Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 1 16 sheet metal gauge
Navigating the complexities of sourcing 1 16 sheet metal gauge can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe, including Vietnam and Brazil. The challenge often lies in understanding the various specifications, applications, and supplier options available for this critical material. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process by providing an in-depth exploration of the 1 16 sheet metal gauge, including its types, applications across industries, and strategies for effectively vetting suppliers.
As you delve into this guide, you will discover key insights into the significance of gauge measurements, the specific requirements for different applications, and the factors influencing pricing. Additionally, we will cover the best practices for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be better positioned to navigate the global market for sheet metal, ultimately enhancing your procurement strategies and ensuring the success of your projects. Whether you are involved in construction, manufacturing, or other sectors requiring sheet metal, this guide is designed to empower you with the tools necessary to make confident, informed choices in your sourcing endeavors.
Understanding 1 16 sheet metal gauge Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | High tensile strength, cost-effective | Construction, automotive, manufacturing | Pros: Affordable, versatile. Cons: Prone to rusting without coating. |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, aesthetic finish | Food processing, medical equipment | Pros: Durable, hygienic. Cons: Higher cost, more challenging to work with. |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, packaging | Pros: Lightweight, good thermal conductivity. Cons: Lower strength compared to steel. |
| Galvanized Steel | Zinc-coated for rust prevention | Construction, HVAC systems | Pros: Rust-resistant, cost-effective. Cons: Coating can wear off over time. |
| Copper | Excellent electrical conductivity, antimicrobial | Electrical applications, plumbing | Pros: High conductivity, resistant to corrosion. Cons: Expensive, can be heavy. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Mild Steel in 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Mild steel is known for its high tensile strength and affordability, making it a popular choice in various industries. Its malleability allows for easy fabrication, which is essential for construction and manufacturing applications. However, buyers should consider that mild steel is prone to rusting, necessitating protective coatings for outdoor or moisture-exposed applications. When sourcing mild steel, B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide quality assurance and certifications.
How Does Stainless Steel Stand Out in 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge Applications?
Stainless steel is distinguished by its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for food processing and medical equipment. This material is durable and easy to clean, which is vital in industries requiring high hygiene standards. However, the higher cost of stainless steel compared to other metals can be a barrier for some buyers. When purchasing, businesses should assess their specific requirements for corrosion resistance and budget constraints, ensuring they choose the right grade.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer as a 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Aluminum’s lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance make it an attractive option for aerospace and automotive applications. Its thermal conductivity is beneficial for heat exchange components. However, aluminum is generally less strong than steel, which may limit its use in structural applications. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of weight savings against the need for strength when selecting aluminum for their projects.
Why Choose Galvanized Steel for 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Galvanized steel features a zinc coating that provides excellent rust resistance, making it suitable for construction and HVAC systems. This material offers a cost-effective solution while maintaining structural integrity. However, the protective coating can wear off over time, especially in harsh environments, which may require ongoing maintenance. Buyers should consider the long-term durability of galvanized steel in their specific applications and evaluate the conditions under which it will be used.
What Are the Unique Properties of Copper in 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Copper is renowned for its superior electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for electrical applications and plumbing. Although it is heavier and more expensive than other metals, its longevity and resistance to corrosion can justify the investment. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to assess the specific application requirements and budget, as copper’s benefits often come with a higher upfront cost.
Key Industrial Applications of 1 16 sheet metal gauge
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 1 16 sheet metal gauge | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Fabrication of vehicle body panels and components | Provides durability and resistance to corrosion | Ensure compliance with safety standards and material certifications. |
| Construction | Structural framing and roofing systems | Enhances structural integrity and longevity | Evaluate local climate conditions for corrosion resistance needs. |
| HVAC Systems | Ductwork and ventilation systems | Improves energy efficiency and airflow management | Consider insulation and thermal properties for specific applications. |
| Agriculture Equipment | Manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts | Increases durability and reduces maintenance costs | Assess compatibility with existing machinery and operational demands. |
| Electrical Enclosures | Production of enclosures for electrical components | Offers protection against environmental factors | Verify compliance with electrical safety standards and environmental regulations. |
How is 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, 1 16 sheet metal gauge is widely utilized for fabricating vehicle body panels and components. This gauge offers an optimal balance between weight and strength, essential for maintaining vehicle performance while ensuring safety. International B2B buyers must ensure that the metal adheres to stringent safety standards and undergoes quality assurance processes to prevent defects during manufacturing. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who can provide certifications for corrosion resistance is critical, particularly in regions with harsh climates.
