Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 1045 steel vs 4140
The global market for steel sourcing presents a myriad of challenges, particularly when it comes to choosing between 1045 steel and 4140 steel. International B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate complex specifications, applications, and cost considerations to make informed decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the critical distinctions between 1045 and 4140 steel, highlighting their unique chemical compositions, mechanical properties, and suitability for various applications.
Buyers will gain insights into the practical implications of these differences, such as how the higher carbon content in 1045 contributes to its strength and impact resistance, while the alloying elements in 4140 enhance its toughness and wear resistance. Additionally, the guide addresses essential factors for supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reputable sources that meet their specific needs.
Cost-effectiveness is another pivotal aspect covered, enabling businesses to weigh the benefits of investing in higher-grade materials against budgetary constraints. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge on sourcing, applications, and supplier considerations, this guide empowers them to make strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Understanding 1045 steel vs 4140 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1045 Carbon Steel | Higher carbon content (0.43-0.50%), good machinability | Machinery parts, automotive components | Pros: Cost-effective, good impact resistance. Cons: Lower hardness than 4140. |
| 4140 Alloy Steel | Alloyed with chromium and molybdenum, high tensile strength | Gears, axles, high-stress components | Pros: Superior toughness and wear resistance. Cons: More expensive, harder to machine. |
| 1045 Heat Treated | Enhanced strength through heat treatment | Structural applications, shafts | Pros: Improved strength and durability. Cons: Limited to specific heat treatment processes. |
| 4140 Quenched and Tempered | Achieves high hardness and toughness | Heavy machinery, tooling | Pros: Excellent performance in high-stress environments. Cons: Requires careful machining techniques. |
| 1045 Cold Drawn | Improved dimensional tolerances and surface finish | Precision components, pins | Pros: Better surface finish, easier to machine. Cons: Limited strength compared to 4140. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 1045 Carbon Steel for B2B Buyers?
1045 carbon steel is a medium carbon steel known for its balance of strength and ductility. With a carbon content ranging from 0.43% to 0.50%, it offers good machinability and impact resistance, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications, including machinery parts and automotive components. B2B buyers should consider its cost-effectiveness, particularly when lower hardness is acceptable for the application. However, it’s essential to note that 1045 is less suitable for applications requiring high wear resistance compared to alloy steels.
How Does 4140 Alloy Steel Compare in Terms of Performance?
4140 alloy steel is characterized by its chromium and molybdenum content, which enhances its hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. It is typically used in high-stress applications such as gears and axles. For B2B buyers, the superior mechanical properties of 4140 justify its higher cost, especially in demanding environments. However, the increased hardness makes it more challenging to machine, necessitating advanced machining techniques. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against the potential increased processing costs.
What Advantages Does Heat Treatment Offer for 1045 Steel?
Heat-treated 1045 steel significantly improves its mechanical properties, making it suitable for structural applications and components like shafts. The heat treatment process can enhance its strength and hardness, allowing it to withstand greater loads. B2B buyers should consider the specific heat treatment processes available, as they can impact the final product’s performance. While heat-treated 1045 steel can be a viable alternative to higher-grade materials, it is essential to ensure compatibility with the intended application to maximize benefits.
Why Choose Quenched and Tempered 4140 Steel for Heavy-Duty Applications?
4140 steel that has undergone quenching and tempering achieves exceptional hardness and toughness, making it ideal for heavy machinery and tooling. This treatment process allows the steel to maintain its performance under high-stress conditions. B2B buyers should be prepared for the intricacies of machining quenched and tempered 4140, as it often requires specialized tools and techniques. While the investment in this type of steel is higher, the long-term durability and performance in demanding applications can justify the cost.
What Are the Benefits of Using Cold Drawn 1045 Steel in Precision Applications?
Cold drawn 1045 steel provides improved dimensional tolerances and a superior surface finish, making it an excellent choice for precision components like pins and fasteners. This manufacturing process enhances the material’s mechanical properties while allowing for easier machining compared to its hot-rolled counterparts. B2B buyers should consider cold drawn 1045 when precision and surface quality are critical, though they must also be mindful of its lower strength in comparison to alloy steels like 4140.
