Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 12l14 vs 1018
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of selecting the right materials for their projects, especially when comparing options like 12L14 and 1018 steel. Understanding the differences between these two carbon steels is essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring product reliability. This guide aims to equip international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Vietnam), with the insights needed to make informed sourcing decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into the distinct properties of 12L14 and 1018 steel, exploring their mechanical characteristics, applications, and relative cost implications. The guide will also address supplier vetting processes, helping you identify reputable vendors who can meet your material needs while maintaining quality standards. By providing a clear comparison of these steel types, we empower you to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence.
Whether you are looking to enhance production capabilities or reduce material costs, understanding the nuances between 12L14 and 1018 steel will be invaluable. This guide will serve as your roadmap to making strategic purchasing decisions that align with your business objectives and operational requirements.
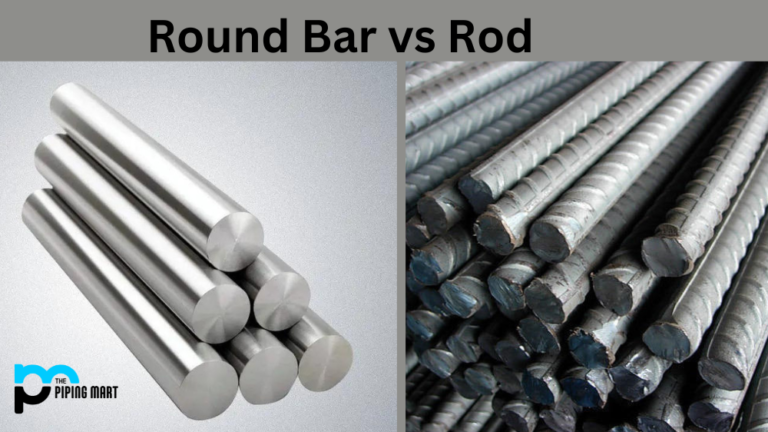
Understanding 12l14 vs 1018 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAE-AISI 1018 | Low carbon content (0.15-0.2%), good weldability, versatile | General machining, automotive components, structural applications | Pros: Cost-effective, good strength and ductility. Cons: Prone to rust, not ideal for high-stress applications. |
| SAE-AISI 12L14 | Leaded steel, higher machinability, slightly higher strength (up to 620 MPa) | Precision machining, threaded components, small parts manufacturing | Pros: Excellent machinability, smoother finish. Cons: Poor corrosion resistance, lead content complicates welding. |
| Cold Drawn 1018 | Enhanced mechanical properties, improved surface finish | High-strength applications, precision components | Pros: Better strength and surface quality than standard 1018. Cons: Higher cost due to processing. |
| Hot Rolled 1018 | Lower strength than cold drawn, less precise dimensions | Structural applications, general fabrication | Pros: Lower cost, readily available. Cons: Less precise and weaker than cold drawn variants. |
| Lead-Free Variants of 12L14 | Similar properties to 12L14 but without lead, compliant with regulations | Applications requiring lead-free materials, environmental considerations | Pros: Complies with health and safety regulations. Cons: Slightly reduced machinability compared to leaded variants. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of SAE-AISI 1018 Steel?
SAE-AISI 1018 steel is a low-carbon steel known for its versatility and good weldability. It is commonly utilized in various applications such as automotive components, general machining, and structural elements. The material’s tensile strength ranges from 430 to 480 MPa, making it suitable for moderate stress applications. However, buyers should consider its susceptibility to rust and its lower performance in high-stress environments. For industries in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where cost-effectiveness is crucial, 1018 offers a balanced option.
How Does SAE-AISI 12L14 Compare in Terms of Machinability?
SAE-AISI 12L14 is characterized by its leaded composition, enhancing its machinability significantly over 1018. This makes it a preferred choice for precision machining applications, such as threaded components and small parts. With a tensile strength of up to 620 MPa, it provides a robust option for manufacturers looking to achieve high-quality finishes. However, its lead content complicates welding processes and raises concerns regarding corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers in Europe and Asia, understanding these trade-offs is essential when selecting materials for high-precision applications.
What are the Advantages of Cold Drawn 1018 for High-Strength Applications?
Cold drawn 1018 steel offers improved mechanical properties and surface finish compared to its standard form. This variant is ideal for high-strength applications, including precision components that require enhanced durability. While it comes at a higher price point due to additional processing, the benefits in strength and quality can justify the investment for manufacturers focused on performance. Companies in regions like Germany and Vietnam can leverage this material for demanding applications, ensuring reliability and longevity in their products.