What Role Does 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Play in Construction?
Within the construction industry, 1 16 sheet metal gauge is employed in structural framing and roofing systems. Its robustness contributes to the overall structural integrity of buildings, ensuring longevity and resistance to environmental factors. Buyers must consider local climate conditions when sourcing this material, as regions with high humidity or salt exposure require enhanced corrosion resistance. Moreover, working with suppliers that provide detailed specifications and compliance documentation can streamline project approvals.
Why is 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Important for HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, 1 16 sheet metal gauge is commonly used for ductwork and ventilation components. This thickness helps to improve energy efficiency and optimize airflow, which are critical for effective heating and cooling. Buyers should assess the thermal properties of the metal to ensure it meets specific operational requirements. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers that offer pre-fabricated solutions can significantly reduce installation time and costs, particularly for large-scale projects.
How is 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Used in Agriculture Equipment?
The agricultural sector relies on 1 16 sheet metal gauge for manufacturing parts of agricultural machinery, such as frames and protective covers. This gauge provides the necessary durability to withstand heavy use and harsh environmental conditions, thereby reducing maintenance costs. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of the metal with existing equipment and consider sourcing from local suppliers to minimize shipping costs and lead times, especially in remote areas.
What is the Application of 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge in Electrical Enclosures?
In the realm of electrical enclosures, 1 16 sheet metal gauge is crucial for creating robust protective casings for electrical components. This thickness offers substantial protection against environmental factors like moisture and dust, enhancing the safety and reliability of electrical systems. It is essential for buyers to verify that their sourcing partners comply with electrical safety standards and environmental regulations to ensure the enclosures meet operational safety requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘1 16 sheet metal gauge’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Gauge Measurement and Thickness
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to sheet metal procurement, struggle with the non-intuitive nature of the gauge system. They often assume that a higher gauge number means a thicker material, which leads to confusion and potentially costly mistakes. For instance, a buyer may order 18-gauge steel expecting it to be thicker than 20-gauge, only to find that it is actually thinner. This misunderstanding can result in order discrepancies, wasted materials, and delays in production schedules.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of sheet metal gauges effectively, buyers should utilize comprehensive gauge conversion charts tailored to the specific type of metal they are working with, such as steel, aluminum, or stainless steel. Before placing an order, it’s advisable to double-check the gauge thickness using reliable resources or consult with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications. Additionally, investing time in training for the procurement team on the gauge system can minimize errors. By ensuring that all stakeholders understand how to interpret gauge measurements accurately, businesses can enhance their material ordering processes and reduce costly mistakes.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Across Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face issues with the quality and consistency of sheet metal supplied by different manufacturers. Variations in the thickness and quality of 16-gauge sheet metal can lead to structural integrity problems in final products. This inconsistency may result from suppliers using different manufacturing processes or tolerances, which can affect project outcomes significantly.
The Solution: To mitigate quality discrepancies, buyers should establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers known for their quality assurance practices. Conducting thorough supplier evaluations, including audits of their manufacturing processes and quality control measures, can help ensure consistent material quality. Moreover, implementing a standardized inspection process upon receipt of the materials can further identify any discrepancies before they affect production. Specifying exact tolerances and requirements in purchase orders will help suppliers understand expectations and reduce variability in the product supplied.