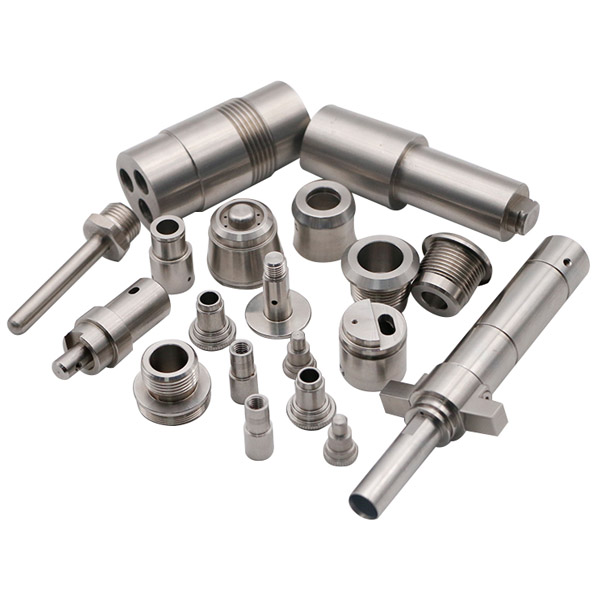
Key Industrial Applications of 1045 steel vs 4140
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 1045 steel vs 4140 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, crankshafts (1045); axles, gears (4140) | Enhanced performance, durability under stress | Consider heat treatment options and machining capabilities. |
| Machinery Manufacturing | Shafts and machinery parts (1045); tooling and dies (4140) | Cost-effective solutions with high strength and wear resistance | Evaluate supplier certifications and material traceability. |
| Oil & Gas | Drill bits and downhole tools (4140); casing components (1045) | Improved reliability and performance in harsh environments | Ensure compliance with industry standards and testing protocols. |
| Construction | Structural components (1045); heavy machinery parts (4140) | Strength and impact resistance for long-lasting structures | Assess material availability and delivery timelines. |
| Mining | Heavy-duty equipment parts (4140); transport components (1045) | Enhanced toughness and wear resistance for challenging conditions | Look for suppliers with experience in high-stress applications. |
How is 1045 Steel Used in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, 1045 steel is often utilized for components that require good impact resistance, such as engine parts and crankshafts. Its higher carbon content provides strength, making it suitable for high-performance vehicles. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Nigeria should consider local regulations regarding material standards and the availability of heat treatment processes to enhance the steel’s properties.
What Role Does 4140 Steel Play in Machinery Manufacturing?
4140 steel, known for its superior toughness and wear resistance due to its alloying elements, is widely used in machinery manufacturing for tooling and dies. This steel is essential for components that undergo significant stress and require longevity. B2B buyers, especially from South America and the Middle East, should focus on sourcing from suppliers who can offer detailed specifications and heat treatment options to meet their operational needs.
How is 4140 Steel Essential in Oil & Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas industry, 4140 steel is critical for manufacturing drill bits and downhole tools, where performance under extreme conditions is paramount. The alloy’s toughness and resistance to wear ensure reliability in harsh environments. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with experience in the sector and ensure compliance with industry standards, particularly for components subjected to rigorous testing.
Why is 1045 Steel Preferred for Construction Applications?
1045 steel is frequently chosen for structural components in construction due to its impact resistance and cost-effectiveness. It is ideal for applications where strength is needed without the additional expense associated with alloy steels. Buyers in Europe and Africa should evaluate the sourcing of 1045 steel based on local availability and the potential need for heat treatment to meet specific structural standards.
How is 4140 Steel Used in Mining Operations?
In the mining industry, 4140 steel is utilized for heavy-duty equipment parts, offering exceptional toughness and wear resistance. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice for transport components and machinery. B2B buyers should consider suppliers with a proven track record in high-stress applications and assess the availability of customized solutions to meet specific operational requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘1045 steel vs 4140’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Balancing Cost and Performance for Industrial Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face a dilemma when choosing between 1045 steel and 4140 steel, particularly regarding cost versus performance. For instance, a manufacturing company in Nigeria may require a material for constructing machinery parts that need to withstand significant wear and tear. They may be inclined to opt for the more cost-effective 1045 steel, but are concerned about whether it will provide the necessary durability and strength in high-stress applications compared to the more expensive 4140 steel.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their specific application requirements. If the application involves moderate stress and impact resistance, 1045 steel can be a viable choice due to its cost-effectiveness. However, for applications with high stress or where failure could lead to safety hazards, investing in 4140 steel is advisable despite the higher initial cost. Buyers should also consider sourcing both materials from suppliers who offer detailed technical specifications and insights into the performance of each steel type in various conditions. Additionally, discussing heat treatment options with suppliers can enhance the performance of either steel, making 1045 more competitive in certain scenarios.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Machinability and Fabrication
The Problem: A buyer in Brazil is responsible for procuring steel for a new production line that requires extensive machining of components. They are uncertain whether to choose 1045 or 4140 steel due to concerns about machinability. The buyer has heard that while 1045 is easier to machine, it may not provide the necessary durability for their application, potentially leading to increased downtime and costs if components fail prematurely.