What Should Buyers Know About Hot Rolled 1018 Steel?
Hot rolled 1018 steel is less precise than its cold drawn counterpart and offers lower strength. However, it is significantly more cost-effective and readily available, making it suitable for structural applications and general fabrication tasks. Buyers should weigh the trade-offs between cost and performance, especially in markets where budget constraints are a priority. For businesses in developing regions, hot rolled 1018 can serve as a practical solution for non-critical applications.
Why Consider Lead-Free Variants of 12L14?
Lead-free variants of 12L14 maintain similar mechanical properties while eliminating lead content, making them compliant with health and environmental regulations. This is particularly relevant for industries that prioritize sustainability and worker safety. While these variants may present slightly reduced machinability, they offer a responsible choice for manufacturers in Europe and other regions with stringent regulations. B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements to determine whether the benefits of lead-free materials align with their operational goals.
Key Industrial Applications of 12l14 vs 1018
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 12l14 vs 1018 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of precision components like gears | Enhanced machinability and surface finish | Availability of leaded vs. non-leaded options; local regulations on lead content. |
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight structural components | Higher strength-to-weight ratio; improved fatigue resistance | Certification standards for aerospace materials; sourcing from reputable suppliers. |
| Machinery & Equipment | Fabrication of shafts and fasteners | Cost-effective production with reliable performance | Quality assurance processes; lead content regulations in target markets. |
| Construction | Production of fittings and structural supports | Durability and ease of machining for custom designs | Compliance with local building codes; availability of corrosion-resistant finishes. |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of electrical components | Improved conductivity and thermal properties | Sourcing from certified manufacturers; consideration of electrical conductivity specifications. |
How is 12L14 Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, 12L14 steel is frequently utilized for manufacturing precision components such as gears and shafts. Its lead content enhances machinability, allowing for smoother finishes and reduced tool wear during production. This is particularly advantageous for manufacturers aiming to maintain high output rates while ensuring quality. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local regulations regarding lead content and its implications for automotive safety standards.
What are the Aerospace Applications for 1018 Steel?
1018 steel finds its place in aerospace applications where lightweight structural components are essential. Its favorable strength-to-weight ratio is crucial in aircraft design, contributing to fuel efficiency and performance. International buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers meet stringent aerospace certification standards, which can vary significantly by region. Additionally, understanding the specific mechanical properties required for different aircraft components is vital.
How Does 12L14 Benefit Machinery and Equipment Fabrication?
In the machinery and equipment sector, 12L14 is favored for fabricating shafts, fasteners, and other components due to its excellent machinability. This leads to cost-effective production and consistent performance, which are critical for maintaining competitive pricing in a global market. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with robust quality assurance processes to ensure that the steel meets their performance requirements, particularly in demanding applications.
Why is 1018 Steel Suitable for Construction Applications?
1018 steel is often used in construction for producing fittings and structural supports. Its durability, combined with ease of machining, allows for the creation of custom designs that meet specific project needs. Buyers in the construction industry should pay close attention to local building codes and standards, as these can dictate the types of materials that are permissible. Additionally, considering corrosion-resistant finishes can enhance the longevity of components exposed to the elements.
What are the Key Considerations for Electronics Manufacturing with 12L14?
