Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 12 gauge aluminum
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality 12 gauge aluminum can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying specifications, applications, and standards across markets, the need for reliable information is paramount. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding 12 gauge aluminum by providing a comprehensive overview of its types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From understanding the nuances of different aluminum alloys to exploring their diverse uses in industries such as automotive, construction, and marine applications, this resource equips you with the insights needed for informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations and logistics, ensuring you are well-prepared to navigate the global marketplace effectively.
By leveraging the information contained within this guide, B2B buyers will not only enhance their knowledge of 12 gauge aluminum but also foster strategic partnerships with suppliers that meet their specific needs. Whether you are in Nigeria seeking durable materials for construction or in Germany looking for lightweight yet strong components for automotive manufacturing, this guide serves as your essential roadmap to making confident and cost-effective procurement choices.
Understanding 12 gauge aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 5052 | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance | Marine, automotive, industrial | Pros: Durable, weldable; Cons: Higher cost than some alloys. |
| Aluminum 3003 | Good formability, moderate strength | Food and chemical processing, residential | Pros: Cost-effective, good for forming; Cons: Lower strength compared to 5052. |
| Aluminum 6061 | Good mechanical properties, versatile | Structural applications, automotive, aerospace | Pros: High strength, good corrosion resistance; Cons: More difficult to weld. |
| Brushed Aluminum | Aesthetic finish, smooth texture | Architectural applications, signage | Pros: Attractive appearance; Cons: Surface may require maintenance. |
| High-Tensile Aluminum | Enhanced strength, lightweight | Fencing, construction, automotive components | Pros: Strong and lightweight; Cons: Can be more expensive. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 12 Gauge Aluminum 5052?
Aluminum 5052 is a high-strength alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine and outdoor applications. It features a thickness of approximately 0.08081 inches (2.053 mm) and is praised for its weldability and formability. This alloy is commonly used in fuel tanks, pressure vessels, and automotive panels. Buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions their products will face, as the corrosion-resistant properties of 5052 can significantly extend the lifespan of components.
How Does Aluminum 3003 Compare in Formability and Strength?
Aluminum 3003 offers good formability and moderate strength, making it suitable for applications such as food processing and residential projects. With a thickness equivalent to 0.08081 inches, it is less robust than 5052 but more cost-effective. Its ease of fabrication allows for efficient production processes. However, buyers should note that while it is versatile, its lower strength may not meet the demands of more heavy-duty applications.
Why Choose Aluminum 6061 for Structural Applications?
Aluminum 6061 is recognized for its good mechanical properties and versatility, often used in structural applications, including automotive and aerospace industries. This alloy provides a thickness of about 0.08081 inches and is favored for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. However, its welding process can be more complex, necessitating specialized equipment and expertise. Buyers should weigh the benefits of strength against potential additional fabrication costs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Brushed Aluminum in Architectural Applications?
Brushed aluminum features a smooth, aesthetic finish, making it a popular choice for architectural projects and signage. This type of aluminum not only enhances visual appeal but also offers some resistance to corrosion. However, the surface may require maintenance to preserve its appearance over time. Buyers should consider the balance between aesthetics and durability when selecting brushed aluminum for their projects.
When Is High-Tensile Aluminum the Best Option?
High-tensile aluminum is designed for applications that require enhanced strength while remaining lightweight, making it ideal for fencing and automotive components. This type of aluminum is particularly beneficial in construction settings where both strength and weight savings are critical. While it offers substantial advantages, buyers should be aware that the price point can be higher compared to standard aluminum options, necessitating a careful evaluation of project budgets and requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of 12 gauge aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 12 gauge aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine & Boat Manufacturing | Hulls and structural components | Lightweight yet durable, enhancing fuel efficiency | Corrosion resistance, compliance with marine standards |
| Automotive | Body panels and chassis components | Reduces overall vehicle weight, improving performance | Strength, formability, and surface finish requirements |
| Construction | Architectural facades and structural supports | Aesthetic appeal combined with structural integrity | Custom sizes, finishes, and local regulations |
| Electrical & Electronics | Enclosures and heat sinks | Excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance | Non-magnetic properties and design flexibility |
| Aerospace | Aircraft skin and internal components | High strength-to-weight ratio for improved performance | Compliance with stringent safety standards and certifications |
How is 12 Gauge Aluminum Utilized in Marine & Boat Manufacturing?