Scenario 3: Cost Management in Sheet Metal Projects
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is managing costs associated with sourcing 16-gauge sheet metal. Buyers may find themselves overpaying for materials due to lack of knowledge about market prices or the availability of alternative materials. Additionally, unexpected price fluctuations can disrupt budgets and project timelines, making it difficult to maintain profitability.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should conduct comprehensive market research to understand current pricing trends and establish relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. Utilizing online platforms that offer real-time pricing and comparisons can help buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, considering alternative materials or gauges that can meet the project’s requirements without compromising quality can provide cost savings. Buyers should also negotiate bulk purchasing agreements or explore long-term contracts to lock in favorable prices and ensure supply stability. By proactively managing supplier relationships and material costs, businesses can maintain better control over their project budgets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 1 16 sheet metal gauge
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
When selecting materials for 1 16 sheet metal gauge, several common options stand out: mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized steel. Each material has unique properties that influence its performance in various applications.
How Does Mild Steel Perform in 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Applications?
Mild steel is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and ductility, making it a popular choice for structural applications. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for general fabrication. However, mild steel is prone to corrosion if not adequately protected.
Pros:
– High strength and durability.
– Cost-effective compared to other metals.
– Easy to fabricate and weld.
Cons:
– Requires surface treatment to prevent rust.
– Not suitable for high-temperature applications without additional coatings.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is essential. Mild steel is widely available and often preferred in regions like South America and Africa due to its low cost and ease of sourcing.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand harsh environments, making it ideal for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. Its ability to maintain structural integrity at high temperatures is another significant advantage.
Pros:
– Excellent corrosion resistance.
– High-temperature tolerance.
– Low maintenance requirements.
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to mild steel.
– More complex to fabricate due to its hardness.
For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is critical, especially in industries requiring high hygiene standards. The preference for stainless steel is growing in these regions due to its durability and aesthetic qualities.
Why Choose Aluminum for 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Applications?
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. However, its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to handle.
– Excellent corrosion resistance.
– Good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons:
– Lower strength compared to steel.
– Higher cost than mild steel.
International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B209. In regions like Brazil and Vietnam, the demand for aluminum is increasing due to its versatility and lightweight properties.
What Role Does Galvanized Steel Play in 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Galvanized steel is mild steel that has been coated with zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in outdoor applications and environments prone to moisture. The galvanization process adds a layer of protection, making it suitable for construction and infrastructure projects.
Pros:
– Enhanced corrosion resistance due to zinc coating.
– Cost-effective and durable.
– Suitable for outdoor applications.
Cons:
– The coating can wear off over time, exposing the base metal.
– Not as aesthetically pleasing as stainless steel.
For international buyers, compliance with standards like ASTM A653 is crucial, especially for construction projects in humid climates. Galvanized steel is widely used in Africa and South America due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge
| Material | Typical Use Case for 1 16 sheet metal gauge | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Structural components, general fabrication | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical containers | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Galvanized Steel | Outdoor structures, construction applications | Enhanced corrosion resistance | Coating can wear off | Low |
This guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in selecting the appropriate material for 1 16 sheet metal gauge applications, considering performance, cost, and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 1 16 sheet metal gauge
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Manufacturing 1/16 sheet metal gauge involves several critical stages, each requiring specialized techniques to ensure precision and quality. The typical manufacturing process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which often begins with selecting the appropriate metal type, such as mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum. For 1/16 gauge, the thickness is approximately 0.0598 inches (1.518 mm).
Once the metal is selected, it is cut into manageable sheets using methods like shearing or laser cutting. This initial step is crucial because the quality of the raw material directly impacts the final product. Suppliers typically perform a thorough inspection of the sheets for any visible defects or inconsistencies before moving on to the next stage.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The forming stage includes various techniques to shape the sheet metal into the desired form. Common methods include:
-
Bending: This involves applying pressure to create angles or curves in the sheet. Equipment like press brakes is often employed for precision bending.
-
Stamping: For high-volume production, stamping presses shape the metal into specific designs and features, such as holes or notches, enhancing functionality.
-
Rolling: In this process, the sheet is passed through rollers to achieve a specified curvature or thickness, ensuring uniformity across the entire sheet.
These techniques must be executed with precision to maintain the integrity of the 1/16 gauge sheet, as even slight deviations can affect the product’s performance in its intended application.