In electronics, 12L14 steel is used for manufacturing components where electrical conductivity is crucial. Its thermal properties and machinability make it an attractive option for producing intricate parts that require precise tolerances. Buyers in this sector, particularly from Europe and Asia, should focus on sourcing from certified manufacturers who can guarantee compliance with electrical conductivity specifications. Understanding the trade-offs between machinability and conductivity can help in selecting the right material for specific applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’12l14 vs 1018′ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Steel for Machining Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with choosing between 12L14 and 1018 steel for their machining projects. While both are popular carbon steels, their distinct properties can significantly impact the performance and cost-effectiveness of the final product. For instance, 12L14 is known for its excellent machinability due to the presence of lead, but it may not be suitable for applications requiring higher tensile strength. Conversely, 1018 is more robust but can be challenging to machine, especially in high-volume production settings. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the need to balance performance, cost, and machinability, leading to potential project delays or increased expenses.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this dilemma, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their project requirements. Begin by assessing the mechanical properties needed for the end product, such as tensile strength, elongation, and machinability. For example, if the project involves intricate machining with tight tolerances, 12L14 may be the superior choice due to its ease of machining and ability to produce clean threads. However, if the application demands higher strength, particularly under cyclic loading conditions, 1018 would be more appropriate. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide samples and specific mechanical property data will help buyers make informed decisions. Implementing a trial phase where both materials are tested in the actual production environment can also yield valuable insights into their performance, ensuring the right choice for future orders.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Material Strength and Durability in Critical Applications
The Problem: Many industries, such as automotive and aerospace, require materials that can withstand significant stress and strain. B2B buyers often face concerns regarding the material strength and durability of 12L14 versus 1018, especially when the components are subjected to harsh operational conditions. Misjudging the strength of the selected steel can lead to premature failure, resulting in costly recalls or safety hazards.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, buyers should engage in a comprehensive risk assessment that considers the operational environment of the components being produced. Understanding the specific loads, fatigue cycles, and environmental factors is crucial. Buyers should also utilize finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to predict how each material will perform under expected stresses. Furthermore, when sourcing materials, it’s advisable to request certifications and detailed mechanical property reports from suppliers. These documents should outline the tensile and yield strength of both 12L14 and 1018, along with other relevant properties. By establishing clear specifications and collaborating closely with suppliers on quality assurance, buyers can ensure that they select the appropriate material for their critical applications, thus minimizing the risk of failure.
Scenario 3: Managing Corrosion Resistance and Surface Finish Requirements
The Problem: Corrosion resistance is a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially those operating in humid or chemically aggressive environments. While 12L14 offers superior machinability, it is more prone to corrosion compared to 1018, which can lead to longer-term maintenance issues and increased lifecycle costs. Buyers may find themselves at a crossroads, needing to balance the machining advantages of 12L14 against the durability and corrosion resistance of 1018.
The Solution: To effectively manage these concerns, buyers should consider implementing protective coatings or surface treatments for their components made from 12L14. Options such as zinc plating, powder coating, or anodizing can significantly enhance corrosion resistance while preserving the benefits of the leaded steel’s machinability. Additionally, buyers should prioritize the selection of appropriate lubricants and cleaning agents during machining to minimize exposure to corrosive elements. It’s also beneficial to work closely with suppliers who specialize in surface treatments, as they can provide guidance on the best practices for preserving material integrity while achieving desired surface finishes. By proactively addressing corrosion issues through coatings and treatments, buyers can enjoy the advantages of 12L14 without compromising on durability, ultimately enhancing the overall performance and longevity of their products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 12l14 vs 1018
What Are the Key Properties of 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
When comparing 12L14 and 1018 steel, both materials exhibit similar base compositions, yet they differ significantly in their mechanical properties and applications.
12L14 Steel is a leaded carbon steel known for its excellent machinability and surface finish. It typically has a tensile strength ranging from 440 to 620 MPa and a yield strength from 260 to 460 MPa. The presence of lead enhances its machining capabilities, making it suitable for precision components such as gears and shafts. However, it is less durable under high-stress conditions due to its lower elongation at break (11% to 25%) compared to 1018.
1018 Steel, on the other hand, is a low-carbon steel that offers a balance of strength and ductility, with tensile strength ranging from 430 to 480 MPa and yield strength from 240 to 400 MPa. It is often used in applications requiring weldability and toughness, such as structural components and automotive parts. The elongation at break for 1018 is higher (17% to 27%), making it more suitable for applications that experience dynamic loading.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using 12L14 vs 1018?
Pros of 12L14:
– Machinability: 12L14 is easier to machine than 1018, which can lead to reduced manufacturing times and costs.
– Surface Finish: The lead content allows for a smoother finish, making it ideal for aesthetic applications.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Often available at a lower price point, especially in hex stock form, which is advantageous for high-volume production.
Cons of 12L14:
– Corrosion Resistance: It is more susceptible to corrosion compared to 1018, requiring protective coatings for longevity.
– Weldability: The presence of lead makes it challenging to weld, limiting its use in applications requiring strong joints.
– Durability: Lower tensile strength and elongation may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros of 1018:
– Strength and Ductility: Offers better overall strength and ductility, making it versatile for various applications.
– Weldability: It can be easily welded, which is crucial for structural applications.
– Availability: Widely available and compliant with international standards, making sourcing easier for global buyers.
Cons of 1018:
– Machinability: It is generally more challenging to machine compared to 12L14, which may increase production times.
– Surface Finish: The finish may not be as smooth as that of 12L14, potentially impacting aesthetic applications.