In the marine industry, 12 gauge aluminum is widely used for constructing hulls and various structural components of boats. Its lightweight nature significantly contributes to better fuel efficiency, essential for commercial and recreational vessels. Additionally, the corrosion resistance of aluminum is crucial in saltwater environments, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing materials that comply with marine industry standards and consider local environmental conditions when selecting aluminum grades.
What Role Does 12 Gauge Aluminum Play in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry employs 12 gauge aluminum for body panels and chassis components, where reducing weight is vital for improving fuel efficiency and performance. This alloy offers high strength and excellent formability, allowing for intricate designs that meet aesthetic and functional requirements. B2B buyers should focus on the specific mechanical properties and surface finishes needed for automotive applications, ensuring compliance with industry safety standards and regulations.
Why is 12 Gauge Aluminum Important in Construction?
In construction, 12 gauge aluminum is utilized for architectural facades and structural supports, combining aesthetic appeal with robust structural integrity. Its lightweight nature allows for easier installation, while its resistance to corrosion ensures durability in various weather conditions. When sourcing aluminum for construction projects, buyers should consider local building codes, custom sizing options, and finishes that align with design specifications.
How Does 12 Gauge Aluminum Benefit Electrical & Electronics Applications?
The electrical and electronics sectors leverage 12 gauge aluminum for enclosures and heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. These properties are essential for maintaining performance and reliability in electronic devices and systems. Buyers should evaluate the non-magnetic characteristics of aluminum, ensuring that it meets the specific design and safety requirements of their applications.
What Are the Aerospace Applications of 12 Gauge Aluminum?
In aerospace, 12 gauge aluminum is critical for aircraft skin and internal components, where a high strength-to-weight ratio is essential for optimal performance. This material helps manufacturers achieve stringent weight limitations while maintaining safety and structural integrity. Sourcing considerations for B2B buyers in this sector include adherence to rigorous safety standards and certifications, as well as the need for specialized processing and fabrication capabilities.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’12 gauge aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Thickness and Gauge Confusion in 12 Gauge Aluminum
The Problem: One of the primary challenges B2B buyers face when sourcing 12 gauge aluminum is understanding the gauge system. The gauge numbers can be misleading, as they do not correspond directly to specific thickness measurements across different metal types. For example, 12 gauge aluminum is approximately 0.08081 inches thick, which can lead to confusion when comparing it to steel or other materials. This misunderstanding can result in purchasing incorrect materials that do not meet project specifications, leading to costly delays and rework.
The Solution: To avoid such pitfalls, B2B buyers should utilize comprehensive gauge conversion charts specific to aluminum. When specifying materials, always refer to a reliable gauge chart that provides actual thickness measurements in both inches and millimeters. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with suppliers who can confirm the gauge and thickness before placing an order. For projects that require precise tolerances, consider requesting samples or prototype sheets to ensure the material meets your specific requirements. Implementing a standardized process for material specification can greatly reduce errors and enhance project efficiency.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Corrosion Resistance Concerns in 12 Gauge Aluminum
The Problem: Buyers in industries such as marine or automotive often prioritize corrosion resistance when selecting materials. While 12 gauge aluminum, particularly alloys like 5052, is known for its superior corrosion resistance, buyers may struggle with ensuring that the specific grade they are purchasing meets the environmental demands of their application. Misalignment in expectations can lead to premature material degradation, affecting performance and safety.
The Solution: To ensure optimal corrosion resistance, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the aluminum alloy grades available. For applications in harsh environments, sourcing high-strength alloys such as 5052 H32 is recommended due to its enhanced durability and resistance to saltwater and chemicals. Collaborating with suppliers who specialize in specific applications can provide valuable insights into the best materials for your needs. Additionally, consider implementing protective coatings or treatments to further enhance corrosion resistance, especially in applications exposed to extreme conditions. Regularly reviewing and updating specifications based on environmental assessments can ensure long-term material performance.