What Assembly Processes Are Involved?
In cases where the sheet metal is part of a larger assembly, such as enclosures or frames, additional assembly processes come into play. These may include welding, riveting, or bolting, depending on the design requirements. The choice of assembly technique is influenced by factors such as the intended use of the product and the materials involved.
How Is Finishing Applied to Enhance Quality?
Finishing processes are essential for improving both the aesthetics and durability of the sheet metal. Common finishing techniques for 1/16 gauge sheet metal include:
-
Painting or Coating: Applying protective coatings or paints to prevent corrosion and enhance appearance.
-
Anodizing: This electrochemical process increases corrosion resistance, particularly for aluminum sheets.
-
Polishing: For aesthetic applications, polishing can provide a smooth, reflective surface.
Each of these finishing processes contributes to the overall quality and longevity of the sheet metal product, making them vital steps in the manufacturing process.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in ensuring that the 1/16 sheet metal gauge meets international standards and customer specifications. Effective QA processes encompass several international and industry-specific standards, alongside robust inspection checkpoints.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding international quality standards is critical. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers maintain a consistent level of quality. Other relevant certifications may include:
-
CE Marking: Indicates conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Particularly important for suppliers in the oil and gas industry, ensuring products meet specific performance requirements.
These certifications signal to buyers that the supplier adheres to recognized quality protocols.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for monitoring product quality at various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive review of the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications before shipping.
Implementing these checkpoints helps mitigate risks and enhances product reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods play a significant role in verifying the quality of 1/16 sheet metal gauge products. Common methods include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and micrometers to measure thickness and dimensions, ensuring they conform to specifications.
-
Tensile Testing: Assessing the material’s strength and ductility, which is essential for applications requiring high durability.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection help identify internal flaws without damaging the material.
These testing methods provide assurance that the product will perform as intended in its application.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to be proactive in verifying the quality control measures of their suppliers. Here are some strategies to consider:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits help assess a supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can be done on-site or through virtual assessments.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from testing and inspections.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and product conformity.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of the following:
-
Local Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations regarding metal products, which can affect compliance and certification.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly, necessitating clear expectations and thorough documentation to avoid misunderstandings.
By being informed about these factors, international buyers can make more educated decisions regarding their suppliers and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 1/16 sheet metal gauge are intricate and require careful consideration. By understanding these aspects, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they partner with suppliers who uphold high standards of quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘1 16 sheet metal gauge’
In the competitive world of B2B procurement, sourcing the right materials is crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in production. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for international buyers looking to procure 1/16 sheet metal gauge, helping you navigate the complexities of material specifications, supplier evaluation, and logistical considerations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first step in the sourcing process. Specify the type of metal (e.g., mild steel, aluminum, stainless steel) and the exact thickness you need (1/16 inch or approximately 1.588 mm). Understanding these specifications helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures you receive the right material for your application.
Step 2: Research Applicable Standards and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the relevant industry standards and regulations that govern sheet metal usage in your region. This may include ISO standards or local compliance requirements. Ensuring that the material meets these standards not only guarantees quality but also helps avoid potential legal issues down the line.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in delivering 1/16 sheet metal gauge, and consider their production capabilities, inventory levels, and delivery timelines.
- Check for Certifications: Verify if suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management.
- Assess Customer Reviews: Look for testimonials and reviews from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Quality
Always request samples of the 1/16 sheet metal gauge before placing a bulk order. Testing samples for thickness, finish, and mechanical properties is essential to ensure they meet your specifications. This step helps identify any discrepancies early on and allows you to make informed decisions.
Step 5: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in discussions about pricing structures and payment terms with your shortlisted suppliers. Consider not only the cost of the material but also additional charges such as shipping, handling, and customs duties. Negotiating favorable payment terms can improve your cash flow and reduce financial risk.
- Inquire About Volume Discounts: If you plan on making large purchases, ask about bulk pricing or discounts for repeat orders.