The Solution: The buyer should consider the specific machining processes involved and the expected lifecycle of the components. If high-volume production is anticipated, opting for 1045 steel can reduce machining time and costs, given its favorable machinability characteristics. However, for critical components that must endure high fatigue or stress levels, using 4140 steel may be justified despite its machining challenges. To facilitate this, the buyer can work closely with machine shops that have experience with both materials. Engaging with suppliers who can provide guidance on the best cutting tools and techniques for each steel type can also optimize the machining process and ensure that the right balance between machinability and material properties is achieved.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Heat Treatment Process
The Problem: A manufacturing firm in Europe is looking to enhance the properties of the steel it uses but is confused about the heat treatment processes for 1045 and 4140 steel. They understand that heat treatment can significantly alter mechanical properties but are unsure how to apply it effectively to achieve desired outcomes, especially when transitioning from one steel type to another.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this issue, the firm should prioritize collaboration with heat treatment specialists. Each steel type responds differently to heat treatment; 4140 can achieve superior hardness and strength through processes like quenching and tempering, while 1045 can be heat-treated to improve its strength but may not reach the hardness levels of 4140. The firm should also consider pre-treatment evaluations to assess the initial mechanical properties of the steel before deciding on a heat treatment strategy. Establishing a close relationship with suppliers who offer tailored heat treatment services can ensure that the firm maximizes the performance of both steel types, allowing them to make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their applications. Regularly reviewing and adjusting their heat treatment protocols as needed can also lead to improved product quality and consistency in performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 1045 steel vs 4140
When evaluating the strategic selection between 1045 steel and 4140 steel, it is crucial to consider their distinct properties, applications, and implications for international B2B buyers. This analysis will focus on four key aspects: mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, manufacturing complexity, and application suitability, particularly for regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of 1045 Steel?
1045 steel is a medium carbon steel known for its strength and impact resistance. With a carbon content of approximately 0.45%, it offers good machinability and can be heat-treated to enhance its hardness. Its mechanical properties include a tensile strength of around 82,000 psi in hot-rolled form and 91,000 psi when cold drawn. However, it is less resistant to wear compared to alloy steels like 4140, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 1045 Steel?
Pros:
– Cost-effective due to its simpler composition.
– Easier to machine and weld compared to higher carbon steels.
– Suitable for applications requiring impact resistance, such as automotive components and machinery parts.
Cons:
– Lower hardness and wear resistance than 4140, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
– Limited performance in environments with high corrosion potential without proper treatment.
How Does 4140 Steel Compare in Terms of Properties?
4140 steel is an alloy steel that includes chromium, molybdenum, and manganese, contributing to its superior hardness and toughness. With a tensile strength of approximately 90,000 psi in hot-rolled form, it is ideal for high-stress applications such as gears, axles, and shafts. The alloying elements enhance its fatigue resistance and wear properties, making it a preferred choice for demanding environments.
What are the Pros and Cons of Using 4140 Steel?
Pros:
– Excellent strength and wear resistance, suitable for high-stress applications.
– Better fatigue resistance and toughness, making it ideal for parts exposed to dynamic loads.
– Can be heat-treated to achieve even higher hardness levels.
Cons:
– More expensive than 1045 due to its complex composition.
– Requires advanced machining techniques, which could increase manufacturing costs and complexity.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards (such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS) is essential. 1045 steel’s cost-effectiveness makes it attractive for projects with budget constraints, while 4140’s superior properties justify its higher price in applications demanding durability and strength. Buyers should also consider logistics and sourcing challenges, as the availability of these materials can vary by region.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for 1045 steel vs 4140 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1045 Steel | Machinery parts, automotive components | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Lower wear resistance and hardness | Low |
| 4140 Steel | Gears, axles, high-stress components | Superior strength and toughness | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
In conclusion, the choice between 1045 and 4140 steel hinges on the specific requirements of the application, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and regional compliance standards. Understanding these factors will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 1045 steel vs 4140
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 1045 Steel and 4140 Steel?