Scenario 3: Customization and Sizing Limitations of 12 Gauge Aluminum
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges related to the customization of 12 gauge aluminum sheets. Standard sizes may not fit the specific requirements of projects, leading to waste or increased costs from additional cutting and processing. This is particularly common in industries like construction and manufacturing, where unique designs are often required.
The Solution: To tackle these customization issues, buyers should seek suppliers that offer tailored solutions for aluminum products. Requesting custom sizes and thicknesses should be part of the procurement process. When placing an order, provide detailed specifications, including dimensions and any necessary tolerances. Additionally, consider establishing partnerships with suppliers who have capabilities for custom cutting and fabrication, which can streamline the production process and reduce lead times. Engaging in early-stage design discussions with your suppliers can also lead to innovative solutions that meet specific project needs without compromising on quality or increasing costs. By prioritizing customization from the outset, buyers can achieve greater efficiency and satisfaction in their projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 12 gauge aluminum
What Are the Key Properties of 12 Gauge Aluminum Alloys?
When selecting 12 gauge aluminum, it’s essential to consider the specific alloy type, as different alloys exhibit varying properties that affect performance in diverse applications. Common alloys for 12 gauge aluminum include 5052, 3003, and 6061. Each of these alloys offers unique advantages and limitations that can impact their suitability for specific projects.
5052 Aluminum: A High-Strength Option
Key Properties: Alloy 5052 is known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. It has a temperature rating suitable for moderate heat applications and can withstand pressures typical in industrial settings.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of 5052 aluminum is its superior weldability and formability, making it ideal for complex shapes and custom fabrications. However, it can be more expensive than other alloys, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious projects.
Impact on Application: 5052 is commonly used in marine applications, automotive fuel tanks, and pressure vessels due to its corrosion resistance. It is particularly effective in environments exposed to saltwater and harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Germany should ensure compliance with ASTM standards, particularly ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate. Understanding local regulations regarding material specifications can also aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
3003 Aluminum: A Versatile Choice
Key Properties: Alloy 3003 is characterized by its good corrosion resistance and workability. It is not as strong as 5052 but offers excellent formability and is lightweight.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of 3003 aluminum lies in its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including cooking utensils and chemical equipment. However, its lower strength compared to 5052 may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: This alloy is often used in applications where moderate strength is acceptable, such as in decorative and architectural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the common standards like DIN 1725 for aluminum products in Europe, ensuring that their selected materials meet local requirements.
6061 Aluminum: The Structural Powerhouse
Key Properties: Alloy 6061 is a heat-treatable aluminum alloy known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand higher temperatures and pressures than 5052 and 3003.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of 6061 aluminum is its versatility, making it suitable for structural applications, including bridges and buildings. However, it is generally more expensive and may require specialized fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application: This alloy is often used in high-stress applications, such as aerospace components and heavy-duty machinery parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as JIS H 4000 in Japan or ASTM B221 for extrusions is crucial for buyers in Africa and the Middle East to ensure quality and safety.
Summary Table of 12 Gauge Aluminum Options
| Material | Typical Use Case for 12 gauge aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5052 | Marine applications, fuel tanks | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to others | High |
| 3003 | Decorative components, cooking utensils | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Lower strength than other alloys | Medium |
| 6061 | Structural applications, aerospace | High strength and versatility | More expensive and complex to fabricate | High |
In conclusion, selecting the right 12 gauge aluminum alloy requires a thorough understanding of the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 12 gauge aluminum
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 12 Gauge Aluminum?
The manufacturing process of 12 gauge aluminum, which typically measures around 0.08081 inches (or 2.053 mm) in thickness, involves several critical stages to ensure that the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-quality aluminum alloy, often 5052 or 6061, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and formability. The aluminum sheets are then cut to size using precision cutting methods such as laser cutting or water jet cutting. This step is crucial, as it sets the foundation for subsequent processes.