Step 6: Plan Logistics and Delivery
Coordinate logistics to ensure timely delivery of your 1/16 sheet metal gauge. Discuss shipping options with suppliers and consider factors such as lead times, freight costs, and the reliability of shipping methods. Effective logistics planning minimizes disruptions in your production schedule.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you have successfully sourced your sheet metal, focus on building a long-term relationship with your supplier. Regular communication and feedback can lead to improved service, better pricing, and priority access to new products or technologies. A strong partnership can be invaluable for future projects and procurement needs.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for 1/16 sheet metal gauge, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 1 16 sheet metal gauge Sourcing
When sourcing 1 16 sheet metal gauge, understanding the cost structure and pricing intricacies is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis will break down the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips tailored for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
The cost of 1 16 sheet metal gauge involves several critical components:
-
Materials: The base material cost varies significantly based on the type of metal (e.g., mild steel, aluminum, stainless steel). Prices fluctuate due to market demand, availability, and global commodity prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in the manufacturing process. Skilled labor for precision cutting and shaping of sheet metal can add to overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tools and machinery for shaping and cutting the metal is a significant factor. Tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs, making them less burdensome per unit for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the sheet metal meets specified standards involves additional costs related to testing and inspection. Certifications may be required depending on the end-use, impacting the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees are crucial, especially for international buyers. Costs may vary based on the shipping method, distance, and any tariffs or customs duties applicable.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to the total cost, which can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Several factors can significantly affect the pricing of 1 16 sheet metal gauge:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes can lead to reduced unit prices due to economies of scale. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better rates for larger Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom orders can drive up costs. If specific dimensions, finishes, or additional processing are required, expect a premium.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) typically come at a higher price. Ensure that the material meets the necessary standards for your application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding who bears the risk and costs at different points in the supply chain is essential for budgeting.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers Sourcing 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Always negotiate terms and prices with suppliers. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts, especially if you’re ordering in bulk or establishing a long-term relationship.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with the material, including maintenance, durability, and potential waste during fabrication.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Be aware of foreign exchange rates, import taxes, and tariffs that may affect the final cost when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Evaluate Supplier Options: Compare multiple suppliers, looking beyond price to assess quality, service levels, and reliability. Obtaining samples before placing large orders can mitigate risks.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: If feasible, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and simplify communication, especially for urgent needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 1 16 sheet metal gauge can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is recommended to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and to verify that the materials meet your specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 1 16 sheet metal gauge With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge
In the realm of metal fabrication, selecting the right material gauge is crucial for achieving optimal performance in various applications. While the 1/16 sheet metal gauge is a popular choice, it’s essential to explore alternative solutions that may better meet specific project requirements or budget constraints. This analysis compares the 1/16 sheet metal gauge with two viable alternatives: 1/8 inch sheet metal and aluminum sheet metal of similar thickness.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 1/16 Sheet Metal Gauge | 1/8 Inch Sheet Metal | Aluminum Sheet Metal (1/8 inch) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good strength; suitable for light-duty applications | Higher strength; better for heavy-duty applications | Lightweight; excellent corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate cost; affordable for many projects | Higher material cost due to thickness | Typically higher than steel; varies with alloy |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to work with; manageable for fabricators | Requires more effort to cut and shape | Lightweight makes handling easier; may require specialized tools |
| Maintenance | Moderate; prone to rust if uncoated | Low; durable but may need coating | Low; naturally resistant to corrosion |
| Best Use Case | HVAC ducts, light frames, appliance casings | Structural components, heavy machinery parts | Marine applications, automotive parts, architectural features |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1/8 Inch Sheet Metal
1/8 inch sheet metal offers a significant increase in thickness compared to the 1/16 gauge. This added thickness translates to enhanced strength and durability, making it an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications, such as structural supports and components in industrial machinery. However, the cost is higher, and the material can be more challenging to work with, requiring specialized cutting and shaping tools. This thickness is ideal for projects where strength is a priority, but the additional weight may be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred.