The manufacturing processes for both 1045 and 4140 steel involve several stages that are critical to achieving the desired mechanical properties and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure steel for specific applications.
Material Preparation: How Are 1045 and 4140 Steel Prepared?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, which primarily include iron and alloying elements. For 1045 steel, the primary alloying element is carbon, whereas 4140 steel includes chromium, molybdenum, and manganese. The quality of the raw materials directly impacts the final product’s properties.
Once sourced, the materials undergo melting in electric arc furnaces (EAF) or induction furnaces. This melting process is crucial as it helps eliminate impurities. The molten steel is then cast into various shapes, such as ingots or billets, which are the starting point for further processing.
Forming Processes: What Techniques Are Used for Shaping Steel?
After casting, both 1045 and 4140 steels are subjected to forming processes like hot rolling or cold drawing. Hot rolling involves heating the steel above its recrystallization temperature, making it easier to shape. This process is typically employed for producing large quantities of steel plates, bars, and rods.
Cold drawing, on the other hand, is a preferred method for achieving precise dimensions and improved surface finish. It involves pulling the steel through a die at room temperature, enhancing its mechanical properties through strain hardening. For B2B buyers, understanding the forming techniques is vital, as it affects the steel’s final application suitability.
Assembly and Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Manufacturing?
The assembly stage may involve welding or machining, depending on the specific application requirements. 4140 steel, with its higher alloy content, is generally preferred for applications requiring high strength and toughness, while 1045 steel is favored for parts needing good machinability and impact resistance.
Finishing processes include heat treatment, which can significantly alter the mechanical properties of both steels. 1045 steel can be easily heat-treated to enhance its strength, while 4140 can achieve superior hardness and toughness through processes like quenching and tempering. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific finishing processes used, as these can greatly influence performance in end-use applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of 1045 and 4140 Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of steel manufacturing, ensuring that the products meet international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding QA processes can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Steel Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers of 1045 and 4140 steel often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API (for the oil and gas sector) are crucial. These certifications indicate that the steel products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria, which is particularly important for high-stakes applications in sectors like construction and automotive.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to ensuring that the manufacturing processes yield high-quality products. Typical QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. Buyers should confirm that suppliers perform rigorous IQC to ensure only the best materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, various tests are conducted to monitor the manufacturing process. Techniques like ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and dimensional checks are common.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves comprehensive testing of the finished products to ensure they meet all specifications. Mechanical testing, such as tensile strength and hardness tests, is performed to verify that the steel meets the required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are transparent about their quality assurance practices. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. This firsthand assessment allows buyers to evaluate compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers understand how a supplier monitors quality throughout the manufacturing process. These reports should outline testing methods, results, and corrective actions taken for any non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct audits locally.
What Are the QC Considerations for International Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
International B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality assurance that may vary by region. For example, regulatory requirements may differ between Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, affecting the certification and compliance processes.
Additionally, buyers should consider the logistics of quality assurance, such as transportation and storage conditions, which can impact steel quality. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers about quality expectations and compliance with local regulations is essential for successful procurement.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 1045 and 4140 steel is vital for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly and finishing processes, and rigorous quality control practices, buyers can ensure they procure steel that meets their specific application needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘1045 steel vs 4140’
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure either 1045 steel or 4140 steel. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of steel is vital for making informed purchasing decisions based on specific application needs, cost considerations, and supplier capabilities.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for determining which steel grade best suits your application. Consider factors such as tensile strength, yield strength, hardness, and weldability. For instance, if your project requires high impact resistance, 1045 might be preferable; whereas, for high-stress applications, 4140 could be the better choice.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Identify the specific applications for which you intend to use the steel. Different applications, such as automotive components or machinery parts, may have unique demands. For example, 4140 is often used for gears and axles due to its superior toughness, while 1045 is ideal for parts that require good machinability and impact resistance.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a purchase, it’s essential to verify the certifications of potential suppliers. Look for ISO certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ASTM. Certifications ensure that the steel meets quality specifications and can help mitigate risks associated with material failures.
Step 4: Compare Pricing Structures
Understand the cost implications of both 1045 and 4140 steels. Generally, 1045 is more cost-effective due to its simpler composition. However, consider the long-term value based on performance requirements; investing in 4140 may be justified for high-stress applications despite its higher upfront cost.