How Do 12L14 and 1018 Impact Specific Applications?
When selecting between 12L14 and 1018, the application plays a crucial role. For instance, 12L14 is ideal for components that require intricate machining and a fine finish, such as precision fasteners and decorative parts. However, it may not be suitable for load-bearing applications due to its lower strength and susceptibility to corrosion.
Conversely, 1018 is better suited for structural components and applications that experience dynamic loads, such as automotive parts and machinery. Its weldability and strength make it a preferred choice in industries where durability is paramount.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing Between 12L14 and 1018?
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM in the U.S., DIN in Germany, JIS in Japan) when selecting materials. 1018 is often more widely recognized and compliant with these standards, making it easier to source and integrate into existing manufacturing processes. Additionally, buyers should assess the availability of protective coatings for 12L14 to mitigate corrosion risks, especially in humid climates.
| Material | Typical Use Case for 12L14 vs 1018 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12L14 Steel | Precision components, fasteners, decorative parts | Excellent machinability and surface finish | Susceptible to corrosion, poor weldability | Low |
| 1018 Steel | Structural components, automotive parts, machinery | Higher strength and ductility, good weldability | More challenging to machine, rougher surface finish | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 12l14 vs 1018
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
When considering the manufacturing processes for 12L14 and 1018 steel, it is essential to understand the typical stages involved: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Both steel types undergo similar processes, yet their distinct properties influence specific techniques and outcomes.
How Is Material Prepared for 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials. For both 12L14 and 1018, the primary raw material is carbon steel, which may undergo alloying to enhance specific characteristics. The preparation phase may involve processes such as:
- Heat Treatment: Depending on the intended application, materials may be heat-treated to achieve desired hardness and mechanical properties.
- Cold Drawing: This process is often utilized for 1018 steel to improve its surface finish and dimensional accuracy. In contrast, 12L14 is typically less rigid due to the lead content, making it easier to machine and fabricate.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in 12L14 and 1018 Steel Manufacturing?
Forming techniques vary based on the desired shape and application of the steel products. Common methods include:
- Machining: Both 12L14 and 1018 can be effectively machined, but 12L14 offers superior ease of machining due to its lead content, which acts as a lubricant during cutting processes. This can lead to reduced tool wear and lower machining costs.
- Forging: This technique may be employed for both types of steel, enhancing their mechanical properties through deformation. 12L14, however, is less commonly forged due to its softer nature compared to 1018.
- Welding: While 1018 can be welded effectively, 12L14 presents challenges due to its lead content, which can create defects in the weld area. Thus, it is generally recommended to avoid welding with 12L14 unless necessary.
How Is Assembly Conducted for 12L14 and 1018 Steel Products?
The assembly of components made from 12L14 and 1018 steel typically involves fastening techniques such as bolting or threading. Given that both steels have comparable tensile strengths, assembly practices largely depend on the application’s demands. For high-stress applications, 1018 may be preferred due to its higher yield strength.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of both 12L14 and 1018 steels to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Key practices include:
What International Standards Apply to 12L14 and 1018 Steel Manufacturing?
Both steel types should comply with internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001, which emphasizes quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be relevant, including:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for products intended for the oil and gas industry, ensuring that materials can withstand harsh operational conditions.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help ensure product integrity. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage verifies the quality of raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to monitor processes and detect defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specifications before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the mechanical and physical properties of both steel types:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and elongation, providing insights into its mechanical properties.
- Hardness Testing: Commonly performed using Brinell or Rockwell methods to evaluate the material’s hardness.
- Microstructural Analysis: Assesses the material’s grain structure, helping to identify any defects or inconsistencies.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control for 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control measures of suppliers. This can involve:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control procedures, testing results, and certifications.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have varying standards, so understanding local regulations is crucial.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as material certifications and test reports, accompany shipments.
- Language and Communication: Clear communication regarding quality expectations is vital, especially when dealing with suppliers from diverse cultural backgrounds.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for 12L14 and 1018 steel is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly methods, and rigorous quality control practices, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’12l14 vs 1018′
When sourcing materials like 12L14 and 1018 steel, B2B buyers must approach the process systematically to ensure they select the right material for their specific needs. This guide provides a checklist to help you navigate the procurement of these two carbon steel types effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clarify your technical requirements. Consider factors such as tensile strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance, as these properties will influence your choice between 12L14 and 1018. For instance, 12L14 is often preferred for its superior machinability due to its lead content, while 1018 is noted for its balance of strength and toughness.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific applications for which you need the steel. Each type of steel has distinct advantages; for example, if your application involves components that require high tensile strength, 12L14 may be more suitable. On the other hand, for applications needing better weldability, 1018 could be the better choice.