Aluminum Sheet Metal (1/8 Inch)
Aluminum sheet metal, particularly in a thickness of 1/8 inch, presents a compelling alternative due to its unique properties. It is significantly lighter than steel, which makes it easier to handle and install. Aluminum also boasts excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor and marine applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. However, it is generally more expensive than steel and may not provide the same level of strength in load-bearing applications. This material is best utilized in sectors such as automotive and architectural design, where weight savings and corrosion resistance are critical.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When selecting the appropriate sheet metal gauge, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and specific application needs. The 1/16 sheet metal gauge is an excellent choice for light-duty applications, while alternatives like 1/8 inch sheet metal and aluminum offer superior strength or unique properties like corrosion resistance. Evaluating the operational context and long-term maintenance needs will help buyers make informed decisions that align with their project goals and budgetary limits. Prioritize understanding the specific requirements of your application to select the most suitable material solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 1 16 sheet metal gauge
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
When evaluating 1 16 sheet metal gauge, several essential technical properties come into play. Understanding these specifications is critical for B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions that align with their project needs.
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the specific composition of the metal, which affects its strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Common grades for 1 16 gauge sheet metal include A36 for mild steel and 304 or 316 for stainless steel. The choice of material grade can significantly influence the performance and longevity of the final product, impacting everything from structural integrity to cost-effectiveness.
2. Thickness
The thickness of 1 16 sheet metal gauge is approximately 0.0598 inches or 1.518 millimeters. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the sheet metal meets the structural requirements of the application. Buyers must ensure that the thickness aligns with their project specifications, as deviations can lead to failure in performance and safety.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. For sheet metal, tolerances can vary based on the manufacturing process and material type. Understanding tolerance levels is vital for ensuring that parts fit together as intended, particularly in applications requiring precision, such as automotive or aerospace manufacturing.
4. Yield Strength
Yield strength measures the maximum stress that a material can withstand while still returning to its original shape. For 1 16 gauge mild steel, yield strength is typically around 36,000 psi (pounds per square inch). Knowing the yield strength helps buyers assess the load-bearing capacity of the material, which is essential for structural applications.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of sheet metal can range from mill finish to polished or coated surfaces. This specification not only affects aesthetics but also impacts corrosion resistance and paint adhesion. Buyers should consider the surface finish required for their applications to ensure durability and compliance with industry standards.
6. Formability
Formability refers to the ease with which a material can be shaped without cracking. For 1 16 gauge sheet metal, the formability can vary based on the material type and heat treatment. Understanding formability is critical for manufacturers who need to bend, stamp, or otherwise manipulate the metal during fabrication.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication in B2B transactions. Below are some common terms that buyers should know when dealing with sheet metal.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of sheet metal, OEMs often require specific gauges and materials for their components, making it crucial for suppliers to understand OEM specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to ensure they can meet their production needs without overcommitting resources. For sheet metal, MOQs can vary based on material type and supplier capabilities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products. For B2B buyers, submitting an RFQ for 1 16 sheet metal gauge allows them to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping costs, risk, and insurance responsibilities, influencing the overall cost and logistics of purchasing sheet metal.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. In the context of sheet metal, lead times can vary based on the gauge, material type, and supplier capabilities. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing 1 16 sheet metal gauge, ultimately enhancing their procurement strategies and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 1 16 sheet metal gauge Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends for the 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Sector?
The global market for sheet metal, particularly the 1 16 gauge segment, is experiencing robust growth driven by several factors. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing is a key driver. As businesses aim for efficiency and cost-effectiveness, the shift towards using 1 16 gauge sheet metal, known for its balance between strength and weight, is evident.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are facilitating seamless transactions, enabling international buyers to access suppliers across borders with ease. Additionally, advancements in automation and artificial intelligence are streamlining production processes, enhancing the quality and consistency of sheet metal products. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these tech-driven trends mean faster delivery times and the potential for lower costs, allowing businesses to remain competitive in a global marketplace.
Furthermore, sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority. Buyers are keen to partner with suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, which is influencing sourcing decisions. The rise of Industry 4.0 is also promoting smarter inventory management and supply chain transparency, allowing B2B buyers to make informed choices based on real-time data.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Ethical Sourcing for 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge?