Step 5: Request Sample Materials
Requesting samples of both steel types can provide valuable insights into their properties and performance. Evaluate the samples for machinability, weldability, and overall quality. This hands-on assessment can help confirm that the selected steel meets your specifications.
Step 6: Analyze Lead Times and Delivery Options
Assess the lead times and delivery capabilities of potential suppliers. Ensure that they can meet your project timelines, especially if you have strict deadlines. Inquire about their logistics strategies and whether they can accommodate international shipping if you are sourcing from different regions.
Step 7: Seek Technical Support and Consultation
Consider suppliers that offer technical support and consultation services. Having access to expert advice can help you navigate complex decisions regarding material selection and processing. This support is particularly important for projects requiring custom solutions or specialized applications.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the procurement process for 1045 and 4140 steel, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs and project requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 1045 steel vs 4140 Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 1045 and 4140 Steel?
When sourcing 1045 and 4140 steel, understanding the cost structure is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The base price of the steel itself is a significant factor. Generally, 1045 steel is more cost-effective than 4140 due to its simpler composition. The additional alloying elements in 4140, such as chromium and molybdenum, increase its base price, making it approximately 20-30% more expensive than 1045.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the steel’s processing. Since 4140 requires more advanced machining techniques due to its hardness, labor costs may be higher compared to 1045. Additionally, overhead costs associated with the production of each steel type can fluctuate depending on the supplier’s operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling and Quality Control: The hardness of 4140 necessitates specialized tooling, which can increase the initial setup costs. Quality control processes also differ; higher quality certifications for 4140 can lead to increased QC expenses, influencing the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transporting steel can be a significant cost factor, especially for international buyers. The weight and volume of orders, particularly for large quantities, can lead to increased shipping costs. Additionally, the choice of Incoterms can affect who bears these costs, impacting the total price.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary significantly based on their market position, brand reputation, and the level of service provided. Buyers should consider these factors when evaluating offers from different suppliers.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 1045 and 4140 Steel?
Several price influencers can affect the cost and availability of both steel types. Understanding these can aid in better negotiation and sourcing strategies.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. However, suppliers may have specific MOQs, especially for 4140 due to its higher processing costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as specific heat treatments or finishes, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Quality and Certifications: The level of quality assurance and certifications required can affect pricing. For instance, if a buyer requires ISO-certified products, they may pay a premium for 4140 steel.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more for their products but offer better quality assurance, timely delivery, and customer support.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Steel?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions about pricing, especially if purchasing in bulk. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate terms based on order size or long-term partnerships.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not just the initial price but also logistics, maintenance, and any potential downtime costs. This approach may reveal that a slightly higher upfront cost for 4140 could save money in long-term durability and performance.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of local tariffs, taxes, and import duties that may affect the final cost. Understanding the local market dynamics can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Supplier Diversification: Consider multiple suppliers to compare pricing and service levels. This approach can lead to better deals and options tailored to specific needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 1045 and 4140 steel can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and geopolitical factors. Therefore, it is advisable to seek current quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and optimal sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 1045 steel vs 4140 With Other Solutions
Introduction: Evaluating Alternatives in Steel Selection
In the realm of industrial applications, selecting the right material is paramount for ensuring performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. While 1045 and 4140 steels offer distinct advantages depending on the application, other alternatives may also fulfill specific needs. This analysis compares these two popular steel grades against alternative materials to aid B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 1045 Steel Vs 4140 | Stainless Steel | High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate strength, good toughness; 4140 has superior hardness and fatigue resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance; lower strength compared to 4140 | High strength and toughness; better ductility than 4140 |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for 1045; 4140 is more expensive due to alloying elements | Higher cost due to alloying and processing | Competitive pricing, often cheaper than 4140 |
| Ease of Implementation | Easier to machine and weld (1045); 4140 requires advanced techniques | Requires specialized tools for machining | Generally easy to work with, but requires attention to welding |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; both grades are durable | Requires regular cleaning to prevent corrosion | Low maintenance; resistant to wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Machinery components, automotive parts (1045); high-stress applications (4140) | Food processing, medical devices, marine applications | Structural components, automotive frames, and heavy equipment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as food processing and medical devices. While it generally has lower tensile strength compared to 4140, it compensates with superior durability and aesthetic appeal. However, the cost of stainless steel can be significantly higher, and machining it often requires specialized tools and techniques, which could increase production time and costs.