Step 3: Research Supplier Capabilities
Identify suppliers that specialize in both 12L14 and 1018 steel. Examine their production capabilities, inventory levels, and quality control processes. It’s essential to partner with suppliers who have a proven track record in your industry to ensure they can meet your quality standards and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Verify Material Certifications
Ensure that the materials you are considering come with appropriate certifications. Request documentation that verifies compliance with international standards such as ASTM or ISO. This step is crucial to mitigate risks associated with material quality and ensure that the steel meets your specifications.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Availability
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers for both 12L14 and 1018 steel. While cost is a significant factor, also consider the availability of the materials. Some suppliers may offer competitive pricing but have long lead times, which could affect your production schedule.
Step 6: Evaluate Lead Times and Logistics
Discuss lead times with potential suppliers to understand how quickly they can deliver the materials. Consider your own supply chain logistics and how the delivery schedules align with your production needs. Efficient logistics can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall operational efficiency.
Step 7: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of both 12L14 and 1018 steel. Conduct tests to evaluate their performance in your specific applications. This hands-on assessment can help you make a more informed decision based on actual performance rather than theoretical properties.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for 12L14 and 1018 steel, ensuring they select the right material for their operational needs while minimizing risks and optimizing costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 12l14 vs 1018 Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
When analyzing the cost structure of 12L14 and 1018 steel, several components must be considered. The primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: Generally, 12L14 is priced lower than 1018 due to its higher demand for specific applications and ease of machining. However, the base metal prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and regional availability.
-
Labor: The machining of 12L14 typically requires less labor due to its lead content, which enhances machinability. This factor can lead to lower labor costs compared to 1018, which may demand more time and effort in machining processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs can vary based on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Since 12L14 often results in quicker cycle times, manufacturers may see reduced overhead expenses compared to 1018.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs may be lower for 12L14 due to its machinability. In contrast, working with 1018 might necessitate more frequent tool changes or higher-quality tools, increasing overall costs.
-
Quality Control: Both materials will require QC processes, but 12L14 may have additional considerations due to its lead content. Buyers should ensure suppliers comply with safety and quality standards, especially if the end products are for sensitive applications.
-
Logistics: Transport costs can be influenced by the sourcing location. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the proximity of suppliers and the associated shipping costs, which can impact the overall pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the competitive landscape and negotiating effectively can help buyers secure better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 12L14 and 1018?
Various factors can influence the pricing of 12L14 and 1018 steel. These include order volume, specifications, customization, material quality, supplier reliability, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger minimum order quantities (MOQs), which can significantly affect overall pricing.
-
Specs and Customization: Specific requirements for dimensions, grades, or finishing can alter costs. Custom orders generally incur higher prices, so buyers should evaluate whether standard sizes will suffice for their applications.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The presence of certifications (like ISO) can influence pricing. Suppliers with verified quality processes may charge a premium but offer better assurance of material performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers are crucial. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record of quality and service, while newer or lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices to attract business.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total landed cost, influencing the final pricing structure.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Optimize Costs?
International B2B buyers can adopt various strategies to ensure cost efficiency when sourcing 12L14 and 1018 steel:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including machining, maintenance, and logistics. This perspective can help justify higher upfront costs for materials that offer better long-term performance.
-
Leverage Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and favorable payment terms.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate the material’s performance and machinability. This practice can prevent costly mistakes and ensure the selected steel meets specific application needs.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: Investigate local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and shorten lead times. Local sourcing can also enhance communication and service.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market conditions, material availability, and pricing trends can provide leverage during negotiations.