Forming Techniques
Once the aluminum sheets are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques, which can include bending, stamping, or deep drawing. These methods are chosen based on the final application of the aluminum sheet. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining can also be employed to achieve precise shapes and dimensions, enhancing the material’s usability in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Assembly and Fabrication
In some applications, the formed aluminum components may need to be assembled or welded. Techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are commonly used for aluminum due to their ability to produce strong, clean welds. The choice of welding technique often depends on the thickness of the material and the specific requirements of the final product.
Finishing Processes
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing treatments such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance and can provide an attractive surface finish. These processes not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the aluminum sheets but also extend their lifespan, making them suitable for outdoor or harsh environment applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in the Production of 12 Gauge Aluminum?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of 12 gauge aluminum, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. This process is typically governed by various quality management systems, such as ISO 9001, which establishes criteria for effective quality management practices.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Aluminum Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. It focuses on meeting customer needs and enhancing satisfaction, which is crucial for B2B suppliers. Additionally, industry-specific standards may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, which ensures compliance with safety and environmental regulations, or API standards for the oil and gas industry.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. These can be categorized into:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring of the manufacturing processes to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of the finished product before shipment to ensure it meets all specifications.
Common testing methods include dimensional inspections, tensile strength tests, and corrosion resistance tests. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing, may also be employed to detect internal defects without damaging the material.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is crucial. Here are several methods to ensure reliability:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess the processes, equipment, and quality management systems in place.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed reports on quality control measures, including results from testing and inspections, helps buyers understand the supplier’s adherence to standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing process and the final products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality.
-
Certifications: Buyers should verify that suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry certifications, which can indicate a commitment to quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
Quality control nuances can vary significantly based on geographic and regulatory contexts. For instance, European buyers may have stricter environmental compliance standards compared to those in other regions. It’s essential for buyers to understand these differences and communicate their specific requirements clearly.
Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences can impact the effectiveness of quality assurance processes. Establishing clear lines of communication and documentation practices can mitigate these issues, ensuring that both parties are aligned in their quality expectations.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 12 gauge aluminum is critical for B2B buyers. By being aware of the stages of production, relevant standards, quality checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and ensure they receive high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’12 gauge aluminum’
Introduction:
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for 12 gauge aluminum. Understanding the nuances of aluminum specifications, supplier evaluation, and logistical considerations can significantly impact the success of your purchase. Use this checklist to streamline your sourcing efforts and ensure that you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first step in sourcing 12 gauge aluminum. This includes determining the alloy type (e.g., 5052, 6061), thickness, dimensions, and any specific finish or coating needs.
– Why it matters: Specificity helps avoid confusion and ensures you receive the correct material for your application.
– What to look for: Refer to gauge charts to confirm that the thickness meets your project requirements, and consider the intended use, such as marine or automotive applications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in aluminum products. Look for companies with a solid reputation and experience in your region or industry.
– Why it matters: A well-established supplier is more likely to provide high-quality materials and reliable service.
– What to look for: Check their website for product offerings, certifications, and customer testimonials to gauge their credibility.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making any commitments, verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place. Common certifications include ISO 9001 and compliance with ASTM standards.
– Why it matters: Certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to industry standards for quality and safety, which is crucial for long-term projects.
– What to look for: Request copies of certifications and inquire about their quality control measures during production and delivery.
Step 4: Request Samples
Obtaining samples of the 12 gauge aluminum you intend to purchase is a crucial step before finalizing your order. This allows you to assess the material’s quality, finish, and suitability for your needs.
– Why it matters: Physical samples help you verify specifications and ensure that the product meets your expectations.
– What to look for: Examine the samples for any defects, such as scratches or uneven surfaces, and ensure they match the specifications provided.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Understanding the total cost, including shipping and any additional fees, is essential for budgeting.
– Why it matters: Comparing prices ensures you get the best value for your investment while considering quality and service.
– What to look for: Look beyond the initial price; consider factors like minimum order quantities and discounts for bulk purchases.