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel
HSLA steel is engineered to provide better mechanical properties and greater resistance to atmospheric corrosion than conventional carbon steels. This material offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications such as structural components and automotive frames. HSLA steel is often more cost-effective than 4140, while still providing adequate strength and toughness. Its ease of machining and welding makes it a practical alternative, though buyers should ensure that it meets the specific requirements of their applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting between 1045 steel, 4140 steel, and alternative materials like stainless steel or HSLA steel, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, including performance, cost, and ease of implementation. For applications demanding high strength and toughness, 4140 may be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for projects focused on cost-efficiency and moderate strength, 1045 steel or HSLA could be more appropriate. Stainless steel is the go-to for environments where corrosion resistance is critical, albeit at a higher price. Ultimately, understanding the unique properties of each material will empower buyers to make the best choice for their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 1045 steel vs 4140
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 1045 Steel and 4140 Steel?
When evaluating 1045 and 4140 steel for industrial applications, several technical properties are crucial for B2B decision-making. Understanding these specifications helps in selecting the right material for specific needs, ensuring product performance, and optimizing costs.
1. Material Grade and Composition
– 1045 Steel: A carbon steel with a carbon content of approximately 0.45%. It is primarily composed of iron and carbon, making it simpler and more cost-effective.
– 4140 Steel: An alloy steel with a carbon content of around 0.40%, enhanced by chromium, molybdenum, and manganese. This composition provides superior hardness and toughness.
B2B Importance: Knowing the material grade helps buyers assess the suitability of steel for their specific applications, influencing both performance and pricing.
2. Mechanical Properties
– Tensile Strength: 1045 typically offers tensile strengths around 82,000 psi (hot rolled) to 91,000 psi (cold drawn), while 4140 ranges from 90,000 psi (hot rolled) to 95,000 psi (cold drawn).
– Yield Strength: 1045 has a yield strength of about 45,000 psi (hot rolled) compared to 65,000 psi for 4140.
B2B Importance: These properties are critical for applications requiring durability and resistance to deformation under stress. Buyers must match these specifications to their operational demands.
3. Hardness and Machinability
– Brinell Hardness: 1045 scores around 163 to 179, whereas 4140 ranges from 197 to 25 (depending on treatment).
– Machinability: 1045 is generally easier to machine due to lower hardness, making it suitable for applications where complex shapes are needed.
B2B Importance: Understanding hardness and machinability helps in selecting the right steel for manufacturing processes, potentially reducing production costs and time.
4. Heat Treatment Capacity
– 1045 Steel: Can be easily heat treated to enhance its strength and toughness, making it versatile for various applications.
– 4140 Steel: Achieves higher hardness through heat treatments like quenching and tempering, essential for high-stress components.
B2B Importance: Buyers should consider heat treatment options to tailor material properties to specific operational requirements, ensuring longevity and reliability.
5. Cost Considerations
– 1045 vs. 4140: 1045 is often more cost-effective due to its simpler composition, while 4140, with its alloying elements, typically comes at a higher price point.
B2B Importance: Cost analysis is vital for budget-conscious buyers, especially in regions where price sensitivity is higher, such as Africa and South America.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Steel Industry?
Understanding industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions involving steel products.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the steel industry, OEMs often specify materials based on performance characteristics.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is significant for buyers as it affects inventory management and cost per unit.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It outlines the specifications of the required steel, including grade, quantity, and delivery timelines, facilitating competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For example, ‘FOB’ (Free on Board) indicates that the seller pays for transportation to a shipping point, while the buyer assumes responsibility thereafter.
5. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)
ASTM standards are critical in the steel industry, defining material specifications and testing methods. Compliance with ASTM standards assures buyers of material quality and performance.
6. Tolerance
This term refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in manufacturing. Understanding tolerance is vital for ensuring that steel components fit correctly in their intended applications, impacting overall project success.
By grasping these properties and terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right materials for their specific industrial applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 1045 steel vs 4140 Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the 1045 Steel vs 4140 Sector
The global steel market continues to evolve, driven by factors such as industrial growth, technological advancements, and regional demand fluctuations. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the dynamics between 1045 and 4140 steel is crucial. Both grades serve distinct applications, with 1045 being favored for its cost-effectiveness and impact resistance, while 4140 is chosen for its superior hardness and toughness under high-stress conditions.