Conclusion
While both 12L14 and 1018 steel have their unique advantages, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influencers is essential for B2B buyers. By adopting strategic sourcing practices, businesses can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they receive the best value for their material investments. Always consider the total cost of ownership and remain adaptable to changing market dynamics to achieve long-term success in sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 12l14 vs 1018 With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Steel Selection for B2B Buyers
When it comes to selecting the right steel for industrial applications, understanding the alternatives available can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall product quality. In the context of comparing 12L14 and 1018 steel, it is essential to evaluate viable alternatives that may better suit specific business needs. Below, we present a comparison of these two steel types against two notable alternatives: A36 Steel and 4140 Steel.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 12L14 Vs 1018 | A36 Steel | 4140 Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate tensile strength, good machinability, leaded for smooth finishes | Lower strength, good weldability, versatile | High tensile strength, excellent hardness |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate, varies by supplier | Low cost, widely available | Higher cost due to alloying elements |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to machine but poor weldability | Easy to fabricate and weld | Requires specialized processes for machining |
| Maintenance | Susceptible to corrosion, requires protective coatings | Moderate maintenance, good corrosion resistance | Low maintenance, excellent wear resistance |
| Best Use Case | Precision machining, non-structural parts | General construction, structural components | Heavy-duty applications, tooling |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
A36 Steel: A Cost-Effective Option for Structural Applications
A36 steel is a low-carbon steel widely used in construction and structural applications. It offers excellent weldability and is readily available at a low cost. However, its tensile strength is lower than both 12L14 and 1018, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. A36 is best used in non-critical structural components where weldability and affordability are prioritized over strength.
4140 Steel: The High-Performance Alternative
4140 steel is an alloy steel known for its high tensile strength and hardness, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as gears, crankshafts, and heavy machinery components. While it offers superior performance compared to 12L14 and 1018, it comes at a higher cost and requires specialized machining processes. Its resistance to wear and fatigue makes it suitable for applications that demand durability and reliability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Steel for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate steel for your business applications involves a careful analysis of performance, cost, and suitability for specific tasks. While 12L14 and 1018 are excellent choices for precision machining and general fabrication, alternatives like A36 and 4140 steel may provide better value depending on your specific requirements. As a B2B buyer, consider your project’s demands, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, to make an informed decision that optimizes both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 12l14 vs 1018
When evaluating materials for manufacturing processes, understanding the technical properties and industry terminology associated with steel grades like 12L14 and 1018 is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are key specifications and terms that will enhance your comprehension of these materials and their application in various industries.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 12L14 and 1018 Steel?
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of steel based on its composition and mechanical properties. SAE-AISI 1018 is a low-carbon steel with good weldability and machinability, making it suitable for various applications. On the other hand, SAE-AISI 12L14 is a leaded steel that offers superior machinability, primarily used in precision machining. Understanding these grades helps buyers select the right material for specific applications, affecting product performance and production costs. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before failure. For 1018, the tensile strength typically ranges from 430 to 480 MPa, while 12L14 ranges from 440 to 620 MPa. This property is vital for applications where the material will experience significant stress, as higher tensile strength can lead to better performance and durability. -
Machinability Rating
Machinability indicates how easily a material can be cut, shaped, or finished. 12L14 is often favored for its excellent machinability due to the presence of lead, which reduces friction during machining. This characteristic can lead to lower manufacturing costs and faster production times, making it a preferred choice for high-volume applications. -
Yield Strength
Yield strength is the amount of stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. 1018 has a yield strength of 240 to 400 MPa, while 12L14 has a yield strength ranging from 260 to 460 MPa. Understanding yield strength is essential for applications that require materials to maintain their shape under load, as it directly impacts the safety and reliability of the final product. -
Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation or scratching. The Brinell hardness for 1018 is 130 to 140, whereas 12L14 ranges from 140 to 170. This property is significant for applications requiring wear resistance, as harder materials can better withstand abrasive conditions.
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Know?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM is important for buyers when sourcing components, as it often influences product quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must consider MOQ when negotiating with suppliers, as it affects inventory levels and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process helps buyers compare costs and negotiate better deals, making it a vital step in procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they can significantly impact delivery costs and risk management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time from the order placement to the delivery of goods. Understanding lead time is essential for inventory management and production planning, particularly in industries where timely delivery is critical. -
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling materials to alter their physical and sometimes chemical properties. This process can enhance hardness, strength, and machinability. Knowledge of heat treatment is crucial for buyers aiming to optimize material performance for specific applications.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can better navigate the complexities of sourcing materials like 12L14 and 1018, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 12l14 vs 1018 Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the 12L14 vs 1018 Steel Sector?
The global steel market is currently experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements, changing consumer demands, and geopolitical factors. In the context of 12L14 and 1018 steel, one of the primary trends is the increasing preference for materials that offer enhanced machinability and cost-effectiveness. 12L14, known for its lead content, is often favored in applications requiring high precision and smooth finishes, making it particularly attractive to manufacturers in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies is impacting sourcing strategies. Automated machining and CNC technologies enable manufacturers to leverage the superior machinability of 12L14, reducing production time and costs. As a result, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, are increasingly considering 12L14 for their manufacturing needs due to its competitive pricing and favorable performance characteristics.