The environmental impact of metal production is a growing concern among international B2B buyers. The sourcing of 1 16 sheet metal gauge is increasingly tied to sustainability practices, as businesses recognize the importance of minimizing their carbon footprint. Buyers are now more inclined to seek suppliers who utilize recycled materials or sustainable production methods, leading to a surge in demand for ‘green’ certifications.
Ethical supply chains are not just a trend but a necessity. Companies that can demonstrate responsible sourcing practices are gaining a competitive edge. This includes ensuring fair labor practices and transparency in the supply chain. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming essential for suppliers looking to attract conscientious buyers.
Moreover, the use of innovative materials that reduce environmental impact is on the rise. For instance, manufacturers are exploring alternatives such as aluminum or composites that offer similar performance characteristics to traditional metals but with a lower environmental impact. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who are committed to sustainability, not only to comply with regulations but also to enhance their brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
How Has the 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Sector Evolved Over Time?
The gauge system for sheet metal has its roots in the British wire industry, evolving over centuries into a standardized method for measuring metal thickness. The 1 16 sheet metal gauge, which corresponds to approximately 1.59 mm in thickness, has become a staple in various industries due to its optimal balance of weight and strength.
Initially used predominantly in construction and manufacturing, the applications of the 1 16 gauge have expanded significantly. Today, it is favored in automotive, aerospace, and even consumer goods, reflecting the material’s versatility. As technology has advanced, the processes for cutting, bending, and forming sheet metal have become more sophisticated, allowing for intricate designs and applications that were previously unattainable.
As global markets continue to develop, the understanding and application of the 1 16 gauge will likely evolve further, influenced by technological innovations and shifting consumer demands. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers who not only understand the material’s past but are also prepared to adapt to future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 1 16 sheet metal gauge
-
How do I determine the thickness of 1/16 sheet metal gauge?
To find the thickness of 1/16 sheet metal gauge, it’s essential to consult a sheet metal gauge chart. In the case of mild steel, 1/16 inch corresponds to approximately 16 gauge, which is 0.0598 inches or 1.518 mm thick. Different metals have varying thicknesses for the same gauge number; thus, always refer to specific material charts for accurate measurements. Understanding this helps ensure that the selected material meets the requirements of your project. -
What is the best type of metal for 1/16 sheet metal gauge applications?
The best type of metal for 1/16 sheet metal gauge largely depends on the intended application. For structural applications, mild steel offers strength and durability at a reasonable cost. If corrosion resistance is critical, stainless steel is ideal. Aluminum is preferred for lightweight applications, while galvanized steel provides additional corrosion protection. Assess your project’s functional requirements to choose the most suitable metal type. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 1/16 sheet metal gauge?
Minimum order quantities for 1/16 sheet metal gauge can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 100 kg to several tons depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the specific metal type. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs upfront to avoid surprises. Some suppliers may offer flexible options for smaller orders, especially if they cater to international buyers. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing 1/16 sheet metal gauge internationally?
To effectively vet suppliers for 1/16 sheet metal gauge, conduct thorough research. Check for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates quality management practices. Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge reliability and service levels. Additionally, consider requesting samples to assess material quality. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also provide insights into their responsiveness and professionalism. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing 1/16 sheet metal gauge?
Payment terms for sourcing 1/16 sheet metal gauge can vary widely. Common practices include a 30% deposit upfront with the balance due upon delivery or a letter of credit for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow capabilities and risk tolerance. It’s crucial to have clear agreements in writing to protect both parties involved in the transaction. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in sheet metal suppliers?