Step 6: Review Logistics and Delivery Options
Consider the logistical aspects of your purchase, including shipping methods, lead times, and delivery locations. Ensure that the supplier can meet your timeline and that they have reliable shipping practices.
– Why it matters: Effective logistics planning can prevent delays in your project due to material shortages.
– What to look for: Ask about their shipping partners, tracking options, and their policy on damaged goods during transit.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Once you have selected a supplier, establish a clear communication plan to facilitate updates and address any potential issues. Regular check-ins can help ensure that your order remains on track.
– Why it matters: Open lines of communication build trust and allow for quick resolutions to any problems that may arise.
– What to look for: Determine who your main point of contact will be and how frequently you will receive updates on your order status.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for 12 gauge aluminum, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their project requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 12 gauge aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 12 Gauge Aluminum?
When sourcing 12 gauge aluminum, understanding the cost structure is critical for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base cost of aluminum fluctuates based on market conditions, alloy type, and thickness. For example, 12 gauge aluminum (approximately 0.100 inches thick) can vary significantly in price depending on whether it is sourced as 5052, 3003, or another alloy. Prices can range from $60 to $100 per sheet, depending on the supplier and specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with cutting, forming, and finishing aluminum sheets. In regions with higher labor rates, such as parts of Europe, these costs can be more pronounced, affecting the overall price of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thus lowering the price for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can add to the initial costs. If the buyer requires unique shapes or sizes, the tooling costs may need to be amortized over the production run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the aluminum meets the required specifications involves testing and inspection. Additional QC measures can increase costs but are vital for maintaining product integrity, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on location and the chosen shipping method. International shipping, particularly to regions like Africa or South America, may involve higher freight rates and customs duties, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, demand, and relationship with the buyer.
What Factors Influence Pricing for 12 Gauge Aluminum?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 12 gauge aluminum, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts, significantly reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should balance their specific requirements against budget constraints to find the best solution.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (such as ISO or ASTM standards) may command a premium price. Buyers in regulated industries must consider these factors carefully.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality assurance but may charge higher prices compared to newer entrants.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade can significantly influence the total cost. Understanding whether costs are inclusive of shipping, insurance, and duties (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing 12 Gauge Aluminum Internationally?
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices and terms. Suppliers may have wiggle room in their pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), not just the upfront price. Consider shipping, handling, and potential costs for rework or returns due to quality issues.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa or South America may face additional challenges, such as currency fluctuations and import tariffs. It’s essential to account for these factors in your pricing strategy.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved product quality.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about global aluminum market trends, as prices can be volatile. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 12 gauge aluminum are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and other factors. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and favorable terms.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 12 gauge aluminum With Other Solutions
When evaluating materials for construction or manufacturing processes, businesses often seek alternatives to 12 gauge aluminum. This analysis explores viable substitutes, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and operational contexts.
| Comparison Aspect | 12 Gauge Aluminum | Steel (Mild Steel) | Composite Materials (Fiberglass) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; corrosion resistant | Strong but heavier; susceptible to rust | Lightweight; good tensile strength; corrosion resistant |
| Cost | Moderate price per sheet; higher than mild steel | Generally lower initial cost; fluctuating prices | Typically higher due to manufacturing complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to cut and fabricate; requires specialized tools for welding | Commonly available; easy to work with conventional tools | Requires specific skills for installation and handling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; retains appearance over time | Requires regular painting or coating to prevent rust | Minimal maintenance; resistant to environmental degradation |
| Best Use Case | Marine, automotive, and architectural applications | Structural components, construction, and automotive frames | Aerospace components and applications where weight reduction is critical |
Pros and Cons of Alternatives to 12 Gauge Aluminum
Steel (Mild Steel)
Mild steel is a traditional alternative to aluminum, known for its strength and affordability. It is widely used in construction and manufacturing due to its easy availability and lower cost. However, mild steel is heavier and prone to rust, necessitating protective coatings or regular maintenance to enhance its lifespan. In applications where weight is a significant concern or corrosion resistance is crucial, mild steel may not be the best choice.