Another significant dynamic is the fluctuating demand for steel resulting from economic recovery post-pandemic. Emerging markets are ramping up production capabilities, leading to increased sourcing opportunities. However, buyers must navigate potential supply chain disruptions, particularly in regions heavily reliant on steel imports. This necessitates a proactive approach to supplier relationships and logistics planning to ensure timely delivery and cost management.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the 12L14 vs 1018 Steel Market?
As global awareness of environmental issues intensifies, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing decisions. Both 12L14 and 1018 steel have relatively low embodied carbon footprints, making them preferable options for environmentally-conscious manufacturers. However, the lead content in 12L14 raises concerns regarding health and environmental safety, leading many companies to seek out lead-free alternatives or ensure that their sourcing practices adhere to strict environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a crucial consideration, especially for international buyers from Europe and North America. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are increasingly being demanded by clients, ensuring that suppliers maintain sustainable practices throughout their operations. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains can help mitigate risks associated with unethical practices, enhancing brand reputation and consumer trust.
In response to these trends, some manufacturers are exploring innovative methods to produce low-lead or lead-free variants of 12L14, which could meet both performance requirements and sustainability goals. This development could reshape the competitive landscape, offering buyers more environmentally friendly options without compromising on quality.
What Is the Historical Context of 12L14 and 1018 Steel in B2B Markets?
The evolution of 12L14 and 1018 steel can be traced back to the early 20th century, when advancements in metallurgy began to allow for more specialized steel formulations. 1018 steel became popular due to its versatility and balance of strength, ductility, and machinability. It quickly found applications in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction.
In contrast, 12L14 emerged in the mid-20th century as a leaded variant designed for enhanced machinability. The introduction of lead allowed for smoother cutting processes and improved surface finishes, making it a preferred choice for high-precision applications. Over the decades, both steels have established themselves as staples in industrial manufacturing, with 12L14 gaining traction as a go-to material for parts requiring intricate machining.
Today, both materials continue to evolve, with ongoing research into improving their properties and addressing environmental concerns. As the global market progresses, understanding the historical context of these materials can provide valuable insights into their future applications and sourcing trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 12l14 vs 1018
-
How do I choose between 12L14 and 1018 steel for my application?
Choosing between 12L14 and 1018 steel largely depends on the specific requirements of your project. 12L14 is leaded steel, known for its excellent machinability and slightly higher tensile strength, making it ideal for precision machining and applications where intricate parts are required. In contrast, 1018 offers good weldability and is often preferred in applications requiring greater strength and ductility. Evaluate factors such as machining needs, strength requirements, and whether welding will be involved to make an informed decision. -
What are the key differences in mechanical properties between 12L14 and 1018?
12L14 steel generally exhibits higher tensile strength and improved machinability compared to 1018. The tensile strength of 12L14 can reach up to 620 MPa, while 1018 ranges from 430 to 480 MPa. Additionally, 12L14 has a higher shear strength and lower elongation at break, indicating it may be less ductile. These differences can significantly impact performance depending on the specific application, so consider the mechanical properties that align best with your project requirements. -
Are there any specific applications where one steel type is preferred over the other?
Yes, each steel type has its preferred applications. 12L14 is often used in high-volume machining environments, such as automotive parts or fasteners, due to its superior machinability and smoother finish. On the other hand, 1018 is commonly found in structural applications, such as frames and supports, where strength and weldability are crucial. Assess your project’s specific needs to determine which steel type aligns better with your intended use. -
What are the typical lead times when sourcing 12L14 and 1018 steel internationally?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier and geographic location. Typically, you can expect lead times of 2-4 weeks for standard orders, but this may increase if customization is required or if sourcing from regions with longer shipping routes. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to obtain accurate timelines and factor in potential delays due to customs or other logistical issues. -
How do I vet suppliers for 12L14 and 1018 steel?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certification standards, and experience in handling the specific steel grades you require. Request references from previous clients and review their quality assurance processes. Additionally, assess their ability to provide documentation on material properties and compliance with international standards. Engaging in direct communication and possibly visiting the facility can further enhance your confidence in their capabilities. -
What customization options are available for 12L14 and 1018 steel?