When sourcing 1/16 sheet metal gauge, it’s vital to ensure that suppliers implement robust quality assurance measures. Look for suppliers who perform regular inspections and testing of materials to meet industry standards. Certifications like ASTM or EN standards are indicators of quality. Additionally, ask about their return and warranty policies, as these can provide further assurance of product reliability. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of 1/16 sheet metal gauge?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing 1/16 sheet metal gauge, especially for international transactions. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations that could affect delivery schedules. Ensure that your supplier has a reliable logistics partner to minimize delays. Understanding the total landed cost, including shipping and duties, is essential for accurate budgeting. -
Can I customize my order for 1/16 sheet metal gauge?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for 1/16 sheet metal gauge orders. Customization can include cutting to specific dimensions, surface treatments, or finishing processes. When placing your order, clearly communicate your requirements to the supplier. Be prepared to discuss lead times and any additional costs associated with customization, as these factors can impact your project timeline.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 1 16 Sheet Metal Gauge Manufacturers & Suppliers List
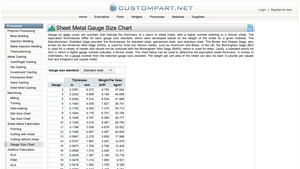
1. CustomPartNet – Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart
Domain: custompartnet.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart: Gauge sizes indicate the thickness of sheet metal, with higher numbers corresponding to thinner sheets. Different standards exist for various materials: 1. Manufacturers’ Standard Gage for steel, galvanized steel, and stainless steel. 2. Brown and Sharpe Gage (American Wire Gage) for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and brass. 3. Birmingham Gage in the UK for various …
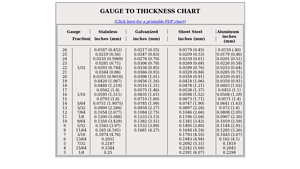
2. Stainless Supply – Gauge to Thickness Chart
Domain: stainlesssupply.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Gauge to Thickness Chart for Stainless, Galvanized Sheet Steel, and Aluminum. The chart includes the following gauges and their corresponding thicknesses in inches and millimeters: 26 (0.0187″ / 0.452mm), 25 (0.0219″ / 0.56mm), 24 (0.0235″ / 0.5969mm), 23 (0.0281″ / 0.71mm), 22 (1/32″ / 0.0293″ / 0.744mm), 21 (0.0344″ / 0.86mm), 20 (0.0355″ / 0.9016mm), 19 (0.0420″ / 1.067mm), 18 (0.0480″ / 1.219m…
3. Metals Depot – Hot Rolled Steel Sheet
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“type”:”Hot Rolled Steel Sheet”,”specification”:”ASTM A1011 CS Type B”,”description”:”Economical steel sheets with slightly grainy surface, ideal for painting.”,”uses”:[“general fabrication”,”equipment panels”,”tool boxes”,”hoppers”,”drip pans”],”thicknesses”:[{“gauge”:16,”thickness”:”.060″,”weight”:”2.50 lb/sqft”},{“gauge”:14,”thickness”:”.075″,”weight”:”3.13 lb/sqft”},{“gauge”:12,”…
4. Steel – 1/16 in Sheet/Flat Stock
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Steel 1/16 in Sheet/Flat Stock Thickness, Industrial Metal Sheets & Flat Stock, available for sale on eBay. Related searches include various thicknesses and types of metal sheets such as 3/16 Sheet Steel, 16 Gauge Stainless Steel Sheet, and more. The product is categorized under Metals & Alloys, specifically in Metal Sheets & Flat Stock. Options for thickness include 1/16 in, 0.025 in, 0.035 in, 0…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 1 16 sheet metal gauge
In navigating the complexities of sourcing 1/16 sheet metal gauge, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance operational efficiency and ensure quality. Understanding the gauge system and its implications on material selection is crucial for making informed decisions that align with project specifications. Leveraging accurate gauge charts will facilitate precise measurements, thereby minimizing errors and reducing material waste.
Furthermore, establishing strong supplier relationships can lead to better pricing, reliable delivery schedules, and access to a wider range of materials, which are vital in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers should also remain aware of regional variations in material standards and availability, which can impact sourcing strategies.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality sheet metal will continue to grow as industries evolve and new applications emerge. By embracing proactive sourcing strategies, B2B buyers can position themselves to capitalize on these opportunities, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective markets. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that meet your specific needs and drive your business forward.