Emerging trends in the B2B sector include the increased adoption of digital sourcing platforms, enabling buyers to compare prices, specifications, and supplier capabilities with ease. This trend is particularly beneficial for buyers in developing markets where access to reliable suppliers can be challenging. Additionally, the push for just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices has heightened the importance of efficient supply chains, prompting buyers to seek suppliers with robust logistics capabilities.
Sourcing strategies are also shifting toward a more localized approach, where businesses prefer regional suppliers to minimize lead times and transportation costs. In regions like Brazil and Nigeria, local steel production is gaining traction, which can reduce dependency on imports and create economic opportunities. Furthermore, as industries increasingly focus on customization, suppliers that offer tailored solutions for both 1045 and 4140 steel are likely to gain competitive advantages.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the 1045 Steel vs 4140 Market?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for B2B buyers, influencing procurement decisions across industries. The environmental impact of steel production, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, necessitates a shift towards greener practices. Buyers are now seeking suppliers who can demonstrate sustainable production methods and adhere to ethical sourcing standards.
In the context of 1045 and 4140 steel, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly looking for manufacturers that have certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. These certifications assure buyers that suppliers are committed to reducing their ecological footprint and promoting responsible resource use.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise. Steel manufacturers are investing in technologies that allow for the recycling of steel and the use of renewable energy sources in production processes. As a result, suppliers who can offer eco-friendly alternatives or demonstrate sustainable practices in their production lines will be more appealing to buyers concerned about their own sustainability goals. This trend not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with global movements toward corporate social responsibility.
What is the Historical Context of 1045 and 4140 Steel Grades for B2B Buyers?
The historical development of 1045 and 4140 steel grades has significantly influenced their current applications and market positioning. 1045 steel, a carbon steel, has been utilized for decades in manufacturing components requiring moderate strength and good impact resistance. Its evolution can be traced back to the early industrial era when the demand for durable materials in machinery and automotive applications began to rise.
Conversely, 4140 steel emerged as an alloy steel designed for more demanding applications. Its formulation, which includes chromium and molybdenum, was developed to meet the needs of industries requiring enhanced toughness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. The introduction of heat treatment processes further advanced its properties, making it a go-to choice for high-stress components like gears and axles.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it informs their material selection based on application requirements and performance expectations. As industries continue to evolve, the historical significance of these steel grades will play a critical role in guiding sourcing decisions and shaping future market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 1045 steel vs 4140
-
1. How do I choose between 1045 steel and 4140 steel for my project?
Choosing between 1045 and 4140 steel depends largely on the specific requirements of your application. If you need a cost-effective solution that offers good impact resistance, 1045 may be the better option. However, if your project requires enhanced strength, toughness, and wear resistance—especially in high-stress environments—4140 is preferable. Consider factors such as machinability, welding capabilities, and potential heat treatment needs, as these will also influence the performance and longevity of the materials in your applications. -
2. What are the primary applications of 1045 and 4140 steel?
1045 steel is commonly used in applications that require good strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for parts like gears, shafts, and automotive components. On the other hand, 4140 steel, known for its superior toughness and wear resistance, is ideal for high-stress applications such as axles, heavy machinery parts, and tooling. Understanding the specific demands of your project will help you determine the most appropriate steel grade for your needs. -
3. What is the typical lead time for sourcing 1045 and 4140 steel internationally?
Lead times for sourcing 1045 and 4140 steel can vary significantly based on supplier location, order size, and current market conditions. Generally, you can expect lead times to range from a few weeks to several months. It is advisable to communicate directly with suppliers about your timeline requirements and to consider factors such as shipping logistics and potential customs delays, particularly when importing into regions like Africa or South America. -
4. How do I evaluate potential suppliers for 1045 and 4140 steel?
When evaluating suppliers for 1045 and 4140 steel, consider their industry reputation, certifications, and experience in international trade. Verify their ability to meet quality standards and ensure they provide clear documentation regarding material specifications and certifications. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness and willingness to accommodate specific requests, such as customization options or bulk orders, which can be crucial for establishing a reliable partnership. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 1045 and 4140 steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely among suppliers, often depending on their production capabilities and inventory levels. Typically, MOQs for 1045 and 4140 steel may range from 1 ton to several tons. It is important to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQs and explore options for smaller orders if necessary, especially if you are testing materials or working on smaller-scale projects. -
6. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers for steel purchases?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers, but common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may also offer credit terms based on your business relationship and order history. It is essential to clarify payment conditions before placing an order to avoid any misunderstandings and to ensure that the terms align with your cash flow management strategies. -