Most suppliers offer various customization options, including different shapes, sizes, and surface treatments. For instance, you can request specific dimensions, finishes, or even pre-machined parts to reduce lead times in your production process. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore available customization options and any associated costs, ensuring that the final product aligns with your project specifications. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 12L14 and 1018 steel?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and region, but typical MOQs for 12L14 and 1018 steel range from 100 kg to 1,000 kg. Smaller quantities may be available but could incur additional fees. It’s essential to clarify MOQs upfront when negotiating with suppliers, especially if you are working on a smaller project or prototype, to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, but common practices include payment upon order confirmation, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). Always negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure you understand any currency exchange risks involved in international transactions. Establishing a clear agreement in writing can help prevent misunderstandings later on.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 12L14 Vs 1018 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Make It From – Steel Comparison Guide
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Make It From – Steel Comparison Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Steel Bar Stocks – Key Characteristics
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around identifying three types of steel bar stocks: 1018, 12L14, and 4140. Key characteristics include: 1. 1018: – Easier to drill than 4140 but may produce stringy swarf. – When heated and quenched, remains pliable due to low carbon content. – Surface finish can be similar to 4140. 2. 12L14: – Known as “Super Leaded stock”; very easy to cut, producing nice chips. – Chips r…
3. The Piping Mart – 12L14 Steel
Domain: blog.thepipingmart.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: 12L14 Steel: Low-carbon leaded steel, high flexibility, machinability, and strength. Excellent for cold working, used in screws, bolts, studs. Can be heat-treated for higher tensile strength. Lower corrosion resistance, less suitable for outdoor use. Superior machinability due to high sulfur and lead content. Ideal for repetitive machining and high-stress applications.
1018 Steel: Low-carbon stee…
4. Qinghe Steel – 12L14 Steel
Domain: qinghesteels.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: 12L14 Steel: Composition – Carbon (C): 0.15%, Manganese (Mn): 0.85-1.15%, Phosphorus (P): 0.04-0.09%, Sulfur (S): 0.26-0.35%, Lead (Pb): 0.15-0.35%. Mechanical Properties – Tensile Strength: 78,000 psi, Yield Strength: 60,000 psi, Elongation: 10%, Hardness: B 84. Machinability: Excellent, suitable for high-speed machining. Weldability: Poor, not recommended for welding. Applications: Bushings, Cou…
5. Hobby Machinist – 12L14 Leaded Steel Bar
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: 12L14 is a leaded steel round bar known for its excellent machinability, cutting like aluminum and providing nicer finishes for various projects. It is not ideal for welding applications and is generally used in situations where parts are not frequently disassembled, such as shafts riding in bearings. The price mentioned is $1 per pound, and the user acquired 155 pounds of round bar drops, mostly …
6. Muzzleloading Forum – 12L14 Steel Barrels
Domain: muzzleloadingforum.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 12L14 steel is not considered a traditional barrel steel but is commonly used in black powder barrels. The recommended minimum wall thickness for safety is .050″ to .080″, with many barrel makers opting for .160″ to .170″ at the breech. The steel has poor shock load numbers and is considered brittle compared to more suitable barrel steels like 1134. The typical internal pressure for standard calib…
7. Reddit – 4140 Pre-Hard & 12L14 Steel
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. 4140 Pre-Hard: Known for making beautiful tight spiral chips and leaving a polished surface finish. Contains chrome and molybdenum, which helps reduce rusting. 2. 12L14: Commonly used for turning jobs, cuts easily but rusts easily like mild steel. Not recommended for welding due to lead content. 3. 4340 HTSR: Preferred for general use, particularly for hobbyist projects. 4. 1018: Suggested for …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 12l14 vs 1018
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of 12L14 versus 1018 steel, it’s clear that both materials have unique advantages tailored to different applications. 12L14, with its superior machinability and tensile strength, is an excellent choice for components requiring intricate machining and operational efficiency. Conversely, 1018 offers robust mechanical properties, making it suitable for applications demanding higher strength and durability.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the decision should consider not only the material properties but also the local availability, cost fluctuations, and specific application requirements. Strategic sourcing can significantly reduce costs while improving product quality and performance.
Looking ahead, businesses should engage in collaborative discussions with suppliers to explore opportunities for bulk procurement, tailored solutions, and innovative applications of these steels. By leveraging the strengths of both 12L14 and 1018, companies can optimize their supply chains and enhance their competitive edge in the market. Now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies and align them with your operational goals for sustained growth and success.