Composite Materials (Fiberglass)
Composite materials, particularly fiberglass, present a modern alternative that is lightweight and offers good tensile strength. They are resistant to corrosion and environmental factors, making them suitable for specialized applications like aerospace components. However, the initial investment is typically higher, and installation requires specific expertise. Fiberglass may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring high structural strength.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate material depends on a variety of factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. For projects requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant options, 12 gauge aluminum stands out. However, if initial cost is a primary concern and weight is less critical, mild steel could be more suitable. For specialized applications where weight reduction is paramount, composites like fiberglass may be the best fit despite their higher cost. By carefully considering these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 12 gauge aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 12 Gauge Aluminum?
When evaluating 12 gauge aluminum, several technical properties are essential for B2B buyers to understand. These properties influence the material’s suitability for various applications, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
1. Material Grade
The most common grades for 12 gauge aluminum include 5052 and 6061. Grade 5052 is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and weldability, making it ideal for marine applications. In contrast, 6061 offers higher strength and is often used in structural applications. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures the material meets specific performance requirements and regulatory standards.
2. Thickness
In the gauge system, 12 gauge aluminum typically measures 0.08081 inches (2.053 mm) thick. Understanding the thickness is crucial as it directly impacts the material’s strength, weight, and application. For example, a thicker gauge can withstand greater loads, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and is critical in manufacturing processes. For 12 gauge aluminum, typical tolerances might range from ±0.005 inches to ±0.015 inches. Precise tolerances ensure that components fit together correctly, reducing the risk of failure in final products.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, providing excellent resistance to corrosion. This property is especially vital for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as marine and chemical processing. Buyers should consider this characteristic when selecting aluminum for outdoor or corrosive settings.
5. Weldability
Weldability indicates how easily aluminum can be welded without compromising its integrity. 5052 aluminum, for instance, is highly weldable and is often used in applications requiring joining multiple pieces. Understanding weldability is crucial for manufacturers to ensure their fabrication processes meet project requirements.
6. Weight
Aluminum is a lightweight material, which is one of its primary advantages. 12 gauge aluminum provides a balance of strength and weight, making it suitable for applications where reducing weight is critical, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to 12 Gauge Aluminum?
Navigating the procurement process involves understanding industry-specific terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of aluminum products, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide quality materials for their applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For aluminum sheets, MOQs can vary based on the supplier and the specific product. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for international buyers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of materials. For buyers, submitting an RFQ for 12 gauge aluminum can facilitate comparisons between suppliers and help negotiate better terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps international buyers understand their obligations and manage risks when purchasing aluminum from abroad.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time required from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times for 12 gauge aluminum can help companies plan their production schedules and avoid delays in their supply chain.
6. Custom Fabrication
This term describes the process of altering standard aluminum sheets to meet specific design requirements. Knowing about custom fabrication options allows buyers to obtain materials tailored to their unique project needs, enhancing the overall functionality of their products.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing 12 gauge aluminum, ultimately leading to better product quality and project success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 12 gauge aluminum Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the 12 Gauge Aluminum Sector
The global market for 12 gauge aluminum is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and marine industries. Notably, the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum make it an attractive choice for manufacturers looking to enhance product performance while reducing overall weight. In regions like Africa and South America, the rise of infrastructure projects is propelling the demand for aluminum, while in Europe and the Middle East, stringent regulations on emissions and sustainability are pushing companies to adopt lighter materials, such as aluminum, in their designs.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping how buyers source aluminum. Digital marketplaces and platforms that connect suppliers and buyers are gaining traction, making it easier for international buyers to find and vet suppliers. Additionally, advancements in supply chain analytics and AI are enabling companies to optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring they can respond swiftly to market fluctuations. International buyers should pay attention to trends like just-in-time manufacturing and local sourcing, which are becoming essential for maintaining competitive advantage in a volatile market.
Moreover, the demand for customized solutions is on the rise. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can offer tailored products, such as specific gauge thicknesses and unique finishes. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Nigeria and Germany, where regulatory and application needs can vary significantly.
