference noted between 16ga and 14ga, with 14ga costing over double. Concern about table flexing when cutting on the tabletop.
6. Steel & Pipes – Stainless Steel Sheet Gauge 16
Domain: store.steelandpipes.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Stainless Steel Sheet Gauge 16”, “Material”: “Stainless Steel 304”, “Finish”: “Polished”, “Cover”: “Anti-Scratch PVC Cover”, “Thickness”: “Gauge 16”, “Dimensions”: “4′ x 8′”, “Weight Per Square Foot”: “2.5 lbs”, “Total Weight”: “80 lbs”, “Cuttable”: “Yes”, “Price”: “$343.93”, “Description”: “Top-quality material offering excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and scratch pro…
7. Competitive Metals – 16-Gauge 304 Stainless Steel Sheet
Domain: competitivemetals.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “16-Gauge 304 Stainless Steel Sheet with 2B Mill Finish”, “Product Code”: “S3042B16”, “Sheet Size”: “24\”x48\””, “Thickness”: “16ga (0.0548\”-0.0648\”)”, “Finish”: “2B Mill Finish”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 16 gauge thickness stainless steel
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of 16 gauge thickness stainless steel presents a valuable opportunity for international B2B buyers across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The advantages of utilizing this material, such as its superior corrosion resistance, excellent fabrication capabilities, and versatility in various applications, make it a preferred choice for many industries.
By partnering with reputable suppliers who understand local market dynamics and can provide customized solutions, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality. It is essential to leverage data-driven insights to make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring that the selected materials meet stringent quality standards while also being cost-effective.
Looking ahead, the demand for 16 gauge stainless steel is expected to grow, fueled by advancements in manufacturing technologies and an increasing focus on sustainable practices. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay abreast of market trends and engage with suppliers who can offer innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs. Embrace this opportunity to strengthen your supply chain and secure a competitive edge in your industry.