7. Can both 1045 and 4140 steel be heat treated, and how does this affect their properties?
Yes, both 1045 and 4140 steel can be heat treated, but the effects on their properties differ. Heat treatment enhances the strength of 1045 steel and makes it suitable for applications requiring increased hardness. In contrast, 4140 steel can achieve significantly higher hardness and toughness levels through processes like quenching and tempering. Understanding how heat treatment affects these materials is critical for optimizing their performance in your specific applications. -
8. What quality assurance measures should I expect from my steel supplier?
Reputable steel suppliers should have stringent quality assurance measures in place, including material certification, compliance with industry standards, and regular testing of mechanical properties. Ask for documentation that verifies the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the steel you are purchasing. Additionally, suppliers should be open to providing samples or conducting inspections before shipment to ensure that the materials meet your specifications and quality expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 1045 Steel Vs 4140 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. ASTM Steel – 1045 vs 4140 Comparison
Domain: astmsteel.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, ASTM Steel – 1045 vs 4140 Comparison, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Practical Machinist – Carbon Steel Comparison
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1045 and 4140 are both carbon steels with similar carbon content. 1045 is noted to be easier to machine than 4140, which is often heat treated (4140HT) for enhanced durability. 4140 is more expensive, approximately double the price of 1045. Users have reported that 4140HT provides better surface finishes and chip formation during machining compared to 1045. 4140 is preferred for applications requi…
3. Make It From – Steel Alloy Comparisons
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Make It From – Steel Alloy Comparisons, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. iForge Iron – Carbon Steel Grades
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1045: Carbon 0.42-0.5; Manganese 0.6-0.9; Phosphorus 0.04; Sulfur 0.05; Tensile Strength 95,000 PSI; Yield Strength 56,000 PSI. 4140: Carbon 0.35-0.43; Manganese 0.75-1; Silicon 0.15-0.35; Chromium 0.8-1.1; Molybdenum 0.15-0.25; Phosphorus 0.035; Sulfur 0.04; Tensile Strength 140,000 PSI; Yield Strength 90,000 PSI. 1045 is a water quench steel, while 4140 is mostly an oil quench steel.
5. Reddit – Steel Comparison for Gunsmithing
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1045 and 4140 are two types of steel materials discussed for gunsmithing applications, particularly in making firearm slides. Key comparisons include:
– **Tensile Strength**: 1045 has similar tensile strength to 4140 but is less tough, with lower elongation at break (15% for 1045 vs 35% for 4140).
– **Heat Treatment**: 4140 requires higher tempering temperatures (up to 700C) and is oil quenched …
6. Eng-Tips – SAE 1045 vs 4140 Comparison
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: SAE 1045 vs 4140: 1. SAE 4140 has better machinability due to lower carbon concentration. 2. 4140 work hardens faster, affecting forming processes. 3. 4140 offers greater hardenability than 1045, meaning it maintains hardness to a greater depth. 4. SAE 1045 has a higher maximum carbon concentration, achieving higher surface hardness. 5. 4140 shows significant improvement in fracture toughness comp…
7. Ota Steel – 1045 Steel
Domain: otaisteel.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1045 Steel:
– Chemical Composition:
– Carbon (C): 0.45%
– Manganese (Mn): 0.60-0.90%
– Hardness: Moderate hardness, suitable for applications requiring a balance between strength and machinability.
– Strength and Toughness: Good strength and toughness, commonly used in manufacturing gears, axles, and machinery components.
– Applications: Shafts, hydraulic cylinders, bushings, gears, conn…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 1045 steel vs 4140
In evaluating 1045 and 4140 steel, it’s essential for international B2B buyers to align their material choices with specific application requirements and budget constraints. 1045 steel, with its higher carbon content, offers superior tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications where impact resistance is key. Conversely, 4140 steel provides enhanced toughness and wear resistance due to its alloying elements, making it better suited for high-stress environments, such as automotive and industrial machinery.
Strategic sourcing of these materials requires a thorough understanding of their mechanical properties and potential applications. Buyers should consider factors such as machinability, weldability, and heat treatment capabilities when making procurement decisions.
As the global market evolves, staying informed about the latest developments in steel technology and pricing trends will be crucial. By leveraging the strengths of both 1045 and 4140 steel, organizations can optimize their supply chains and enhance product performance.
For businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers to secure the best materials for your specific needs. Explore your options today to ensure your competitive edge in the market.