How Are Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing Impacting the 12 Gauge Aluminum Market?
As global awareness of environmental issues grows, the importance of sustainability in sourcing materials like 12 gauge aluminum cannot be overstated. The aluminum industry has made strides in reducing its carbon footprint, yet it still faces scrutiny regarding energy consumption and waste management. International buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled aluminum and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is also becoming a key consideration for B2B buyers. Companies are expected to maintain transparent supply chains that adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Buyers should seek suppliers that possess certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building materials, which signal a commitment to responsible sourcing. These certifications can not only enhance a company’s reputation but also appeal to environmentally conscious clients and consumers.
In the context of 12 gauge aluminum, selecting suppliers that utilize green materials and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can significantly impact a company’s brand value and market positioning. Buyers should actively engage with potential suppliers to understand their sourcing practices, ensuring that they align with their own sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of 12 Gauge Aluminum in B2B Markets?
The use of aluminum in industrial applications has a rich history dating back to the early 19th century, but its adoption in the sheet metal sector gained momentum post-World War II. The development of advanced alloys, such as 5052 and 6061, allowed for increased strength and versatility, making aluminum an ideal material for a variety of applications, including construction and transportation.
The gauge system, which measures the thickness of aluminum sheets, has also evolved over time. While the gauge system is not standardized, understanding the specific thicknesses associated with 12 gauge aluminum (approximately 0.0808 inches or 2.053 mm) is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they meet industry specifications and regulatory requirements. This historical context provides valuable insights into the ongoing innovations and trends shaping the aluminum market today, helping buyers make informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 12 gauge aluminum
-
How do I determine the appropriate thickness of 12 gauge aluminum for my project?
To select the right thickness of 12 gauge aluminum, refer to a gauge conversion chart. For aluminum, 12 gauge typically measures 0.08081 inches or 2.053 mm. Consider the specific requirements of your application, including strength, weight, and environmental conditions, as different projects may necessitate different thicknesses. If unsure, consult with your supplier for recommendations based on your intended use, whether it’s for marine applications, automotive parts, or construction. -
What is the best aluminum alloy for corrosion resistance in harsh environments?
For applications exposed to harsh environments, the 5052 aluminum alloy is highly recommended. It offers superior corrosion resistance, particularly against saltwater and chemicals, making it ideal for marine, automotive, and industrial applications. Its strength and durability, combined with excellent weldability, ensure that it can withstand demanding conditions. Always confirm the specific alloy’s properties with your supplier to ensure it meets your project’s requirements. -
What should I consider when vetting international suppliers of 12 gauge aluminum?
When vetting international suppliers, focus on their reputation, certifications, and experience in the industry. Request samples to evaluate quality, and check for compliance with international standards such as ISO or ASTM. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication can help assess their reliability and responsiveness, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 12 gauge aluminum?
Minimum order quantities for 12 gauge aluminum can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 kg to several tons. It’s advisable to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility on MOQs, especially for first-time buyers or ongoing contracts. Always clarify the pricing structure in relation to the MOQ to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing 12 gauge aluminum internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier and the country of origin. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, requiring payment after receipt of goods. For first-time transactions, many suppliers may request upfront payment or a deposit. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit for added security in international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my aluminum products?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation from your supplier, such as mill test reports or certificates of compliance. Establish clear specifications and tolerances prior to order placement. Consider third-party inspections if the order is substantial or critical to your operations. Building a strong relationship with your supplier, including regular communication about quality expectations, can also facilitate better QA practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing 12 gauge aluminum?
When importing 12 gauge aluminum, consider shipping methods, costs, and transit times. Factor in customs clearance processes, tariffs, and any import regulations specific to your country. It’s advisable to work with a logistics partner experienced in handling metal imports to navigate these complexities. Additionally, ensure that your supplier can provide appropriate packaging to prevent damage during transit. -
What applications are suitable for 12 gauge aluminum in various industries?
12 gauge aluminum is widely used across multiple industries due to its strength and lightweight properties. Common applications include structural components in construction, automotive parts, marine vessel components, and manufacturing of fuel tanks. Its excellent weldability also makes it suitable for custom fabrication projects. When selecting aluminum for specific applications, consider factors such as weight restrictions, corrosion exposure, and required durability to ensure optimal performance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 12 Gauge Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metal Supermarkets – Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Chart – Metal Supermarkets offers a variety of metals including mild steel, aluminum, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, bronze, and copper. The chart provides gauge numbers and their corresponding thickness in inches and millimeters for different metals. For example, 18 gauge mild steel is 0.0478 inches (1.214 mm) thick, while 18 gauge aluminum is 0.0403 inches (1.024 mm) thic…
2. DM Steel – Aluminum Sheet 5052 12 Gauge
Domain: dmsteel.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Sheet 5052 – 12 Gauge / (.100)
3. Metals Depot – Aluminum Sheet Types
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Sheet Types: 3003-H14, 5052-H32, 6061-T6. 3003-H14: Excellent weldability and formability, good corrosion resistance, applications include fuel tanks, food & chemical handling, trailer siding & roofing. Mill Finish, Non-magnetic, Brinell = 40, Tensile = 22,000, Yield = 21,000. 5052-H32: Superior corrosion resistance, good weldability, excellent formability, applications include tanks, mar…
4. RMFG – Aluminum Gauge Thickness Chart
Domain: rmfg.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Gauge Thickness Chart: Comprehensive reference for aluminum gauge thickness in inches and millimeters. Gauge Numbers and corresponding thicknesses: 7 GA – 0.144 in (3.67 mm), 8 GA – 0.129 in (3.26 mm), 9 GA – 0.114 in (2.91 mm), 10 GA – 0.102 in (2.59 mm), 11 GA – 0.091 in (2.31 mm), 12 GA – 0.081 in (2.05 mm), 14 GA – 0.064 in (1.63 mm), 16 GA – 0.051 in (1.29 mm), 18 GA – 0.040 in (1.02…
5. Protocase – Aluminum General Purpose Enclosures
Domain: protocase.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Aluminum for General Purpose Enclosures:
– Corrosion resistant and lightweight.
– Lower structural stiffness than steel (about 1/3), requiring thicker gauge.
– Finishes available: Powdercoat, No Finish, Grained Finish.
– Fasteners: Typically stainless steel; aluminum fasteners are soft and not stocked.
– Aluminum alloys available:
– 5052 Aluminum – H32: Optimal for sheet metal work, easy t…
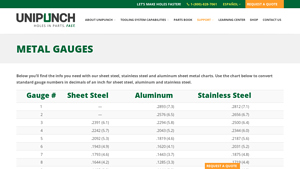
6. Unipunch – Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: unipunch.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal Gauge Chart for Steel, Aluminum, and Stainless Steel. Gauge numbers with corresponding thickness in inches and millimeters for sheet steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Example: Gauge 1 – Steel: .2893 (7.3mm), Aluminum: .2812 (7.1mm); Gauge 2 – Steel: .2576 (6.5mm), Aluminum: .2656 (6.7mm); continues down to Gauge 29.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 12 gauge aluminum
In the competitive landscape of industrial materials, 12 gauge aluminum stands out due to its unique combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility. This makes it an ideal choice for applications ranging from automotive to marine sectors. Strategic sourcing of this material allows international buyers to not only secure high-quality aluminum but also optimize costs and ensure timely delivery.
Understanding the specific needs of your market—whether it’s the demanding environments of Africa or the precision requirements in Germany—can significantly enhance procurement strategies. Buyers should leverage gauge conversion charts to accurately assess thickness specifications, ensuring that the materials meet project requirements. Moreover, engaging with reputable suppliers who offer customization options can facilitate tailored solutions that align with diverse industry demands.
As we look ahead, the global aluminum market is poised for growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials. Now is the time for B2B buyers to reassess their sourcing strategies for 12 gauge aluminum to stay competitive. By prioritizing quality and supplier partnerships, companies can position themselves advantageously in their respective markets. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and elevate your projects with premium aluminum solutions.